
Consider the following particulate-level representation of a chemical equation:
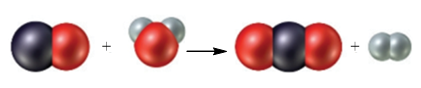
The white spheres represent hydrogen atoms, the black sphere represents a carbon atom, and the red spheres represent oxygen atoms. (a) Write a balanced chemical equation representing this reaction. (b) Write a word description of the reaction on the particulate and molar levels.
(a)
Interpretation:
The balanced chemical equation representing the given particulate–level reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
In a balanced chemical equation, all the reactants and products are written with their stoichiometric coefficients and their physical states. The number of atoms of an element on both sides of a balanced chemical equation is equal.
Answer to Problem 1E
The chemical equation that represents the given particulate–level reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is,
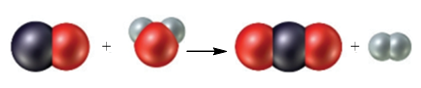
Figure 1
The black sphere represents carbon atom, white spheres represents hydrogen atom and red sphere represents oxygen atom. The chemical equation that represents the given particulate–level reaction is,
The given reaction is balanced as the number of atoms on both the sides of equation is same.
The chemical equation that represents the given particulate–level reaction is,
(b)
Interpretation:
The word description of the given particulate–level reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
In a balanced chemical equation, all the reactants and products are written with their stoichiometric coefficients and their physical states. The number of atoms of an element on both sides of a balanced chemical equation is equal.
Answer to Problem 1E
The given particulate–level reaction involves the reaction of one molecule of carbon monoxide with one molecule of water resulting in the formation of one molecule of carbon dioxide and one molecule of hydrogen.
The given reaction at molar levels involves the reaction of one mole of carbon monoxide with one mole of water resulting in the formation of one mole of carbon dioxide and one mole of hydrogen.
Explanation of Solution
The chemical equation that represents the given particulate–level reaction is,
The given reaction is balanced as the number of atoms on both the sides of equation is same.
In the given reaction at particulate levels, one molecule of carbon monoxide reacts with one molecule of water to form one molecule of carbon dioxide and one molecule of hydrogen.
In the given reaction at molar levels, one mole of carbon monoxide reacts with one mole of water to form one mole of carbon dioxide and one mole of hydrogen.
The given particulate–level reaction involves the reaction of one molecule of carbon monoxide with one molecule of water resulting in the formation of one molecule of carbon dioxide and one molecule of hydrogen.
The given reaction at molar levels involves the reaction of one mole of carbon monoxide with one mole of water resulting in the formation of one mole of carbon dioxide and one mole of hydrogen.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Bundle: Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach, 6th + LMS Integrated for OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- What spectral features allow you to differentiate the product from the starting material? Use four separate paragraphs for each set of comparisons. You should have one paragraph each devoted to MS, HNMR, CNMR and IR. 2) For MS, the differing masses of molecular ions are a popular starting point. Including a unique fragmentation is important, too. 3) For HNMR, CNMR and IR state the peaks that are different and what makes them different (usually the presence or absence of certain groups). See if you can find two differences (in each set of IR, HNMR and CNMR spectra) due to the presence or absence of a functional group. Include peak locations. Alternatively, you can state a shift of a peak due to a change near a given functional group. Including peak locations for shifted peaks, as well as what these peaks are due to. Ideally, your focus should be on not just identifying the differences but explaining them in terms of functional group changes.arrow_forwardQuestion 6 What is the major product of the following Diels-Alder reaction? ? Aldy by day of A. H о B. C. D. E. OB OD Oc OE OAarrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- In the solid state, oxalic acid occurs as a dihydrate with the formula H2C2O4 C+2H2O. Use this formula to calculate the formula weight of oxalic acid. Use the calculated formula weight and the number of moles (0.00504mol) of oxalic acid in each titrated unknown sample recorded in Table 6.4 to calculate the number of grams of pure oxalic acid dihydrate contained in each titrated unknown sample.arrow_forward1. Consider a pair of elements with 2p and 4p valence orbitals (e.g., N and Se). Draw their (2p and 4p AO's) radial probability plots, and sketch their angular profiles. Then, consider these orbitals from the two atoms forming a homonuclear л-bond. Which element would have a stronger bond, and why? (4 points)arrow_forwardWrite the reaction and show the mechanism of the reaction. Include the mechanism for formation of the NO2+ 2. Explain, using resonance structures, why the meta isomer is formed. Draw possible resonance structures for ortho, meta and para.arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





