
Consider the following particulate-level representation of a chemical equation:
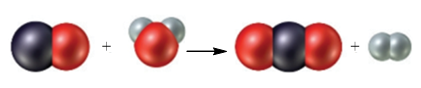
The white spheres represent hydrogen atoms, the black sphere represents a carbon atom, and the red spheres represent oxygen atoms. (a) Write a balanced chemical equation representing this reaction. (b) Write a word description of the reaction on the particulate and molar levels.
(a)
Interpretation:
The balanced chemical equation representing the given particulate–level reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
In a balanced chemical equation, all the reactants and products are written with their stoichiometric coefficients and their physical states. The number of atoms of an element on both sides of a balanced chemical equation is equal.
Answer to Problem 1E
The chemical equation that represents the given particulate–level reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is,
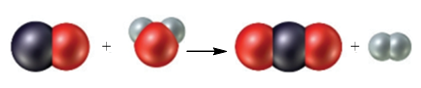
Figure 1
The black sphere represents carbon atom, white spheres represents hydrogen atom and red sphere represents oxygen atom. The chemical equation that represents the given particulate–level reaction is,
The given reaction is balanced as the number of atoms on both the sides of equation is same.
The chemical equation that represents the given particulate–level reaction is,
(b)
Interpretation:
The word description of the given particulate–level reaction is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
In a balanced chemical equation, all the reactants and products are written with their stoichiometric coefficients and their physical states. The number of atoms of an element on both sides of a balanced chemical equation is equal.
Answer to Problem 1E
The given particulate–level reaction involves the reaction of one molecule of carbon monoxide with one molecule of water resulting in the formation of one molecule of carbon dioxide and one molecule of hydrogen.
The given reaction at molar levels involves the reaction of one mole of carbon monoxide with one mole of water resulting in the formation of one mole of carbon dioxide and one mole of hydrogen.
Explanation of Solution
The chemical equation that represents the given particulate–level reaction is,
The given reaction is balanced as the number of atoms on both the sides of equation is same.
In the given reaction at particulate levels, one molecule of carbon monoxide reacts with one molecule of water to form one molecule of carbon dioxide and one molecule of hydrogen.
In the given reaction at molar levels, one mole of carbon monoxide reacts with one mole of water to form one mole of carbon dioxide and one mole of hydrogen.
The given particulate–level reaction involves the reaction of one molecule of carbon monoxide with one molecule of water resulting in the formation of one molecule of carbon dioxide and one molecule of hydrogen.
The given reaction at molar levels involves the reaction of one mole of carbon monoxide with one mole of water resulting in the formation of one mole of carbon dioxide and one mole of hydrogen.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach
- Provide steps and explanation please.arrow_forwardDraw a structural formula for the major product of the acid-base reaction shown. H 0 N + HCI (1 mole) CH3 N' (1 mole) CH3 You do not have to consider stereochemistry. ● • Do not include counter-ions, e.g., Na+, I, in your answer. . In those cases in which there are two reactants, draw only the product from 989 CH3 344 ? [Farrow_forwardQuestion 15 What is the major neutral organic product for the following sequence? 1. POCI₂ pyridine ? 2. OsO4 OH 3. NaHSO Major Organic Product ✓ OH OH 'OH OH 'OH 'CIarrow_forward
- Could you please solve the first problem in this way and present it similarly but color-coded or step by step so I can understand it better? Thank you!arrow_forwardCould you please solve the first problem in this way and present it similarly but color-coded or step by step so I can understand it better? Thank you!arrow_forwardCould you please solve the first problem in this way and present it similarly but (color-coded) and step by step so I can understand it better? Thank you! I want to see what they are doingarrow_forward
- Can you please help mne with this problem. Im a visual person, so can you redraw it, potentislly color code and then as well explain it. I know im given CO2 use that to explain to me, as well as maybe give me a second example just to clarify even more with drawings (visuals) and explanations.arrow_forwardPart 1. Aqueous 0.010M AgNO 3 is slowly added to a 50-ml solution containing both carbonate [co32-] = 0.105 M and sulfate [soy] = 0.164 M anions. Given the ksp of Ag2CO3 and Ag₂ soy below. Answer the ff: Ag₂ CO3 = 2 Ag+ caq) + co} (aq) ksp = 8.10 × 10-12 Ag₂SO4 = 2Ag+(aq) + soy² (aq) ksp = 1.20 × 10-5 a) which salt will precipitate first? (b) What % of the first anion precipitated will remain in the solution. by the time the second anion starts to precipitate? (c) What is the effect of low pH (more acidic) condition on the separate of the carbonate and sulfate anions via silver precipitation? What is the effect of high pH (more basic)? Provide appropriate explanation per answerarrow_forwardPart 4. Butanoic acid (ka= 1.52× 10-5) has a partition coefficient of 3.0 (favors benzene) when distributed bet. water and benzene. What is the formal concentration of butanoic acid in each phase when 0.10M aqueous butanoic acid is extracted w❘ 25 mL of benzene 100 mL of a) at pit 5.00 b) at pH 9.00arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





