
a.
Prepare
a.
Explanation of Solution
Journal:
Journal is the method of recording monetary business transactions in chronological order. It records the debit and credit aspects of each transaction to abide by the double-entry system.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
Ø Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
Ø Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, and expenses.
Prepare journal entry to record the given transactions.
| Event Number | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit (Amount in $) | Credit (Amount in $) |
| 1. | Salaries Payable | 2,100 | |
| Cash | 2,100 | ||
| (To record the salaries paid from the Year 7) | |||
| 2. | Equipment (1) | 9,000 | |
| Van (2) | 27,000 | ||
| Cash | 36,000 | ||
| (To record the purchase made on equipment and van) | |||
| 3.5/1 | Prepaid rent | 9,000 | |
| Cash | 9,000 | ||
| (To record the payment of office rent in advance) | |||
| 4. | Supplies | 300 | |
| Accounts payable | 300 | ||
| (To record the purchase of supplies on account ) | |||
| 5. | Merchandise inventory | 33,600 | |
| Cash | 33,600 | ||
| (To record the purchase of alarms system for cash) | |||
| 6 | Allowance for doubtful accounts | 2,350 | |
| | 2,350 | ||
| (To record the allowance fir doubtful accounts) | |||
| 7 a. | Accounts receivable | 66,700 | |
| Alarms sales revenue | 66,700 | ||
| (To record the sales made on account) | |||
| 7.b | Cost of goods sold (3) | 32,290 | |
| Merchandise inventory | 32,290 | ||
| (To record the cost goods sold ) | |||
| 8. | Accounts receivable-credit card | 34,560 | |
| Accounts receivable | 50,000 | ||
| Credit card expense | 1,440 | ||
| Monitoring service revenue | 86,000 | ||
| (To record the monitoring services provided on account) | |||
| 9. | Maintenance expense | 45 | |
| Office supplies expense | 28 | ||
| Miscellaneous Expense | 11 | ||
| Cash short\over (4) | 4 | ||
| Cash | 88 | ||
| (To record the replenished petty cash fund) | |||
| 10. | Cash | 34,560 | |
| Accounts receivable-credit card | 34,560 | ||
| (To record the amount collected on due) | |||
| 11. | Salaries expense | 52,000 | |
| Cash | 52,000 | ||
| (To record the payment of salaries) | |||
| 12. | Cash | 115,000 | |
| Accounts receivable | 115,000 | ||
| (To record the amount collected on accounts receivable) | |||
| 13. | Advertising expense | 12,500 | |
| Cash | 12,500 | ||
| (To record the cash paid on advertising expense) | |||
| 14. | Utilities expense | 6,800 | |
| Cash | 6,800 | ||
| (To record the cash paid on utilities expense) | |||
| 15. | Cash | 12,000 | |
| Land | 4,000 | ||
| Gain on sale of land | 8,000 | ||
| (To record the sale made on land) | |||
| 16. | Accounts payable | 300 | |
| Cash | 300 | ||
| (To record the payment of accounts payable) | |||
| 17. | Dividend | 10,000 | |
| Cash | 10,000 | ||
| (To record the dividend paid to the shareholders) | |||
| 18. | Supplies Expense (5) | 370 | |
| Supplies | 370 | ||
| (To record the supplies that was on hand at the end of the year.) | |||
| 19. | Rent Expense (6) | 9,600 | |
| Prepaid rent | 9,600 | ||
| (To recognize the rent that was expired) | |||
| 20. | Uncollectible Accounts Expense (7) | 3,501 | |
| Allowance for doubtful accounts | 3,501 | ||
| (To recognize uncollectible accounts expense for the year) | |||
| 21. | 14,900 | ||
| | 14,900 | ||
| (To recognize the depreciation expense on the equipment and the van) | |||
| 22. | Salaries Expense | 1,500 | |
| Salaries payable | 1,500 | ||
| (To record the accrued salaries at December 31, Year 8) |
(Table 1)
Note:
Since the equipment is appraised by $10,000 and the van is appraised by $30,000. The book value of equipment and van is identified by using the proportion of 1:3
Working Note:
Calculate of equipment cost:
Calculate of van cost:
Calculate the cost of goods sold:
| Cost of goods sold | ||
| Unit (A) |
Cost per unit ($) (B) | Total |
| 18 | 285 | 5,130 |
| 97 | 280 | 27,160 |
| Total | 32,290 | |
Table (2) (3)
Calculate the value of cash short over:
Calculate the value of supplies expense
Calculate rent expense:
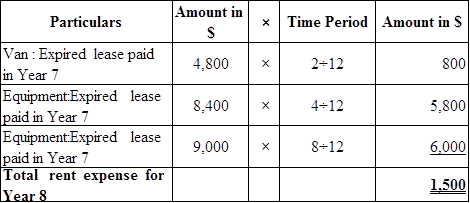
Table (3) (6)
Calculate uncollectible accounts expense:
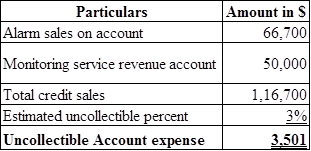
Table (4) (7)
Calculate the depreciation expense for equipment using straight line method:
Calculation depreciation expense of van using double declining method:
Calculation of total depreciation expense:
b.
Post the transaction to T- accounts.
b.
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
T-account refers to an individual account, where the increase or decrease in the value of specific asset, liability,
This account is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.’ An account consists of the three main components which are as follows:
- (a) The title of the account
- (b) The left or debit side
- (c) The right or credit side
| Cash | ||||
| Bal. | 93,708 | 1. | 2,100 | |
| 10. | 34,560 | 2. | 36,000 | |
| 12. | 115,500 | 3. | 9,000 | |
| 15. | 12,000 | 5. | 33,600 | |
| 9. | 88 | |||
| 11. | 52,000 | |||
| 13. | 12,500 | |||
| 14. | 6,800 | |||
| 16. | 300 | |||
| 17. | 10,000 | |||
| Bal. | 93,380 | |||
| Petty Cash | ||||
| Bal. | 100 | |||
| Accounts Receivable | ||||
| Bal. | 22,540 | |||
| 7a. | 66,700 | 6. | 2,350 | |
| 8. | 50,000 | 12. | 115,500 | |
| Bal. | 21,390 | |||
| Accounts Rec. Credit Cards | |||
| 8. | 34,560 | 10. | 34,560 |
| Bal. | 0 | ||
| Allow. for Doubt. Accounts | |||
| 6. | 2,350 | Bal. | 1,334 |
| 20. | 3,501 | ||
| Bal. | 2,485 | ||
| Supplies | |||
| Bal. | 250 | ||
| 4. | 300 | 18. | 370 |
| Bal. | 180 | ||
| Accounts Payable | |||
| 16. | 300 | 4. | 300 |
| Bal. | -0- | ||
| Salaries Payable | |||
| Bal. | 2,100 | ||
| 1. | 2,100 | 22. | 1,500 |
| Bal. | 1,500 | ||
| Common Stock | ||||
| Bal. | 50,000 | |||
| Bal. | 75,894 | ||
| Dividends | |||
| 17. | 10,000 | ||
| Bal. | 10,000 | ||
| Alarm Sales Revenue | ||||
| 7a. | 66,700 | |||
| Bal. | 66,700 | |||
| Monitoring Service Rev. | |||
| 8. | 86,000 | ||
| Bal. | 86,000 | ||
| Cost of Goods Sold | |||
| 7b. | 32,290 | ||
| Bal. | 32,290 | ||
| Advertising Expense | |||
| 13. | 12,500 | ||
| Bal. | 12,500 | ||
| Credit Card Expense | |||
| 8. | 1,440 | ||
| Bal. | 1,440 | ||
| Depreciation Expense | |||||
| 21. | 14,900 | ||||
| Bal. | 14,900 | ||||
| Maintenance Expense | |||||
| 9. | 45 | ||||
| Bal. | 45 | ||||
| Prepaid Rent | |||
| Bal. | 3,600 | ||
| 3. | 9,000 | 19. | 9,600 |
| Bal. | 3,000 | ||
| Merchandise Inventory | |||
| Bal. | 5,130 | 7b. | 32,290 |
| 5. | 33,600 | ||
| Bal. | 6,440 | ||
| Equipment | |||
| 2. | 9,000 | ||
| Bal. | 9,000 | ||
| Van | |||
| 2. | 27,000 | ||
| Bal. | 27,000 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation | |||
| 21. | 14,900 | ||
| Bal. | 14,900 | ||
| Land | |||
| Bal. | 4,000 | 15. | 4,000 |
| Bal. | -0- | ||
| Miscellaneous Expense | ||||
| 9. | 11 | |||
| Bal. | 11 | |||
| Office Supplies Expense | |||
| 9. | 28 | ||
| Bal. | 28 | ||
| Rent Expense | |||
| 19. | 9,600 | ||
| Bal. | 9,600 | ||
| Salaries Expense | ||||||
| 11. | 52,000 | |||||
| 22. | 1,500 | |||||
| Bal. | 53,500 | |||||
| Supplies Expense | |||
| 18. | 370 | ||
| Bal. | 370 | ||
| Uncollectible Accts. Exp. | |||
| 20. | 3,501 | ||
| Bal. | 3,501 | ||
| Utilities Expense | |||
| 14. | 6,800 | ||
| Bal. | 6,800 | ||
| Cash Short/Over | |||
| 9. | 4 | ||
| Bal. | 4 | ||
| Gain on Sale of Land | |||
| 15. | 8,000 | ||
| Bal. | 8,000 | ||
c.
Prepare
c.
Explanation of Solution
Trial balance:
Trial balance is the summary of accounts, and their debit and credit balances at a given point of time. It is usually prepared at end of the accounting period. Debit balances are listed in left column and credit balances are listed in right column. The totals of debit and credit column should be equal. Trial balance is useful in the preparation of the financial statements.
Prepare trial balance.
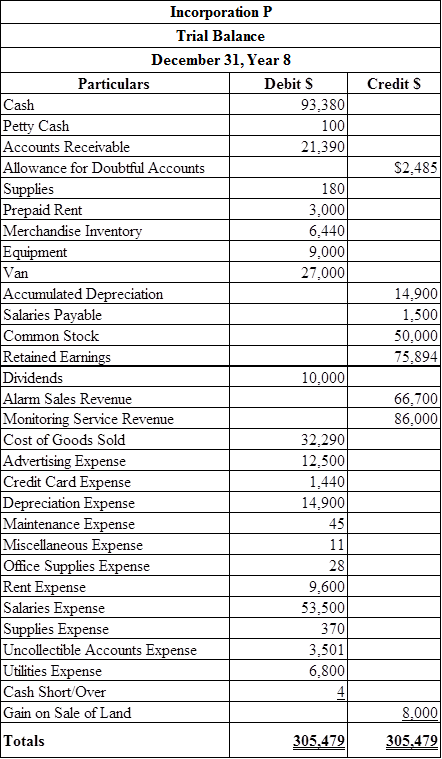
(Table 5)
Therefore, the total of debit, and credit columns of trial balance is $305,479.
d.
Prepare an income statement, statement of changes in stockholder’s equity,
d.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
Income statement is a financial statement that shows the net income or net loss by deducting the expenses from the revenues and vice versa.
Statement of changes in stockholders' equity:
Statement of changes in stockholders' equity records the changes in the owners’ equity during the end of an accounting period by explaining about the increase or decrease in the capital reserves of shares.
Balance Sheet:
Balance sheet summarizes the assets, the liabilities, and the stockholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Statement of cash flows
Statement of cash flow is a financial statement that shows the cash and cash equivalents of a company for a particular period of time. It shows the net changes in cash, by reporting the sources and uses of cash as a result of operating, investing, and financing activities of a company.
Prepare an income statement, statement of changes in stockholder’s equity, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows of Company P as follows:
| Company P | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, Year 8 | ||
| Particulars | Amount in $ | Amount in $ |
| Revenues: | ||
| Monitoring Service Revenue | 86,000 | |
| Alarm Sales Revenue | 66,700 | |
| Total Revenues | 152,700 | |
| Cost of Goods Sold | (32,920) | |
| Gross Margin | 120,410 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Advertising Expense | 12,500 | |
| Credit card Expense | 1,440 | |
| Depreciation Expense | 14,900 | |
| Office Supplies Expense | 28 | |
| Maintenance Expense | 45 | |
| Miscellaneous Expense | 11 | |
| Rent Expense | 9,600 | |
| Salaries Expense | 53,500 | |
| Supplies Expense | 370 | |
| Uncollectible Accounts Expense | 3,501 | |
| Utilities Expense | 6,800 | |
| Cash Short and Over | 4 | |
| Total Operating Expenses | 102,699 | |
| Net Operating Income | 17,711 | |
| Non-Operating Items | ||
| Gain on sale of land | 8,000 | |
| Net Income | 25,711 | |
(Table 6)
Therefore, the net income of Company P is $25,711.
| Company P | ||
| Statement of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, Year 8 | ||
| Particulars | Amount in $ | Amount in $ |
| Beginning Common Stock | 50,000 | |
| Plus: Common Stock Issued | - | |
| Ending Common Stock | 50,000 | |
| Beginning Retained Earnings | 75,894 | |
| Plus: Net Income | 25,711 | |
| Less: Dividends | (10,000) | |
| Ending Retained Earnings | 91,605 | |
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | 141,605 | |
(Table 7)
Therefore, the total stockholder’s equity is $141,605
| Company P | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| As of December 31, Year 8 | ||
| Particulars | Amount in $ | Amount in $ |
| Assets: | ||
| Cash | 93,380 | |
| Petty Cash | 100 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 21,390 | |
| Allowance for doubtful accounts | (2,485) | 18,905 |
| Supplies | 180 | |
| Prepaid Rent | 3,000 | |
| Merchandise Inventory | 6,440 | |
| Equipment | 9,000 | |
| Van | 27,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation | (14,900) | 21,100 |
| Total Assets | 143,105 | |
| Liabilities: | ||
| Salaries Payable | 1,500 | |
| Total Liabilities | 1,500 | |
| Stockholders’ Equity: | ||
| Common Stock | 50,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | 91,605 | |
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | 141,605 | |
| Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | 143,105 | |
(Table 8)
Therefore, the total assets of Company P are $143,105, and the total liabilities and stockholders’ equity is $143,105.
| Company P | ||
| Statement of Cash Flows | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, Year 8 | ||
| Particulars | Amount in $ | Amount in $ |
| Cash Flows From Operating Activities: | ||
| Cash Receipts from Customers (11) | 150,060 | |
| Cash Payment for Expenses (12) | (116,388) | |
| Net Cash Flow from operating activities | 33,672 | |
| Cash Flows From Investing Activities: | ||
| Inflow from Sale of Land | 12,000 | |
| Outflow to Purchase Equip. and Van | (36,000) | |
| Net Cash Flow from investing activities | (24,000) | |
| Cash Flows From Financing Activities: | ||
| Cash Payments for Dividends | (10,000) | |
| Net Cash Flow from financing activities | (10,000) | |
| Net Increase in Cash | (328) | |
| Plus: Beginning Cash Balance | 93,808 | |
| Ending Cash Balance | 93,880 | |
(Table 9)
Therefore, the net increase in cash of Company P for the year ended December 31, Year 8 is, $93,880.
Working note:
Calculate the total cash from customers
Calculate total cash payment for expense
e.
Prepare closing entries of Company P.
e.
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries:
Closing entries are those journal entries, which are passed to transfer the final balances of temporary accounts, (all revenues account, all expenses account and dividend) to retained earnings. Closing entries produce a zero balance in each temporary account.
Prepare closing entries of Company P as follows:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit in $ | Credit in $ |
| Dec. 31 | Alarm Sales Revenue | 66,700 | |
| Monitoring Service Revenue | 86,000 | ||
| Gain on sale of land | 8,000 | ||
| Retained Earnings | 106,700 | ||
| (To close all revenue accounts) | |||
| Dec. 31 | Retained Earnings | 134,989 | |
| Cost of Goods Sold | 32,290 | ||
| Advertising Expense | 12,500 | ||
| Credit card Expense | 1,440 | ||
| Depreciation Expense | 14,900 | ||
| Maintenance Expense | 45 | ||
| Miscellaneous Expense | 11 | ||
| Office supplies Expense | 28 | ||
| Rent Expense | 9,600 | ||
| Salaries Expense | 53,500 | ||
| Supplies Expense | 370 | ||
| Uncollectible Accounts Expense | 3,501 | ||
| Utilities Expense | 6,800 | ||
| Cash Short and Over | 4 | ||
| (To close all expense account) | |||
| Dec. 31 | Retained Earnings | 10,000 | |
| Dividends | 10,000 | ||
| (To close dividends account) |
(Table 10)
Closing entry for revenue account:
In this closing entry, the service revenue and gain on sale of land accounts are closed by transferring the amount of service revenue and gain on sale of land accounts to retained earnings in order to bring the revenue account balance to zero. Hence, debit the service revenue account for $160,700 and credit the retained account for $160,700.
Closing entry for expenses account:
In this closing entry, all expense accounts are closed by transferring the amount of total expense to the retained earnings in order to bring the expense account balance to zero. Hence, debit the retained earnings for $134,989 and credit supplies account for $134,989.
Closing entry for dividends account:
In this closing entry, the dividends account is closed by transferring the amount of dividends to retained earnings in order to bring the dividends account balance to zero. Hence, debit the retained earnings for $10,000 and credit dividends account for $10,000.
f.
Post the closing entries to the T-account, and prepare a post-closing trial balance.
f.
Explanation of Solution
Post the closing entries to the T-account:
| Cash | |||
| Bal. | 93,380 | ||
| Petty Cash | |||
| Bal. | 100 | ||
| Accounts Receivable | |||
| Bal. | 21,390 | ||
| Allow. for Doubt. Accts. | |||
| Bal. | 2,485 | ||
| Supplies | |||
| Bal. | 180 | ||
| Prepaid Rent | |||
| Bal. | 3,000 | ||
| Merchandise Inventory | |||
| Bal. | 6,440 | ||
| Equipment | |||
| Bal. | 9,000 | ||
| Accumulated Depr. | |||
| Bal. | 14,900 | ||
| Salaries Payable | |||
| Bal. | 1,500 | ||
| Common Stock | |||
| Bal. | 50,000 | ||
| Retained Earnings | |||||
| Bal. | 75,894 | ||||
| cl. | 134,989 | cl | 160,700 | ||
| cl. | 10,000 | ||||
| Bal. | 91,605 | ||||
| Dividends | |||
| Bal. | 10,000 | cl | 10,000 |
| Bal. | -0- | ||
| Alarm Sales Revenue | ||||
| cl. | 66,700 | Bal. | 66,700 | |
| Bal. | -0- | |||
| Monit. Service Revenue | |||
| cl. | 86,000 | Bal. | 86,000 |
| Bal. | -0- | ||
| Cost of Goods Sold | |||
| Bal. | 32,290 | cl | 32,290 |
| Bal. | -0- | ||
| Advertising Expense | |||
| Bal. | 12,500 | cl | 12,500 |
| Bal. | -0- | ||
| Credit Card Expense | |||
| Bal. | 1,440 | cl. | 1,440 |
| Bal. | -0- | ||
| Depreciation Expense | |||
| Bal. | 14,900 | cl. | 14,900 |
| Bal. | -0- | ||
| Maintenance Expense | |||
| Bal. | 45 | cl. | 45 |
| Bal. | -0- | ||
| Miscellaneous Expense | |||
| Bal. | 11 | cl. | 11 |
| Bal. | -0- | ||
| Office Supplies Expense | |||
| Bal. | 28 | cl. | 28 |
| Bal. | -0- | ||
| Rent Expense | |||
| Bal. | 9,600 | cl. | 9,600 |
| Bal. | -0- | ||
| Salaries Expense | |||
| Bal. | 53,500 | cl. | 53,500 |
| Bal. | -0- | ||
| Supplies Expense | ||||
| Bal. | 370 | cl. | 370 | |
| Bal. | -0- | |||
| Uncoll. Accts. Expense | |||
| Bal. | 3,501 | cl. | 3,501 |
| Bal. | -0- | ||
| Utilities Expense | |||
| Bal. | 6,800 | cl. | 6,800 |
| Bal. | -0- | ||
| Cash Short/Over | |||
| Bal. | 4 | Bal. | 4 |
| Bal. | -0- | ||
| Gain on Sale of Land | |||
| cl. | 8,000 | Bal. | 8,000 |
| Bal. | -0- | ||
Prepare a post-closing trial balance:
| Company P | ||
| Post-Closing Trial Balance | ||
| December 31, Year 8 | ||
| Account Titles | Debit in $ | Credit in $ |
| Cash | 93,380 | |
| Petty Cash | 100 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 21,390 | |
| Allowance for doubtful accounts | 2,485 | |
| Supplies | 180 | |
| Prepaid Rent | 3,000 | |
| Merchandise Inventory | 6,440 | |
| Equipment | 9,000 | |
| Van | 27,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation | 14,900 | |
| Salaries Payable | 1,500 | |
| Common Stock | 50,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | 91,605 | |
| Totals | 160,490 | 160,490 |
(Table 11)
Therefore, the total of debit, and credit columns of post-closed trial balance is $160,490.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Fundamental Financial Accounting Concepts
- Please provide the solution to this financial accounting question using proper accounting principles.arrow_forwardBelow is information for Blue Company. Using this information, answer the following questions on the "Calculation" tab in the file. Show your work (how you got your answer) and format appropriately. Blue company has prepared the following contribution format income statement based on a sales volume of 1,000 units (the relevant range of production is 500 to 1,500 units): Sales $ 40,000 Variable expenses 24,000 Contribution margin 16,000 NOTE: Use the amounts in the original fact pattern to the left as your basis for the questions below. Fixed expenses 12,000 Net operating income $ 4,000 Questions: 1. What is the contribution margin per unit? 2. What is the contribution margin ratio? 3. What is…arrow_forwardI am looking for help with this financial accounting question using proper accounting standards.arrow_forward
- General accountingarrow_forwardPlease explain the correct approach for solving this general accounting question.arrow_forwardRobin Corporation has ordinary income from operations of $30,000, net long-term capital gain of $10,000, and net short-term capital loss of $15,000. What is the taxable income for 2010? a) $25,000. b) $27,000. c) $28,500. d) $30,000. e) None of the above.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





