
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The equation for the reaction that takes place to increase the solubility of
Concept Introduction: The solubility of a salt is defined as amount of salt dissolved in per 100 mL of the solvent at a constant temperature.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of aluminium ions and hydroxide ion forms aluminium hydroxide but it can also form
The precipitate is more soluble in very acidic and basic solutions.
The equations for reaction to increase the solubility of
The reaction in acidic solution is represented as follows:
The reaction in basic medium is represented as follows:
(b)
Interpretation: This is to be shown that the solubility of
Concept Introduction:
For a salt, the expression for solubility product can be written as follows:
The solubility product constant can be represented as follows:
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The relation between K,
Or,
The equilibrium constant expression can be represented as follows:
For the above reaction,
If ionization constant of water is used in this expression, the above expression can be rearranged as follows:
On rearranging,
Or,
The solubility product of
This can be rearranged as follows:
Also,
From equation (1) and (2),
(b)
Interpretation: The solubility of
Concept Introduction: The relation between solubility and hydrogen ion concentration can be represented as follows:
The relation between pH and hydrogen ion concentration can be represented as follows:
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The given value of K is 40.0 and solubility product constant is
The solubility of
Putting the value of K,
Or,
Now, for pH value 4, the hydrogen ion concentration will be
Similarly, for pH value 5, the hydrogen ion concentration will be
Thus, for pH value 6 -12, the solubility of
| pH | |
| 6 | |
| 7 | |
| 8 | |
| 9 | |
| 10 | |
| 11 | |
| 12 | |
| 13 | |
| 14 |
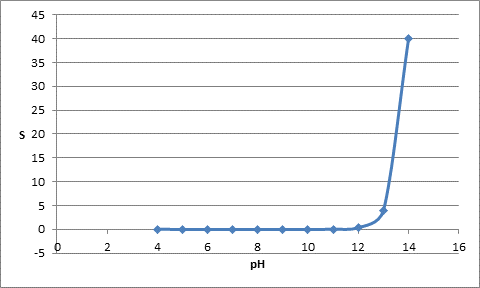
The table for pH and solubility can be represented as follows:
| pH | S |
| 4 | 0.02 |
| 5 | |
| 6 | |
| 7 | |
| 8 | |
| 9 | |
| 10 | |
| 11 | |
| 12 | 0.4 |
| 13 | 4 |
| 14 | 40 |
The plot can be represented as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Chemical Principles
- Name the major organic product of the following action of 4-chloro-4-methyl-1-pentanol in neutral pollution 10+ Now the product. The product has a molecular formula f b. In a singly hain, the starting, material again converts into a secule with the molecular kormula CIO. but with comply Draw the major organic structure inhalationarrow_forwardMacmillan Learning Alcohols can be oxidized by chromic acid derivatives. One such reagent is pyridinium chlorochromate, (C,H,NH*)(CICTO3), commonly known as PCC. Draw the proposed (neutral) intermediate and the organic product in the oxidation of 1-butanol by PCC when carried out in an anhydrous solvent such as CH₂C₁₂. PCC Intermediate OH CH2Cl2 Draw the intermediate. Select Draw Templates More с H Cr о Product Draw the product. Erase Select Draw Templates More H о Erasearrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. A C6H5 CH3arrow_forward
- Provide the reagents for the following reactions.arrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound Z, I have to add two compounds A1 and A2. Indicate which compounds are needed. P(C6H5)3arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. O CH3CH2NH2, TSOH Select to Draw >arrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





