
Student Solutions Manual for Zumdahl/Zumdahl/DeCoste?s Chemistry, 10th Edition
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957510
Author: ZUMDAHL, Steven S.; Zumdahl, Susan A.; DeCoste, Donald J.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 169CP
Cholesterol (C27H46O) has the following structure:
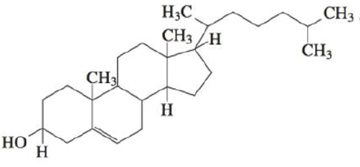
In such shorthand structures, each point where lines meet represents a carbon atom, and most H atoms are not shown. Draw the complete structure showing all carbon and hydrogen atoms. (There will be four bonds to each carbon atom.)
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
What is the total energy cost associated with the compound below adopting the shown conformation?
CH3
HH
DH
CH3
ΗΝ,
Draw Final Product
C
cyclohexanone
pH 4-5
Edit Enamine
H3O+
CH3CH2Br
THF, reflux
H
Edit Iminium Ion
How many hydrogen atoms are connected to the indicated carbon atom?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Student Solutions Manual for Zumdahl/Zumdahl/DeCoste?s Chemistry, 10th Edition
Ch. 8 - Distinguish between the terms electronegativity...Ch. 8 - When an element forms an anion, what happens to...Ch. 8 - Define the term lattice energy. Why,...Ch. 8 - Explain how bond energies can be used to estimate...Ch. 8 - Prob. 5RQCh. 8 - Explain the terms resonance and delocalized...Ch. 8 - Define formal charge and explain how to calculate...Ch. 8 - Give two requirements that should be satisfied for...Ch. 8 - Consider the following compounds: CO2, SO2, KrF2,...Ch. 8 - Explain the electronegativity trends across a row...
Ch. 8 - The ionic compound AB is formed. The charges on...Ch. 8 - Prob. 3ALQCh. 8 - The bond energy for a CH bond is about 413 kJ/mol...Ch. 8 - Prob. 5ALQCh. 8 - Which has the greater bond lengths: NO2 or NO3?...Ch. 8 - The following ions are best described with...Ch. 8 - The second electron affinity values for both...Ch. 8 - What is meant by a chemical bond? Why do atoms...Ch. 8 - Why are some bonds ionic and some covalent?Ch. 8 - How does a bond between Na and Cl differ from a...Ch. 8 - Arrange the following molecules from most to least...Ch. 8 - Does a Lewis structure tell which electron come...Ch. 8 - True or false? In general, a large atom has a...Ch. 8 - What is the central idea of the VSEPR model?Ch. 8 - In Section 8.13 of the text, the term effective...Ch. 8 - Describe the type of bonding that exists in die...Ch. 8 - Some plant fertilizer compounds are (NH4)2SO4,...Ch. 8 - Some of the important properties of ionic...Ch. 8 - What is the electronegativity trend? Where does...Ch. 8 - Give one example of a compound having a linear...Ch. 8 - When comparing the size of different ions, the...Ch. 8 - In general the higher the charge on the ions in an...Ch. 8 - Combustion reactions of fossil fuels provide most...Ch. 8 - Which of the following statements is/are true?...Ch. 8 - Prob. 29QCh. 8 - The molecules BF3, CF4, CO2, PF5, and SF6 are all...Ch. 8 - Without using Fig. 3-4, predict the order of...Ch. 8 - Without using Fig. 3-4, predict the order of...Ch. 8 - Without using Fig. 3-4, predict which bond in each...Ch. 8 - Without using Fig. 3-4, predict which bond in each...Ch. 8 - Prob. 35ECh. 8 - Prob. 36ECh. 8 - Which of the following incorrectly shows the bond...Ch. 8 - Indicate the bond polarity (show the partial...Ch. 8 - Predict the type of bond (ionic, covalent, or...Ch. 8 - List all the possible bonds that can occur between...Ch. 8 - Hydrogen has an electronegativity value between...Ch. 8 - Rank the following bonds in order of increasing...Ch. 8 - State whether or not each of the following has a...Ch. 8 - The following electrostatic potential diagrams...Ch. 8 - Prob. 45ECh. 8 - Prob. 46ECh. 8 - Predict the empirical formulas of the ionic...Ch. 8 - Predict the empirical formulas of the ionic...Ch. 8 - Write electron configurations for a. the cations...Ch. 8 - Write electron configurations for a. the cations...Ch. 8 - Which of the following ions have noble gas...Ch. 8 - What noble gas has the same electron configuration...Ch. 8 - Give the formula of a negative ion that would have...Ch. 8 - Prob. 54ECh. 8 - Give three ions that are isoelectronic with neon....Ch. 8 - Consider the ions Sc3+, Cl, K+, Ca2+, and S2....Ch. 8 - Prob. 57ECh. 8 - For each of the following groups, place the atoms...Ch. 8 - Which compound in each of the following pairs of...Ch. 8 - Which compound in each of the following pairs of...Ch. 8 - Use the following data for potassium chloride to...Ch. 8 - Use the following data for magnesium fluoride to...Ch. 8 - Consider the following energy changes: E(kJ/mol)...Ch. 8 - Compare the electron affinity of fluorine to the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 65ECh. 8 - Use the following data (in kJ/mol) to estimate E...Ch. 8 - Rationalize the following lattice energy values:...Ch. 8 - The lattice energies of FeCl3, FeCl2, and Fe2O3...Ch. 8 - Use bond energy values (Table 3-3) to estimate E...Ch. 8 - Use bond energy values (Table 3-3) to estimate E...Ch. 8 - Prob. 71ECh. 8 - Acetic acid is responsible for the sour taste of...Ch. 8 - Use bond energies to predict E for the following...Ch. 8 - The major industrial source of hydrogen gas is by...Ch. 8 - Use bond energies to estimate E for the combustion...Ch. 8 - Prob. 76ECh. 8 - Prob. 77ECh. 8 - Consider the following reaction: A2+B22AB E =...Ch. 8 - Compare your answers from parts a and b of...Ch. 8 - Compare your answers from Exercise 72 to the H...Ch. 8 - The standard enthalpies of formation for S(g),...Ch. 8 - Use the following standard enthalpies of formation...Ch. 8 - The standard enthalpy of formation for N2H2(g) is...Ch. 8 - The standard enthalpy of formation for NO(g) is...Ch. 8 - Write Lewis structures that obey the octet rule...Ch. 8 - Write Lewis structures that obey the octet rule...Ch. 8 - Write Lewis structures that obey the octet rule...Ch. 8 - Write Lewis structures that obey the octet rule...Ch. 8 - One type of exception to the octet rule are...Ch. 8 - Lewis structures can be used to understand why...Ch. 8 - The most common exceptions to the octet rule are...Ch. 8 - Prob. 92ECh. 8 - Write Lewis structures for the following. Show all...Ch. 8 - Prob. 94ECh. 8 - Benzene (C6H6) consists of a six-membered ring of...Ch. 8 - Borazine (B3N3H6) has often been called inorganic...Ch. 8 - An important observation supporting the concept of...Ch. 8 - Consider the following bond lengths: CO143pmC9O123...Ch. 8 - A toxic cloud covered Bhopal, India, in December...Ch. 8 - Prob. 103ECh. 8 - Prob. 104ECh. 8 - Write Lewis structures that obey the octet rule...Ch. 8 - Write Lewis structures for the species in Exercise...Ch. 8 - Oxidation of the cyanide ion produces the stable...Ch. 8 - When molten sulfur reacts with chlorine gas, a...Ch. 8 - Carbon and sulfur form compounds with each other...Ch. 8 - Prob. 112ECh. 8 - Predict the molecular structure and bond angles...Ch. 8 - Predict die molecular structure and bond angles...Ch. 8 - There are several molecular structures based on...Ch. 8 - Two variations of the octahedral geometry (see...Ch. 8 - Prob. 117ECh. 8 - Consider the molecular structures illustrated in...Ch. 8 - Predict the molecular structure (including bond...Ch. 8 - Predict the molecular structure (including bond...Ch. 8 - Predict the molecular structure (including bond...Ch. 8 - Predict the molecular structure (including bond...Ch. 8 - Prob. 123ECh. 8 - Which of the molecules in Exercise 120 have net...Ch. 8 - Which of the molecules in Exercise 121 have net...Ch. 8 - Which of the molecules in Exercise 122 have net...Ch. 8 - Write Lewis structures and predict the molecular...Ch. 8 - Write Lewis structures and predict whether each of...Ch. 8 - Consider the following Lewis structure where E is...Ch. 8 - Consider the following Lewis structure where E is...Ch. 8 - Two different compounds exist having the formula...Ch. 8 - Two different compounds have the formula XeF2Cl2....Ch. 8 - Arrange the following in order of increasing...Ch. 8 - For each of the following, write an equation that...Ch. 8 - Use bond energies (table 3-3), values of electron...Ch. 8 - Write Lewis structures for CO32, HCO3, and H2CO3....Ch. 8 - Which member of the following pairs would you...Ch. 8 - What do each of the following sets of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 139AECh. 8 - Although both Br3 and I3 ions are known, the F3...Ch. 8 - Prob. 142AECh. 8 - Which of the following molecules have not dipole...Ch. 8 - Prob. 145AECh. 8 - Look up the energies for the bonds in CO and N2....Ch. 8 - Classify the bonding in each of the following...Ch. 8 - List the bonds PCl, PF, OF, and SiF from least...Ch. 8 - Arrange the atoms and/or ions in the following...Ch. 8 - Use the following data to estimate E for the...Ch. 8 - Use bond energy values to estimate E for the...Ch. 8 - Which of the following compounds or ions exhibit...Ch. 8 - The formulas of several chemical substances are...Ch. 8 - Predict the molecular structure, bond angles, and...Ch. 8 - Use Coulombs Jaw, V=Q1Q240r=2.311019Jnm(Q1Q2r) to...Ch. 8 - Prob. 156CPCh. 8 - Calculate the standard heat of formation of the...Ch. 8 - Given the following information: Energy of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 159CPCh. 8 - Think of forming an ionic compound as three steps...Ch. 8 - The compound NF3 is quite stable, but NCl3, is...Ch. 8 - Three processes that have been used for the...Ch. 8 - The compound hexaazaisowurtzitane is one of the...Ch. 8 - Many times extra stability is characteristic of a...Ch. 8 - The study of carbon-containing compounds and their...Ch. 8 - Draw a Lewis structure for the N,...Ch. 8 - Prob. 167CPCh. 8 - Consider the following computer-generated model of...Ch. 8 - Cholesterol (C27H46O) has the following structure:...Ch. 8 - A compound, XF5, is 42.81% fluorine by mass....Ch. 8 - Identify the following elements based on their...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Identify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forwardIdentify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forwardchoose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forward
- Why isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forwardOH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forward
- Complete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardQ Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in basic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. Zn(s) → Zn(OH)₄²⁻(aq)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133109655
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Stoichiometry - Chemistry for Massive Creatures: Crash Course Chemistry #6; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UL1jmJaUkaQ;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Bonding (Ionic, Covalent & Metallic) - GCSE Chemistry; Author: Science Shorts;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p9MA6Od-zBA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
General Chemistry 1A. Lecture 12. Two Theories of Bonding.; Author: UCI Open;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dLTlL9Z1bh0;License: CC-BY