
Concept explainers
LO3 LO4 10.
| Year | Cash Flow (A) | Cash Flow (B) |
| 0 | –$78,500 | –$78,500 |
| 1 | 43,000 | 21,000 |
| o | 29,000 | 28,000 |
| 3 | 23,000 | 34,000 |
| 4 | 21,000 | 41,000 |
a. What is the IRR for each of these projects? If you apply the IRR decision rule, which project should the company accept? Is this decision necessarily correct?
b. If the required return is 11 percent, what is the NPV for each of these projects? Which project will you choose if you apply the NPV decision rule?
c. Over what range of discount rates would you choose Project A? Project B? At what discount rate would you be indifferent between these two projects? Explain.
a)
To calculate: The IRR (Internal Rate of Return) for the proposed projects of Company Z, the project that the company must accept and discuss whether the taken decision is appropriate
Introduction:
The IRR (Internal Rate of Return) is a rate of discount which makes the predictable investment’s NPV equal to zero.
The NPV (Net Present Value) is a capital budgeting technique which is used to assess the investment that, in turn, is utilized to identify the profitability in a proposed investment.
Answer to Problem 10QP
As IRR is higher in Project A when compared to Project B, Project A can be accepted. However, it is not the appropriate decision because the criterion of IRR has a problem in ranking for mutually exclusive projects.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Company Z has identified two mutually exclusive projects where the cash flows of Project A are $43,000, $29,000, $23,000, and $21,000 for year1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. The cash flows of Project B are $21,000, $28,000, $34,000, and $41,000 for year 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. The initial costs for both the projects are $78,500 respectively.
Note:
- NPV is the difference between the present values of the cash inflows from the present value of cash outflows.
- The IRR is the rate of interest which makes the project’s NPV equal to zero. Hence, using the available information, assume that NPV is equal to zero and form an equation to compute the IRR.
Equation of NPV to compute IRR assuming that NPV is equal to zero:
Compute IRR for Project A using a spreadsheet:
Step 1:
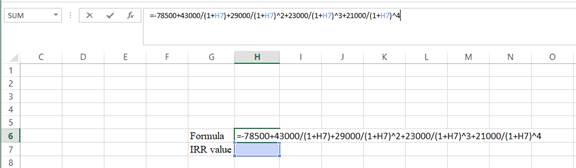
- Type the equation of NPV in H6 in the spreadsheet and consider the IRR value as H7
Step 2:
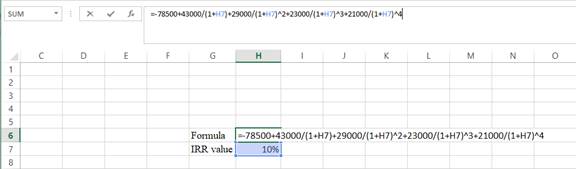
- Assume the IRR value as 10%
Step 3:
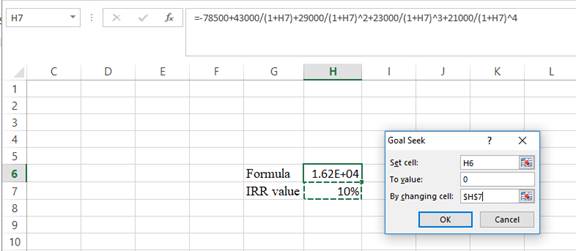
- In the spreadsheet, go to data and select the what-if analysis.
- In the what-if analysis, select goal seek.
- In set cell, select H6 (the formula).
- The “To value” is considered as 0 (the assumption value for NPV).
- The H7 cell is selected for the by changing cell.
Step 4:
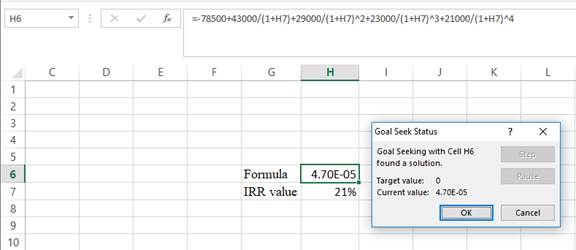
- Following the previous step, click OK in the goal seek. The goal seek status appears with the IRR value.
Step 5:
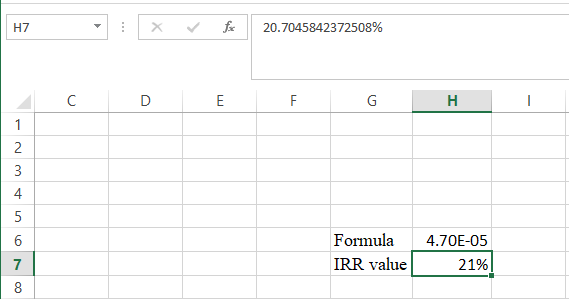
- The value appears to be 20.7045842372508%.
Hence, the IRR value is 20.70%.
Compute IRR for Project B using a spreadsheet:
Step 1:
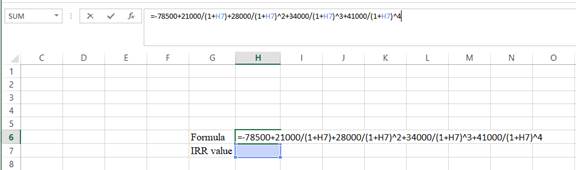
- Type the equation of NPV in H6 in the spreadsheet and consider the IRR value as H7.
Step 2:
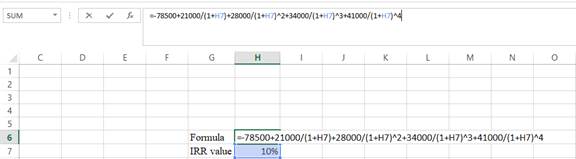
- Assume the IRR value as 10%.
Step 3:
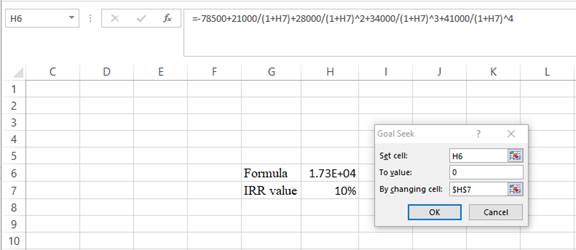
- In the spreadsheet, go to data and select the what-if analysis.
- In the what-if analysis, select goal seek.
- In set cell, select H6 (the formula).
- The “To value” is considered as 0 (the assumption value for NPV).
- The H7 cell is selected for the by changing cell.
Step 4:
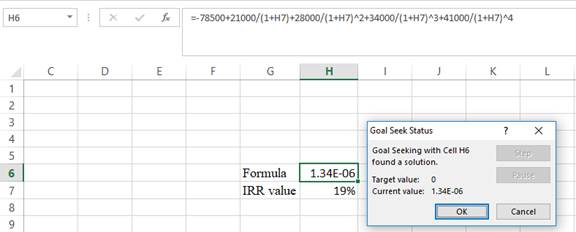
- Following the previous step click OK in the goal seek. The goal seek status appears with the IRR value,
Step 5:
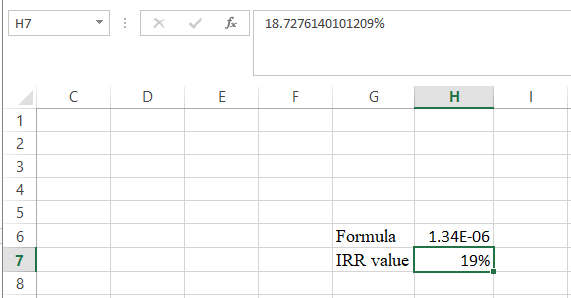
- The value appears to be 18.7276140101209%.
Hence, the IRR value is 18.73%.
b)
To calculate: The NPV for the projects to choose the best project for the company
Introduction:
The IRR (Internal Rate of Return) is a rate of discount which makes the predictable investment’s NPV equal to zero.
The NPV (Net Present Value) is a capital budgeting technique which is used to assess the investment that, in turn, is utilized to identify the profitability in a proposed investment.
Answer to Problem 10QP
As NPV is greater in Project B, the company must accept Project B.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Company Z has identified two mutually exclusive projects where the cash flows of Project A are $43,000, $29,000, $23,000, and $21,000 for year1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. The cash flows of Project B are $21,000, $28,000, $34,000, and $41,000 for year 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. The initial costs for both the projects are $78,500 respectively.
Note:
- NPV is the difference between the present values of the cash inflows from the present value of cash outflows.
- The IRR is the rate of interest which makes the project’s NPV equal to zero. Hence, using the available information, assume that NPV is equal to zero and form an equation to compute the IRR.
Formula to calculate the NPV:
Compute NPV for Project A:
Hence, the NPV for Project A is $14,426.54.
Compute NPV for Project B:
Note: The rate is given at 11%.
Hence, the NPV for project B is $15,012.82.
c)
To calculate: The rates of discount at which the company will select Project A and Project B and the discount rate in which the company will be indifferent in selecting between the two projects
Introduction:
The IRR (Internal Rate of Return) is a rate of discount which makes the predictable investment’s NPV equal to zero.
The NPV (Net Present Value) is a capital budgeting technique which is used to assess the investment that, in turn, is utilized to identify the profitability in a proposed investment.
Answer to Problem 10QP
At the rate of discount above 12.21%, the company must choose Project A, and for the rate below 12.21%, the company should choose Project B. Hence, it is indifferent at the discount rate of 12.21%.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Company Z has identified two mutually exclusive projects where the cash flows of Project A are $43,000, $29,000, $23,000, and $21,000 for year1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. The cash flows of Project B are $21,000, $28,000, $34,000, and $41,000 for year 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. The initial costs for both the projects are $78,500 respectively.
Note:
- NPV is the difference between the present values of the cash inflows from the present value of cash outflows.
- The IRR is the rate of interest which makes the project’s NPV equal to zero. Hence, using the available information, assume that NPV is equal to zero and form an equation to compute the IRR.
Equation to calculate the crossover rates:
Compute the discount rate using spreadsheet
Step 1:
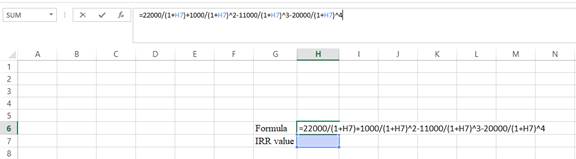
- Type the equation of NPV in H6 in the spreadsheet and consider the R value as H7.
Step 2:
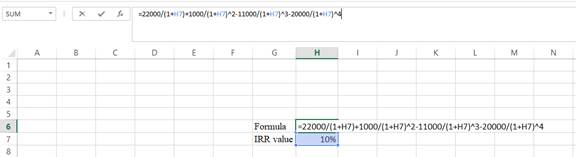
- Assume the R value as 10%.
Step 3:
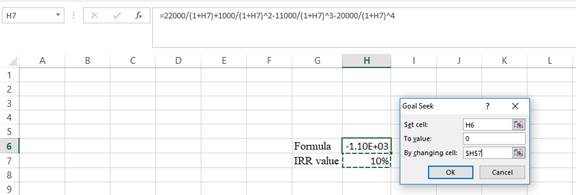
- In the spreadsheet, go to data and select the what-if analysis.
- In the what-if analysis, select goal seek.
- In set cell, select H6 (the formula).
- The “To value” is considered as 0 (the assumption value for NPV).
- The H7 cell is selected for the by changing cell.
Step 4:
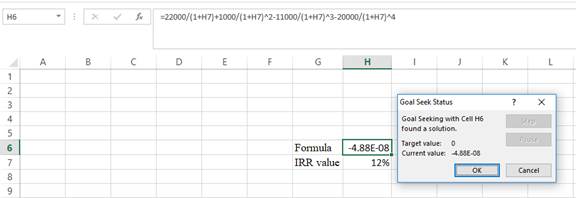
- Following the previous step click OK in the goal seek. The goal seek status appears with the R value.
Step 5:
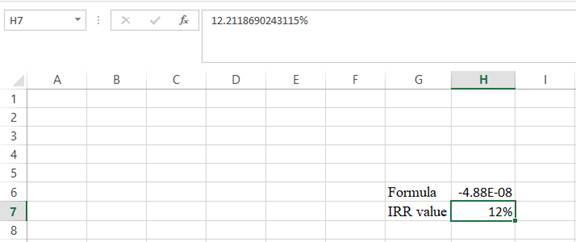
- The value appears to be 12.2118690243115%.
Hence, the R value is 12.21%.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
ESSENTIALS CORPORATE FINANCE + CNCT A.
- How a does researcher ensure that consulting recommendations are data-driven? What does make it effective, and sustainable? Please help explain and give the example How does DMAC help researchers to improve their business processes? How to establish feedback loops for ongoing refinement. Please give the examplesarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardExplain what the business model of payday lenders, title pawn lenders, and “credit approved” used car dealers.arrow_forward
- The current NPV of a $30 million bond with 9% interest, 8% coupon rate, and discounted at $95arrow_forwardCould you please help to explain the DMAIC phases and how a researcher would use them to conduct a consulting project? What is a measure process performance and how to analyze the process? What is an improve process performance and how the control improves process and future process performance?arrow_forwardConsider the two stocks below. Graph the frontier of combinations of the two stocks. Show the effect on the frontier of varying the correlation from −1 to +1. 1 2 3 Mean A B C D TWO STOCKS Varying the correlation coefficient Stock A Stock B 3.00% 8.00% 4 Sigma 15.00% 22.00% 5 Correlation 0.3000 Farrow_forward
- Lindsay is 30 years old and has a new job in web development. She wants to make sure that she is financially sound by the age of 55, so she plans to invest the same amount into a retirement account at the end of every year for the next 25 years. (a) Construct a data table in Excel that will show Lindsay the balance of her retirement account for various levels of annual investment and return. If Lindsay invests $10,000 at return of 6%, what would be the balance at the end of the 25th year? Note that because Lindsay invests at the end of the year, there is no interest earned on the contribution for the year in which she contributes. Round your answer to a whole dollar amount. $ (b) Develop a two-way table for annual investment amounts of $5,000 to $20,000 in increments of $1,000 and for returns of 0% to 12% in increments of 1%. From the 2-way table, what are the minimum annual investments Lindsay must contribute for annual rates ranging from 6% to 11%, if she wants to…arrow_forwardDoes Airbnb have any impaired assets? If so, what are they?arrow_forward1. Consider two assets with the following returns: State Prob. of state R1 R2 1 2/3 .03 .05 2 1/3 .09 .02arrow_forward
- Bright wood! Seating sells reclining chairs for $55.00 per unit. The variable cost is 322 per unit. Each reclining chair requires 5 direct labor hours and 3 machine hours to produce. ibution margin pemachine hon Wrightwood Manufacturing has a break-even point of 1,500 units. The sales price per unit is $18. and the variable cost per us $13. If the company sells 3,500 units, what will its net income be? Crestwood Industries provides the following budget data for its Processing Department for the year 2022: ⚫ Manufacturing Overhead Costs=250 ⚫ Direct Labor Costs $1,234,500 Determine the manufacturing overhead application rate under the base of Direct Labor Costs. Modesto Accessories manufactures two types of wallets leather and canvas. The company allocates manufacturing overhead using a single plant wide rate with direct labor cost as the allocation base. $48 Estimated Overhead Costs = 30,600 Direct Labor Cost per Leather Wallet Direct Labor Cost per Canvas Wallet = $52 Number of…arrow_forwardNo Aiarrow_forwardNo aiarrow_forward

 Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning


