
Concept explainers
For the following exercises, use this scenario: A health-conscious company decides to make a trail mix Out Of almonds, dried cranberries, and chocolate-covered cashews. The nutritional information for these items is shown in Table 1. 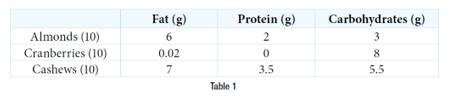
68.For the "energy-booster" mix, there are 1,000 pieces in the mix, containing 145 g of protein and 625 g of carbohydrates. If the number of almonds and cashews summed together is equivalent to the amount of cranberries, how many of each item is in the trail mix?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
College Algebra By Openstax
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
- Solve the problemsarrow_forwardSolve the problems on the imagearrow_forwardAsked this question and got a wrong answer previously: Third, show that v3 = (−√3, −3, 3)⊤ is an eigenvector of M3 . Also here find the correspondingeigenvalue λ3 . Just from looking at M3 and its components, can you say something about the remaining twoeigenvalues? If so, what would you say?arrow_forward
- Determine whether the inverse of f(x)=x^4+2 is a function. Then, find the inverse.arrow_forwardThe 173 acellus.com StudentFunctions inter ooks 24-25/08 R Mastery Connect ac ?ClassiD-952638111# Introduction - Surface Area of Composite Figures 3 cm 3 cm 8 cm 8 cm Find the surface area of the composite figure. 2 SA = [?] cm² 7 cm REMEMBER! Exclude areas where complex shapes touch. 7 cm 12 cm 10 cm might ©2003-2025 International Academy of Science. All Rights Reserved. Enterarrow_forwardYou are given a plane Π in R3 defined by two vectors, p1 and p2, and a subspace W in R3 spanned by twovectors, w1 and w2. Your task is to project the plane Π onto the subspace W.First, answer the question of what the projection matrix is that projects onto the subspace W and how toapply it to find the desired projection. Second, approach the task in a different way by using the Gram-Schmidtmethod to find an orthonormal basis for subspace W, before then using the resulting basis vectors for theprojection. Last, compare the results obtained from both methodsarrow_forward
- Plane II is spanned by the vectors: - (2) · P² - (4) P1=2 P21 3 Subspace W is spanned by the vectors: 2 W1 - (9) · 1 W2 1 = (³)arrow_forwardshow that v3 = (−√3, −3, 3)⊤ is an eigenvector of M3 . Also here find the correspondingeigenvalue λ3 . Just from looking at M3 and its components, can you say something about the remaining twoeigenvalues? If so, what would you say? find v42 so that v4 = ( 2/5, v42, 1)⊤ is an eigenvector of M4 with corresp. eigenvalue λ4 = 45arrow_forwardChapter 4 Quiz 2 As always, show your work. 1) FindΘgivencscΘ=1.045. 2) Find Θ given sec Θ = 4.213. 3) Find Θ given cot Θ = 0.579. Solve the following three right triangles. B 21.0 34.6° ca 52.5 4)c 26° 5) A b 6) B 84.0 a 42° barrow_forward
- Q1: A: Let M and N be two subspace of finite dimension linear space X, show that if M = N then dim M = dim N but the converse need not to be true. B: Let A and B two balanced subsets of a linear space X, show that whether An B and AUB are balanced sets or nor. Q2: Answer only two A:Let M be a subset of a linear space X, show that M is a hyperplane of X iff there exists ƒ€ X'/{0} and a € F such that M = (x = x/f&x) = x}. fe B:Show that every two norms on finite dimension linear space are equivalent C: Let f be a linear function from a normed space X in to a normed space Y, show that continuous at x, E X iff for any sequence (x) in X converge to Xo then the sequence (f(x)) converge to (f(x)) in Y. Q3: A:Let M be a closed subspace of a normed space X, constract a linear space X/M as normed space B: Let A be a finite dimension subspace of a Banach space X, show that A is closed. C: Show that every finite dimension normed space is Banach space.arrow_forward• Plane II is spanned by the vectors: P12 P2 = 1 • Subspace W is spanned by the vectors: W₁ = -- () · 2 1 W2 = 0arrow_forwardThree streams - Stream A, Stream B, and Stream C - flow into a lake. The flow rates of these streams are not yet known and thus to be found. The combined water inflow from the streams is 300 m³/h. The rate of Stream A is three times the combined rates of Stream B and Stream C. The rate of Stream B is 50 m³/h less than half of the difference between the rates of Stream A and Stream C. Find the flow rates of the three streams by setting up an equation system Ax = b and solving it for x. Provide the values of A and b. Assuming that you get to an upper-triangular matrix U using an elimination matrix E such that U = E A, provide also the components of E.arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL


