
(a)
Interpretation: The nucleophile, leaving group and product formed needs to be identify for the given substitution reaction.
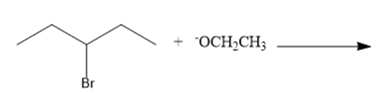
Concept Introduction: In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, the electron rich nucleophile attacks on the electrophilic center of an electrophile (electron deficient) to form nucleophile substituted product. Here, nucleophile can be neutral or have a negative charge. The substitution of nucleophile on the electrophile causes leaving group to leave the electrophile.
(b)
Interpretation: The nucleophile, leaving group and product formed needs to be identify for the given substitution reaction.
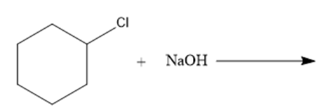
Concept Introduction: In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, the electron rich nucleophile attacks on the electrophilic center of an electrophile (electron deficient) to form nucleophile substituted product. Here, nucleophile can be neutral or have a negative charge. The substitution of nucleophile on the electrophile causes leaving group to leave the electrophile.
(c)
Interpretation: The nucleophile, leaving group and product formed needs to be identify for the given substitution reaction.
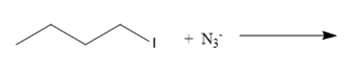
Concept Introduction: In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, the electron rich nucleophile attacks on the electrophilic center of an electrophile (electron deficient) to form nucleophile substituted product. Here, nucleophile can be neutral or have a negative charge. The substitution of nucleophile on the electrophile causes leaving group to leave the electrophile.
(d)
Interpretation: The nucleophile, leaving group and product formed needs to be identify for the given substitution reaction.
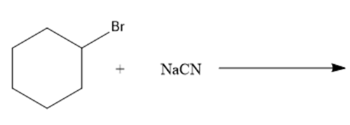
Concept Introduction: In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, the electron rich nucleophile attacks on the electrophilic center of an electrophile (electron deficient) to form nucleophile substituted product. Here, nucleophile can be neutral or have a negative charge. The substitution of nucleophile on the electrophile causes leaving group to leave the electrophile.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
ORG CHEM CONNECT CARD
- Rank the compounds below from lowest to highest melting point.arrow_forward18 Question (1 point) Draw the line structure form of the given partially condensed structure in the box provided. :ÖH HC HC H2 ΙΩ Н2 CH2 CH3 CH3 partially condensed formarrow_forwardsomeone else has already submitted the same question on here and it was the incorrect answer.arrow_forward
- The reaction: 2NO2(g) ⇌ N2O4(g) is an exothermic reaction, ΔH=-58.0 kJ/molrxn at 0°C the KP is 58.If the initial partial pressures of both NO2(g) and N2O4(g) are 2.00 atm:A) Is the reaction at equilibrium? If not, what is the value of Q? B) Which direction will the reaction go to reach equilibrium? C) Use an ICE table to find the equilibrium pressures.arrow_forwardThe dissociation of the weak acid, nitrous acid, HNO2, takes place according to the reaction: HNO2 (aq) ⇌ H+(aq) + NO2–(aq) K=7.2 X 10-4 When 1.00 mole of HNO2 is added to 1.00 L of water, the H+ concentration at equilibrium is 0.0265 M.A) Calculate the value of Q if 1.00 L of water is added? B) How will reaction shift if 1.00 L of water is added?arrow_forwardSuppose a certain copolymer elastomeric material “styrene-butadiene rubber”) contains styrene ("S") monomers –(C8H8)– and butadiene ("B") monomers –(C4H6)– and that their numerical ratio S:B = 1:8. What is the mass ratio mS:mB of the two monomers in the material? What is the molecular mass M of a macromolecule of this copolymer with degree of polymerization n = 60,000? Data: AC = 12.01 u, AH = 1.008 u.arrow_forward
- Lab Questions from Lab: Gravimetric Determination of Calcium as CaC2O4•H2O What is the purpose of the methyl red indicator? Why does a color change to yellow tell you that the reaction is complete? Why is the precipitate rinsed with ice-cold water in step 4? Why not room temperature or hot water? Why is it important that the funnels be placed in a desiccator before weighing (steps 1 and 5)?arrow_forwardWhat mass of ethylene glycol, HOCH2CH2OH, Mustbe added to 5.50 kg of water to antifreeze that would work for the car radiator to -10.0 degrees celcius? MM (g/mol): 62.07arrow_forwardWhat is the molarity of a 0.393 m glucose solution if its density is 1.16 g/mL? MM glucose 180.2 g/molarrow_forward
- The rate constant for the decay of a radioactive element is 2.28 × 10⁻³ day⁻¹. What is the half-life of this element in days?arrow_forwardHandwritten pleasearrow_forwardChoose the best reagents to complete the following reaction. i H A B 1. CH3CH2Na 2. H3O+ 1. CH3CH2MgBr 2. H3O+ 1. CH3MgBr Q C 2. H3O+ 1. H3O+ D 2. CH3MgBr 00 OH Q E CH³MgBrarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
