
(a)
Interpretation: The nucleophile, leaving group and product formed needs to be identify for the given substitution reaction.
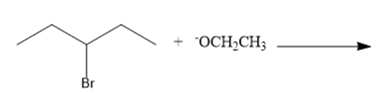
Concept Introduction: In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, the electron rich nucleophile attacks on the electrophilic center of an electrophile (electron deficient) to form nucleophile substituted product. Here, nucleophile can be neutral or have a negative charge. The substitution of nucleophile on the electrophile causes leaving group to leave the electrophile.
(b)
Interpretation: The nucleophile, leaving group and product formed needs to be identify for the given substitution reaction.
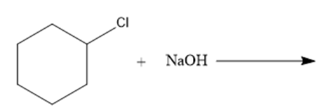
Concept Introduction: In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, the electron rich nucleophile attacks on the electrophilic center of an electrophile (electron deficient) to form nucleophile substituted product. Here, nucleophile can be neutral or have a negative charge. The substitution of nucleophile on the electrophile causes leaving group to leave the electrophile.
(c)
Interpretation: The nucleophile, leaving group and product formed needs to be identify for the given substitution reaction.
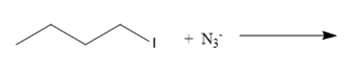
Concept Introduction: In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, the electron rich nucleophile attacks on the electrophilic center of an electrophile (electron deficient) to form nucleophile substituted product. Here, nucleophile can be neutral or have a negative charge. The substitution of nucleophile on the electrophile causes leaving group to leave the electrophile.
(d)
Interpretation: The nucleophile, leaving group and product formed needs to be identify for the given substitution reaction.
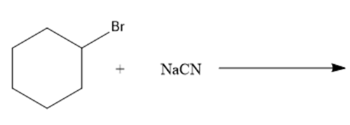
Concept Introduction: In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, the electron rich nucleophile attacks on the electrophilic center of an electrophile (electron deficient) to form nucleophile substituted product. Here, nucleophile can be neutral or have a negative charge. The substitution of nucleophile on the electrophile causes leaving group to leave the electrophile.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Connect Online Access 1-Semester for Organic Chemistry
- Can the target compound be efficiently synthesized in good yield from the substituted benzene of the starting material? If yes, draw the synthesis. Include all steps and all reactants.arrow_forwardThis is a synthesis question. Why is this method wrong or worse than the "correct" method? You could do it thiss way, couldn't you?arrow_forwardTry: Draw the best Lewis structure showing all non-bonding electrons and all formal charges if any: (CH3)3CCNO NCO- HN3 [CH3OH2]*arrow_forward
- What are the major products of the following reaction? Draw all the major products. If there are no major products, then there is no reaction that will take place. Use wedge and dash bonds when necessary.arrow_forwardZeolites. State their composition and structure. Give an example.arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and show all reactionsarrow_forward
- Don't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardIX) By writing the appropriate electron configurations and orbital box diagrams briefly EXPLAIN in your own words each one of the following questions: a) The bond length of the Br2 molecule is 2.28 Å, while the bond length of the compound KBr is 3.34 Å. The radius of K✶ is 1.52 Å. Determine the atomic radius in Å of the bromine atom and of the bromide ion. Br = Br b) Explain why there is a large difference in the atomic sizes or radius of the two (Br and Br). Tarrow_forwardWhen 15.00 mL of 3.00 M NaOH was mixed in a calorimeter with 12.80 mL of 3.00 M HCl, both initially at room temperature (22.00 C), the temperature increased to 29.30 C. The resultant salt solution had a mass of 27.80 g and a specific heat capacity of 3.74 J/Kg. What is heat capacity of the calorimeter (in J/C)? Note: The molar enthalpy of neutralization per mole of HCl is -55.84 kJ/mol.arrow_forward
- When 15.00 mL of 3.00 M NaOH was mixed in a calorimeter with 12.80 mL of 3.00 M HCl, both initially at room temperature (22.00 C), the temperature increased to 29.30 C. The resultant salt solution had a mass of 27.80 g and a specific heat capacity of 3.74 J/Kg. What is heat capacity of the calorimeter (in J/C)? Note: The molar enthalpy of neutralization per mole of HCl is -55.84 kJ/mol. Which experimental number must be initialled by the Lab TA for the first run of Part 1 of the experiment? a) the heat capacity of the calorimeter b) Mass of sample c) Ti d) The molarity of the HCl e) Tfarrow_forwardPredict products for the Following organic rxn/s by writing the structurels of the correct products. Write above the line provided" your answer D2 ①CH3(CH2) 5 CH3 + D₂ (adequate)" + 2 mited) 19 Spark Spark por every item. 4 CH 3 11 3 CH 3 (CH2) 4 C-H + CH3OH CH2 CH3 + CH3 CH2OH 0 CH3 fou + KMnDy→ C43 + 2 KMn Dy→→ C-OH ") 0 C-OH 1110 (4.) 9+3 =C CH3 + HNO 3 0 + Heat> + CH3 C-OH + Heat CH2CH3 - 3 2 + D Heat H 3 CH 3 CH₂ CH₂ C = CH + 2 H₂ → 2 2arrow_forwardWhen 15.00 mL of 3.00 M NaOH was mixed in a calorimeter with 12.80 mL of 3.00 M HCl, both initially at room temperature (22.00 C), the temperature increased to 29.30 C. The resultant salt solution had a mass of 27.80 g and a specific heat capacity of 3.74 J/Kg. What is heat capacity of the calorimeter (in J/C)? Note: The molar enthalpy of neutralization per mole of HCl is -55.84 kJ/mol.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
