
Concept explainers
(a)
Make a table of values and draw the graph for the relation
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Make a table:
| y | |
| -3 | -9 |
| -2 | -4 |
| -1 | -1 |
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | -1 |
| 2 | -4 |
| 3 | -9 |
Now , plot the above coordinates and join them to get the graph of relation
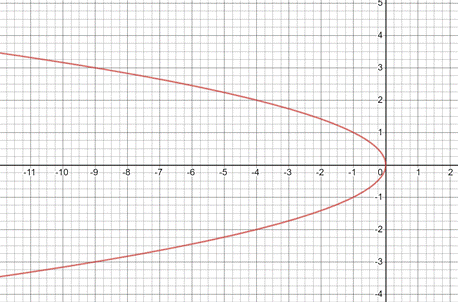
(b)
Make a table of values and draw the graph for the relation
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Make a table:
| y | |
| -3 | 11 |
| -2 | 6 |
| -1 | 3 |
| 0 | 2 |
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 6 |
| 3 | 11 |
Now , plot the above coordinates and join them to get the graph of relation
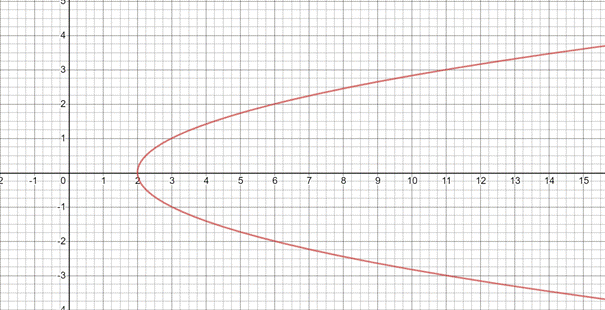
(c)
Make a table of values and draw the graph for the relation
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Make a table:
| y | |
| -4 | 9 |
| -3 | 4 |
| -2 | 1 |
| -1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 4 |
| 2 | 9 |
Now , plot the above coordinates and join them to get the graph of relation
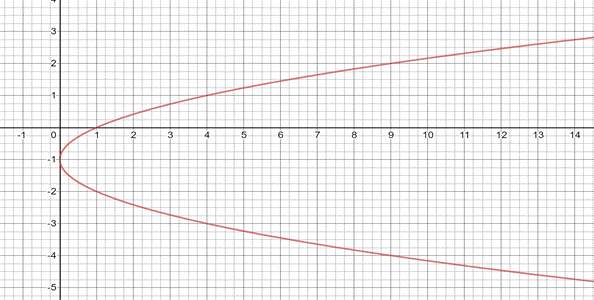
(d)
Make a table of values and draw the graph for the relation
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Make a table:
| y | |
| -4 | 11 |
| -3 | 6 |
| -2 | 3 |
| -1 | 2 |
| 0 | 3 |
| 1 | 6 |
| 2 | 11 |
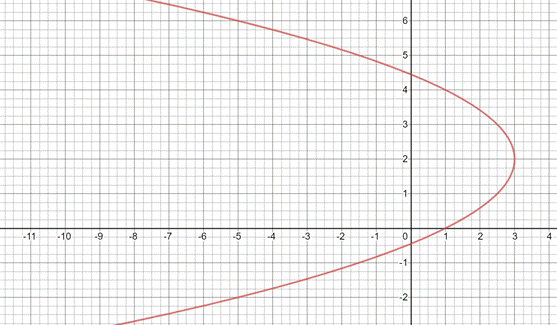
Now , plot the above coordinates and join them to get the graph of relation

(e)
Make a table of values and draw the graph for the relation
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Make a table:
| y | |
| -1 | |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 2.5 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 3 | 2.5 |
| 4 | 1 |
| 5 | -1.5 |
Now , plot the above coordinates and join them to get the graph of relation
Chapter 7 Solutions
Algebra and Trigonometry: Structure and Method, Book 2
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
College Algebra (7th Edition)
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
- Safari File Edit View History Bookmarks Window Help Ο Ω OV O mA 0 mW ర Fri Apr 4 1 222 tv A F9 F10 DII 4 F6 F7 F8 7 29 8 00 W E R T Y U S D பட 9 O G H J K E F11 + 11 F12 O P } [arrow_forwardSo confused. Step by step instructions pleasearrow_forwardIn simplest terms, Sketch the graph of the parabola. Then, determine its equation. opens downward, vertex is (- 4, 7), passes through point (0, - 39)arrow_forward
- In simplest way, For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. a) y = x 2 + 16 x + 39 b) y = 5 x2 - 50 x - 120arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step Write each quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = - 4( x + 6)2 + 36arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. 1) y = - 2 x2 - 28 x + 64 2) y = 6 x2 + 36 x - 42arrow_forward
- Write each relation in standard form a)y = 5(x + 10)2 + 7 b)y = 9(x - 8)2 - 4arrow_forwardIn simplest form and step by step Write the quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = 3(x - 1)2 - 147arrow_forwardStep by step instructions The path of a soccer ball can be modelled by the relation h = - 0.1 d 2 + 0.5 d + 0.6, where h is the ball’s height and d is the horizontal distance from the kicker. a) Find the zeros of the relation.arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





