
Concept explainers
Future scientists: Education professionals refer co science technology, engineering, and mathematics as the STEM disciplines. The Alliance for Science and Technology Research in America reported in 2013 that 28% of freshmen entering college planned to major in a STEM discipline.
A random sample of 85 freshmen is selected.
- Is it appropriate to use the normal approximation to find the
probability chat less than 30% of the freshmen in the sample are planning to major in a STEM discipline? If so, find the probability. If not, explain why not - A new sample of 150 freshmen is selected. Find the probability that less than 30% of the freshmen in this sample are planning to major in a STEM discipline.
- Find the probability that the proportion of freshmen in the sample of 150 who plan to major in a STEM discipline is between 0.30 and 0.35.
- Find the probability that more than 32% of the freshmen in the sample of 150 are planning to major in a STEM discipline.
- Would it be unusual if less than 25% of the freshmen in the sample of 150 were planning to major in a STEM discipline?
(a)
>To find:
Whether it is appropriate to use the normal approximation to find the probability that less than 30% of freshmenhave expressed interest in a STEM discipline as major.
Answer to Problem 21E
It is possible to use the normal distribution. The probability that less than 30% of freshmen have expressed interest in a STEM discipline is 0.65935.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Educational professionals refer to science, technology, engineering and mathematics as the STEM disciplines. 28% of freshman entering college expressed interest in a STEM discipline Major. A randomsample of 85 freshmen is selected.
Formula used: A random variable is normally distributed when
Where n is the number of sample and p is the success probability.
The mean is
The standard deviation is
Calculation:
28% of freshman are planningto major in a STEM discipline and a random sample of 85 freshmen is selected.
Then
Therefore, it is possible to use thenormal distribution.
Let
The mean is
The standard deviation is
We need to find
The z-score is given by
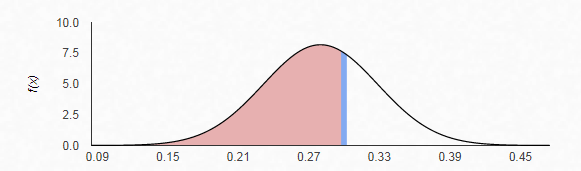
Therefore, from the standardize normal distribution table, the area to the left of
Hence, the probability that less than 30% of freshmen have expressed interest in a STEM discipline is 0.65935.
(b)
>To find:
the probability that less than 30% of freshmen have expressed interest in a STEM discipline as major.
Answer to Problem 21E
the probability that less than 30% of freshmen have expressed interest in a STEM discipline as major is 0.70711.
Explanation of Solution
Formula used:
The mean is
The standard deviation is
The z-score is given by
Calculation:
28% of freshman are planning to major in a STEM discipline and a random sample of 150 freshmen is selected.
Then
Let
The mean is
The standard deviation is
We need to find
The z-score is given by
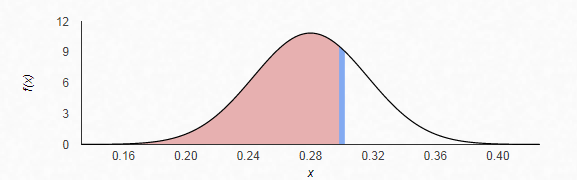
Therefore, from the standardize normal distribution table, the area to the left of
Hence, the probability that less than 30% of freshmen have expressed interest in a STEM discipline as major is 0.70711.
(c)
>To find:
The probability that the sample proportion of the freshmen who have expressed interest in a STEM discipline as major is between 0.30 and 0.35.
Answer to Problem 21E
The probability that the sample proportion of freshmen who have expressed interest in a STEM discipline as major is between 0.30 and 0.35, is 0.26465.
Explanation of Solution
Formula used: The z-score is given by
Calculation:
Let
The mean is
The standard deviation is
We need to find
The z-score is given by
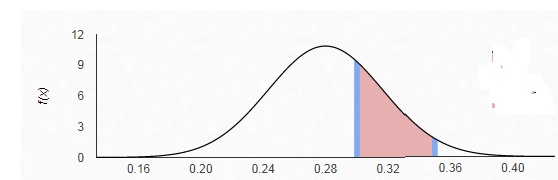
Therefore, from the standardize normal distribution table, the area to
Hence, the probability that the sample proportion of the freshmen who have expressed interest in a STEM discipline as major is between 0.30 and 0.35 is 0.26465.
(d)
>To find:
The probability that more than 32% of freshmen in the sample of 150 have expressed interest in a STEM discipline as major.
Answer to Problem 21E
The probability that more than 32% of freshmen in the sample of 150 have expressed interest to a major in STEM discipline is 0.13787.
Explanation of Solution
Formula used: The z-score is given by
Calculation:
Let
The mean is
The standard deviation is
We need to find
The z-score is given by
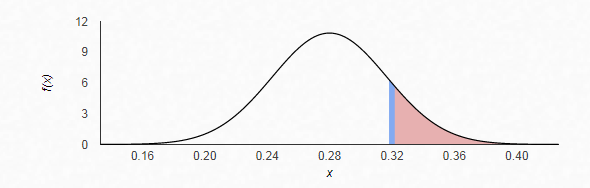
Therefore, from the standardize normal distribution table, the area to the right of
Hence, the probability that more than 32% of freshmen in the sample of 150 have expressed interest in to major in a STEM discipline is 0.13787.
(e)
>To find:
Whether it is unusual if less than 25% of the freshmen in the sample of 150have expressed interest in a STEM discipline.
Answer to Problem 21E
Less than 25% of the freshmen in the sample of 150have expressed interest in a STEM discipline is not unusual.
Explanation of Solution
Formula used: The z-score is given by
Calculation:
Let
The mean is
The standard deviation is
We will compute the probability that sample proportion is less than 0.25. If the probability is less than 0.05, then the event is unusual.
We need to find
The z-score is given by
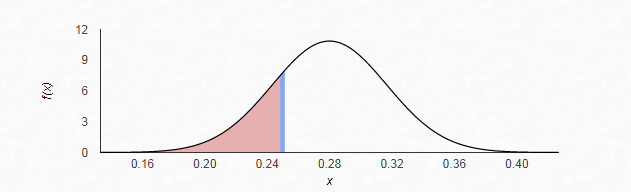
Therefore, from the standardize normal distribution table, the area to the right of
Thus, the probability that less than 25% of the freshmen in the sample of 150have expressed interest to a major in a STEM discipline is 0.20684.
Since the probability is greater than 0.05, the given event isnot unusual.
Hence,less than 25% of the freshmen in the sample of 150have expressed interest to a major in STEM discipline is not unusual.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Elementary Statistics (Text Only)
- Harvard University California Institute of Technology Massachusetts Institute of Technology Stanford University Princeton University University of Cambridge University of Oxford University of California, Berkeley Imperial College London Yale University University of California, Los Angeles University of Chicago Johns Hopkins University Cornell University ETH Zurich University of Michigan University of Toronto Columbia University University of Pennsylvania Carnegie Mellon University University of Hong Kong University College London University of Washington Duke University Northwestern University University of Tokyo Georgia Institute of Technology Pohang University of Science and Technology University of California, Santa Barbara University of British Columbia University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill University of California, San Diego University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign National University of Singapore McGill…arrow_forwardName Harvard University California Institute of Technology Massachusetts Institute of Technology Stanford University Princeton University University of Cambridge University of Oxford University of California, Berkeley Imperial College London Yale University University of California, Los Angeles University of Chicago Johns Hopkins University Cornell University ETH Zurich University of Michigan University of Toronto Columbia University University of Pennsylvania Carnegie Mellon University University of Hong Kong University College London University of Washington Duke University Northwestern University University of Tokyo Georgia Institute of Technology Pohang University of Science and Technology University of California, Santa Barbara University of British Columbia University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill University of California, San Diego University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign National University of Singapore…arrow_forwardA company found that the daily sales revenue of its flagship product follows a normal distribution with a mean of $4500 and a standard deviation of $450. The company defines a "high-sales day" that is, any day with sales exceeding $4800. please provide a step by step on how to get the answers in excel Q: What percentage of days can the company expect to have "high-sales days" or sales greater than $4800? Q: What is the sales revenue threshold for the bottom 10% of days? (please note that 10% refers to the probability/area under bell curve towards the lower tail of bell curve) Provide answers in the yellow cellsarrow_forward
- Find the critical value for a left-tailed test using the F distribution with a 0.025, degrees of freedom in the numerator=12, and degrees of freedom in the denominator = 50. A portion of the table of critical values of the F-distribution is provided. Click the icon to view the partial table of critical values of the F-distribution. What is the critical value? (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardA retail store manager claims that the average daily sales of the store are $1,500. You aim to test whether the actual average daily sales differ significantly from this claimed value. You can provide your answer by inserting a text box and the answer must include: Null hypothesis, Alternative hypothesis, Show answer (output table/summary table), and Conclusion based on the P value. Showing the calculation is a must. If calculation is missing,so please provide a step by step on the answers Numerical answers in the yellow cellsarrow_forwardShow all workarrow_forward
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
 Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning





