
Mechanics of Materials
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780133254426
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: Prentice Hall
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 7.2, Problem 7.27P
The beam is slit longitudinally along both sides. If it is subjected to a shear of V=250 kN, compare the maximum shear stress in the beam before and after the cuts were made.
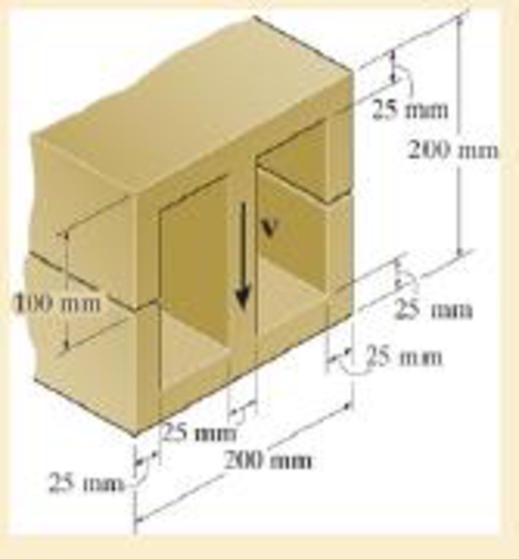
Probs. 7–27/28
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
CORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED.
18: Determine the maximum shear and moment that would be experienced by a 10 m beam if a three-wheelmoving load of 10 kN, 30 kN, and 5 kN respectively will pass it by. The distance between the 1st and 2nd load is 1 m and the distance between the 2nd and 3rd load is 3 m.ANS: Vmax = 40 kN ; Mmax = 100.014 kN-m
CORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED.
5: A 12-m simply supported bridge is constructed with 100-mm concrete slab deck supported by precastconcrete stringers spaced 800 mm on center. Analyze the stringers when subjected to a moving load consisting of 3 evenly spaced axle loads at 3 m and equivalent to 20 kN, 30 kN and 40 kN respectively. The self-weight of the stringers is 8.5 kN/m and the concrete deck has a unit weight of 24 kN/m3 . Neglect all other superimposed loads. Calculate: (a) the maximum shear force in the stringers; (b) the maximum bending moment in the stringers.
Answer: Vmax = 135.020 KN, Mmax = 477.388 KN-M
CORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED.
19: A 22-wheeler truck is crossing over 25 m bridge. The dimensions between the axles of the truck are shownin the figure below. Axles 1 to 3 carry a 90 kN load each, axles 4 and 5 carry a 65 kN load each, and the axle directly below the cab of the truck has a load of 100 kN. Determine the maximum shear and moment on the bridge.ANS: Vmax = 374.92 kN ; Mmax = 1,702.229 kN-m
Chapter 7 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials
Ch. 7.2 - In each case, calculate the value of Q and t that...Ch. 7.2 - If the beam is subjected to a shear force of V =...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the shear stress at points A and B if...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the absolute maximum shear stress in the...Ch. 7.2 - If the beam is subjected to a shear force of V =20...Ch. 7.2 - If the beam is made from four plates and subjected...Ch. 7.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 7.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 7.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 7.2 - Prob. 7.4P
Ch. 7.2 - Prob. 7.5PCh. 7.2 - The wood beam has an allowable shear stress of...Ch. 7.2 - The shaft is supported by a thrust bearing at A...Ch. 7.2 - The shaft is supported by a thrust bearing at A...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the largest shear force V that the...Ch. 7.2 - If the applied shear force V = 18 kip, determine...Ch. 7.2 - The overhang beam is subjected to the uniform...Ch. 7.2 - *7-12. The beam has a rectangular cross section...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the maximum shear stress in the strut if...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the maximum shear force V that the strut...Ch. 7.2 - 7-15. The strut is subjected to a vertical shear...Ch. 7.2 - Prob. 7.16PCh. 7.2 - If the beam is subjected to a shear of V=15 kN,...Ch. 7.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 7.2 - If the wide-flange beam is subjected to a shear of...Ch. 7.2 - Prob. 7.20PCh. 7.2 - If the beam is made from wood having an allowable...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the shear stress at point B on the web...Ch. 7.2 - Determine the maximum shear stress acting at...Ch. 7.2 - Prob. 7.24PCh. 7.2 - 7-25. Determine the maximum shear stress in the...Ch. 7.2 - 7-26. The beam has a square cross section and is...Ch. 7.2 - The beam is slit longitudinally along both sides....Ch. 7.2 - The beam is to be cut longitudinally along both...Ch. 7.2 - The beam has a rectangular cross section and is...Ch. 7.2 - The beam in Fig.6-48f is subjected to a fully...Ch. 7.3 - The two identical boards are bolted together to...Ch. 7.3 - Two identical 20-mm-thick plates are bolted to the...Ch. 7.3 - The boards are bolted together to form the...Ch. 7.3 - The boards are bolted together to form the...Ch. 7.3 - Prob. 7.32PCh. 7.3 - Prob. 7.33PCh. 7.3 - Prob. 7.34PCh. 7.3 - Prob. 7.35PCh. 7.3 - Prob. 7.36PCh. 7.3 - Prob. 7.37PCh. 7.3 - Prob. 7.38PCh. 7.3 - A beam is constructed from three boards bolted...Ch. 7.3 - The simply supported beam is built up from three...Ch. 7.3 - The simply supported beam is built up from three...Ch. 7.3 - The T-beam is constructed as shown. If each nail...Ch. 7.3 - Prob. 7.43PCh. 7.3 - Prob. 7.44PCh. 7.3 - Prob. 7.45PCh. 7.3 - 7–46. The beam is subjected to a shear of V = 800...Ch. 7.3 - The beam is made from four boards nailed together...Ch. 7.3 - The beam is made from three polystyrene strips...Ch. 7.5 - A shear force of V=300 kN is applied to the box...Ch. 7.5 - A shear force of V=450 kN is applied to the box...Ch. 7.5 - A shear force of V = 18 kN is applied to the box...Ch. 7.5 - A shear force of V = 18 kN is applied to the box...Ch. 7.5 - The aluminum strut is 10 mm thick and has the...Ch. 7.5 - The aluminum strut is 10 mm thick and has the...Ch. 7.5 - Prob. 7.56PCh. 7.5 - Prob. 7.57PCh. 7.5 - Prob. 7.58PCh. 7.5 - Prob. 7.59PCh. 7.5 - The built-up beam is formed by welding together...Ch. 7.5 - The assembly is subjected to a vertical shear of V...Ch. 7.5 - 7–62. Determine the shear-stress variation over...Ch. 7.5 - 7–63. Determine the location e of the shear...Ch. 7.5 - Determine the location e of the shear center,...Ch. 7.5 - The beam supports a vertical shear of V=7 kip....Ch. 7.5 - The stiffened beam is constructed from plates...Ch. 7.5 - The pipe is subjected to a shear force of V=8 kip....Ch. 7.5 - *7–68. A thin plate of thickness t is bent to form...Ch. 7.5 - A thin plate of thickness t is bent to form the...Ch. 7.5 - 7–70. Determine the location e of the shear...Ch. 7 - The beam is fabricated from four boards nailed...Ch. 7 - The T-beam is subjected to a shear of V = 150 kN....Ch. 7 - The member is subject to a shear force of V = 2...Ch. 7 - Determine the shear stress at points B and C on...Ch. 7 - Determine the maximum shear stress acting at...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- CORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. 1. A H = 6 m cantilever retaining wall is subjected to a soil pressurelinearly varying from zero at the top to 90 kPa at the bottom. As an additionalsupport, it is anchored at depth y = 2 m. with maximum tension equal to 25kN. Assume that the stem provides fully retrained support. Draw the shearand moment diagram of the wall to calculate the following: (a) Maximumpositive bending moment per linear meter; (b) maximum negative bendingmoment per linear meter; (c) maximum shear force per linear meter. answer: +MMax = 440 kn-m, -Mmax = 0kn-M, Vmax = 245 KNarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. 17: A simply supported beam with the section shown below has an allowableflexural shearing stress of 43 MPa. (a) Determine the maximum allowable shearing force onthe section. And (b) what is the minimum thickness of plate that should be welded at theflanges if the section is to withstand a total shearing force of 200 kN. The additional plate willhave its base dimension equal to the flange dimension.ANS: V = 179.333 kN ; t = 23.181 mmarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. Answer: A = 0.207 L(M)arrow_forward
- Qu 4 The 12-kg slender rod is attached to a spring, which has an unstretched length of 2 m. If the rod is released from rest when 0 = 30°, determine its angular velocity at the instant 0 = 90°. 2 m B k = 40 N/m 2 marrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. 13: A cantilever beam is of length 1.5 m,loaded by a concentrated load P at its tip as shown inFig. 8-18(a), and is of circular cross section (R = 100 mm),having two symmetrically placed longitudinal holes asindicated. The material is titanium alloy, having anallowable working stress in bending of 600 MPa.Determine the maximum allowable value of the verticalforce P. ANS: P = 236,589.076 N = 236.589 kNarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. 15: Consider a beam having an I-type cross section as shown in Fig. 8-45. Ashearing force V of 150 kN acts over the section. Determine the maximum and minimumvalues of the shearing stress in the vertical web of the section.ANS: fv(max) = 44.048 MPa ; fv(min) = 33.202 MPaarrow_forward
- CORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. 12: A steel cantilever beam 16 ft 8 in in length is subjected to a concentrated load of 320 lb acting at the freeend of the bar. A commercially available rolled steel section, designated as W12x32, is used for the beam. Assume that the total depth of the beam is 12 in, and the neutral axis of the section is in the middle. Determine the maximum tensile and compressive stresses. (Properties of commercially available rolled steel section provided in the table. Z = section modulus). ANS: σT = σC = 1,572.482 lb/in2arrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. 14: Two ½-in x 8-in cover plates are welded to two channels 10 in high to formthe cross section of the beam shown in Fig. 8-59. Loads are in a vertical plane and bendingtakes place about a horizontal axis. The moment of inertia of each channel about ahorizontal axis through the centroid is 78.5 in4. If the maximum allowable elastic bendingstress is 18,000 lb/in2, determine the maximum bending moment that may be developedin the beam.ANS: 1,236,000 lb-in.arrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. 11: A beam of circular cross section is 7 in in diameter. It is simply supported at each end and loaded by twoconcentrated loads of 20,000 lb each, applied 12 in from the ends of the beam. Determine the maximum bending stressin the beam. ANS: σ = 7,127.172 lb/in2arrow_forward
- using the theorem of three moments, find all the reactions and supportsarrow_forward(An ellipsoidal trapping region for the Lorenz equations) Show that there is a certain ellipsoidal region E of the form rx2 + σy2 + σ(z − 2r)2 ≤ C such that all trajectories of the Lorenz equations eventually enter E and stay in there forever. For a much stiffer challenge, try to obtain the smallest possible value of C with this property.arrow_forwardA) In a factory, an s-type pitot tube was used to calculate the velocity of dry air for a point inside a stack. Calculate the velocity at that point (ft/sec) using following conditions: ● • • Pressure = 30.23 ± 0.01 in Hg (ambient) Pitot tube coefficient = 0.847 ± 0.03 Temperature = 122 ± 0.1 F (stack) Temperature = 71.2 ± 0.1 F (ambient) AP = 0.324 ± 0.008 in H2O (pitot tube) • AP = 0.891 ± 0.002 in H2O (stack) B) Find the dominant error(s) when determining precision for the problem. C) For part A, what is the precision in ft/sec for the velocity?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Differences between Temporary Joining and Permanent Joining.; Author: Academic Gain Tutorials;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PTr8QZhgXyg;License: Standard Youtube License