
Find the values for each.
a. tα/2 and n = 18 for the 99% confidence interval for the
b. tα/2 and n = 23 for the 95% confidence interval for the mean
c. tα/2 and n = 15 for the 98% confidence interval for the mean
d. tα/2 and n = 10 for the 90% confidence interval for the mean
e. tα/2 and n = 20 for the 95% confidence interval for the mean
(a)
To find: The critical value
Answer to Problem 3E
The critical value
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Calculation:
Degrees of freedom:
Critical value:
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain the critical value using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability > OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘t’ distribution.
- In Degrees of freedom, enter 17.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Choose Probability Value and Both Tail for the region of the curve to shade.
- Enter the Probability value as 0.01.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
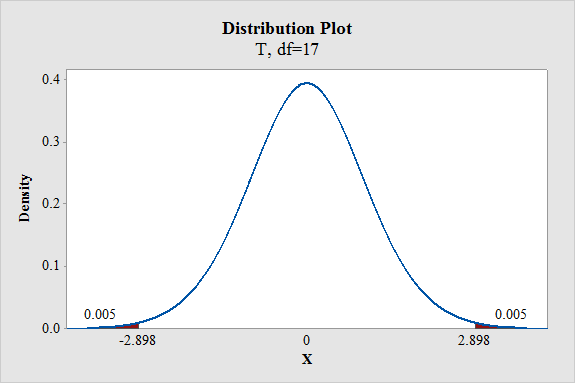
From the output, the critical value
(b)
To find: The critical value
Answer to Problem 3E
The critical value
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Calculation:
Degrees of freedom:
Critical value:
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain the critical value using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability> OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘t’distribution.
- In Degrees of freedom, enter 22.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Choose Probability Value and Both Tail for the region of the curve to shade.
- Enter the Probability value as 0.05.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
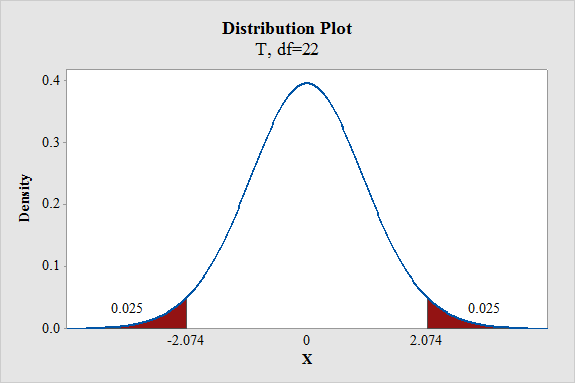
From the output, the critical value
(c)
To find: The critical value
Answer to Problem 3E
The critical value
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Calculation:
Degrees of freedom:
Critical value:
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain the critical value using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability> OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘t’distribution.
- In Degrees of freedom, enter 14.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Choose Probability Value and Both Tail for the region of the curve to shade.
- Enter the Probability value as 0.02.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
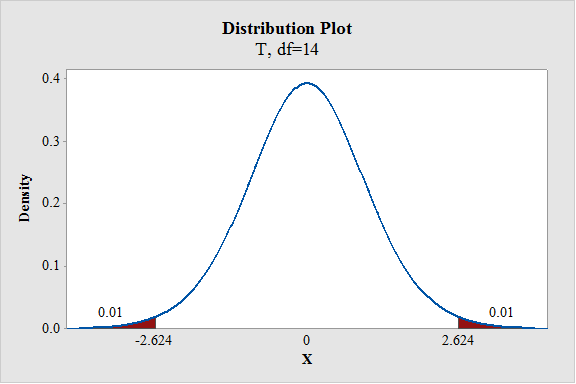
From the output, the critical value
(d)
To find: The critical value
Answer to Problem 3E
The critical value
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Calculation:
Degrees of freedom:
Critical value:
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain the critical value using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability > OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘t’ distribution.
- In Degrees of freedom, enter 9.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Choose Probability Value and Both Tail for the region of the curve to shade.
- Enter the Probability value as 0.10.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
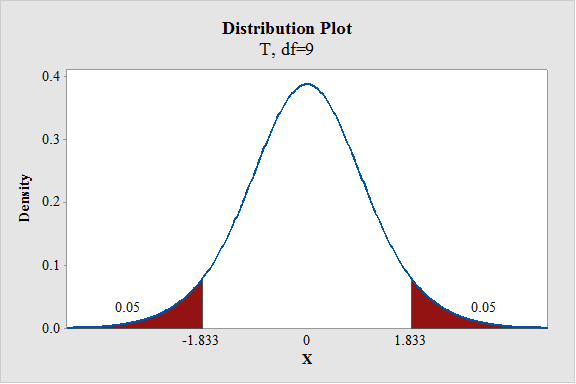
From the output, the critical value
(e)
To find: The critical value
Answer to Problem 3E
The critical value
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Calculation:
Degrees of freedom:
Critical value:
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain the critical value using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability > OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘t’ distribution.
- In Degrees of freedom, enter 19.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Choose Probability Value and Both Tail for the region of the curve to shade.
- Enter the Probability value as 0.05.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
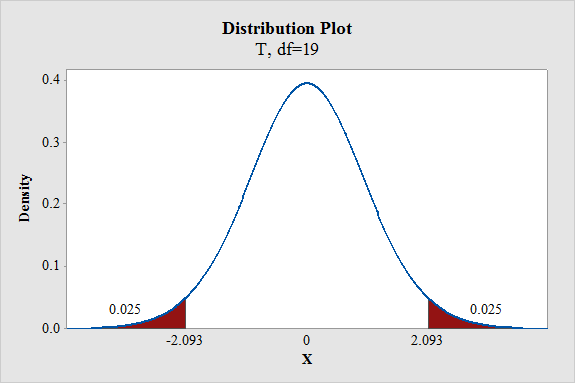
From the output, the critical value
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Connect Plus Statistics Hosted by ALEKS Access Card 52 Weeks for Elementary Statistics: A Step-By-St
- 2 (VaR and ES) Suppose X1 are independent. Prove that ~ Unif[-0.5, 0.5] and X2 VaRa (X1X2) < VaRa(X1) + VaRa (X2). ~ Unif[-0.5, 0.5]arrow_forward8 (Correlation and Diversification) Assume we have two stocks, A and B, show that a particular combination of the two stocks produce a risk-free portfolio when the correlation between the return of A and B is -1.arrow_forward9 (Portfolio allocation) Suppose R₁ and R2 are returns of 2 assets and with expected return and variance respectively r₁ and 72 and variance-covariance σ2, 0%½ and σ12. Find −∞ ≤ w ≤ ∞ such that the portfolio wR₁ + (1 - w) R₂ has the smallest risk.arrow_forward
- 7 (Multivariate random variable) Suppose X, €1, €2, €3 are IID N(0, 1) and Y2 Y₁ = 0.2 0.8X + €1, Y₂ = 0.3 +0.7X+ €2, Y3 = 0.2 + 0.9X + €3. = (In models like this, X is called the common factors of Y₁, Y₂, Y3.) Y = (Y1, Y2, Y3). (a) Find E(Y) and cov(Y). (b) What can you observe from cov(Y). Writearrow_forward1 (VaR and ES) Suppose X ~ f(x) with 1+x, if 0> x > −1 f(x) = 1−x if 1 x > 0 Find VaRo.05 (X) and ES0.05 (X).arrow_forwardJoy is making Christmas gifts. She has 6 1/12 feet of yarn and will need 4 1/4 to complete our project. How much yarn will she have left over compute this solution in two different ways arrow_forward
- Solve for X. Explain each step. 2^2x • 2^-4=8arrow_forwardOne hundred people were surveyed, and one question pertained to their educational background. The results of this question and their genders are given in the following table. Female (F) Male (F′) Total College degree (D) 30 20 50 No college degree (D′) 30 20 50 Total 60 40 100 If a person is selected at random from those surveyed, find the probability of each of the following events.1. The person is female or has a college degree. Answer: equation editor Equation Editor 2. The person is male or does not have a college degree. Answer: equation editor Equation Editor 3. The person is female or does not have a college degree.arrow_forwardneed help with part barrow_forward
- Suppose you know that Bob's test score is above the mean, but he doesn't remember by how much. At least how many students must score lower than Bob?arrow_forwardIf a baby's weight is at the median, what's her percentile?arrow_forwardAt the same restaurant as in Question 19 with the same normal distribution, what's the chance of it taking no more than 15 minutes to get service?arrow_forward
 Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt



