
Air enters the evaporator section of a window air conditioner at 100 kPa and 27°C with a volume flow rate of 6 m3/min. The refrigerant-134a at 120 kPa with a quality of 0.3 enters the evaporator at a rate of 2 kg/min and leaves as saturated vapor at the same pressure. Determine the exit temperature of the air and the rate of entropy generation for this process, assuming (a) the outer surfaces of the air conditioner are insulated and (b) heat is transferred to the evaporator of the air conditioner from the surrounding medium at 32°C at a rate of 30 kJ/min.
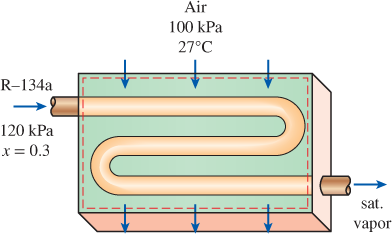
FIGURE P7–180
a)
The exit temperature of air and the entropy generated during the process.
Answer to Problem 180RP
The exit temperature of air is
The entropy generated during the process is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression to calculate the initial enthalpy of the refrigerant.
Here, initial enthalpy is
Write the expression to calculate the initial entropy of the refrigerant.
Here, initial entropy is
Write the expression to calculate the mass flow rate of air.
Here, mass flow rate of air is
Write the expression for the mass balance of the system.
Here, mass flow rate into the control system is
Write the expression for the energy balance equation for closed system.
Here, rate of energy transfer into the control volume is
Write the expression for the rate of entropy balance for the system.
Here, rate of entropy in the system is
Conclusion:
From Table A-12, “Saturated refrigerant-134a-Pressure table”, Obtain the following properties at saturated pressure of 120 kPa
Saturated liquid enthalpy,
Evaporated enthalpy,
Saturated vapor enthalpy,
Saturated vapor entropy,
Saturated liquid entropy,
Evaporated entropy,
Substitute
Substitute
Refrigerant –134a enters and leaves at the same pressure. Hence,
From Table A-1E, “the molar mass, gas constant and critical–point properties table”, select the gas constant of air at room temperature as
Substitute
Substitute
Here, mass flow rate of refrigerant is
Substitute
Here, mass flow rate of air is
Substitute
From the Table A-2, “Ideal-gas specific heats of various common gases”, select the value of the specific heat at constant pressure value of air as
Substitute 27 C for
Hence, the exit temperature of air is
For the steady flow system, change of entropy in the system is zero.
Substitute
Substitute
Hence, the entropy generated during the process is
b)
The exit temperature of air and the entropy generated during the process.
Answer to Problem 180RP
The exit temperature of air is
The entropy generated during the process is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the energy balance equation for closed system.
Here, rate of energy transfer into the control volume is
Write the expression for the rate of entropy balance for the system.
Here, rate of entropy in the system is
Conclusion:
Substitute
Here, rate of heat gain from the surrounding is
Substitute 27 C for
Hence, the exit temperature of air is
For the steady flow system, change of entropy in the system is zero.
Substitute
Substitute
Hence, the entropy generated during the process is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
EBK THERMODYNAMICS: AN ENGINEERING APPR
- A continuous flow calorimeter was used to obtain the calorific value of a sample of fuel and the following data collected: Mass of fuel: 2.25 kgInlet water temperature: 11 ° COutlet water temperature 60 ° CQuantity of water: 360 Liters Calorimeter efficiency: 85%Calculate the calorific value of the sample ( kJ / kg ).arrow_forwardChapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... Scoresarrow_forwardmylabmastering.pearson.com Chapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... P Pearson MyLab and Mastering Scoresarrow_forwardanswer the fallowing Brake Specific Fuel Consumption - 0.3 kg/kwh, Mechanical Efficiency- 90% Calorific Value of Fuel -45 MJ/kg. Given these values, find the indicated power, indicated thermal efficiency and brake thermal efficiencyarrow_forwardProblem 6. The circular plate shown rotates about its vertical diameter. At the instant shown, the angular velocity ₁ of the plate is 10 rad/s and is decreasing at the rate of 25 rad/s². The disk lies in the XY plane and Point D of strap CD moves upward. The relative speed u of Point D of strap CD is 1.5 m/s and is decreasing at the rate of 3 m/s². Determine (a) the velocity of D, (b) the acceleration of D. Answers: =0.75 +1.299]-1.732k m/s a=-28.6 +3.03-10.67k m/s² 200 mm x Zarrow_forwardProblem 1. The flywheel A has an angular velocity o 5 rad/s. Link AB is connected via ball and socket joints to the flywheel at A and a slider at B. Find the angular velocity of link AB and the velocity of slider B at this instant. (Partial Answer: @ABN = -2î + 2.25; red Z -1.2 ft C -7 Y -1.5 ft- B 2.0 ftarrow_forwardNeed help pleasearrow_forwardPROBLEM 15.225 The bent rod shown rotates at the constant rate @₁ = 5 rad/s and collar C moves toward point B at a constant relative speed u = 39 in./s. Knowing that collar C is halfway between points B and D at the instant shown, determine its velocity and acceleration. Answers: v=-45 +36.6)-31.2 k in./s āc = -2911-270} in./s² 6 in 20.8 in. 14.4 in.arrow_forwardNeed help, please show all work, steps, units and please box out and round answers to 3 significant figures. Thank you!..arrow_forwardNeed help, please show all work, steps, units and please box out and round answers to 3 significant figures. Thank you!...arrow_forwardFL y b C Z Determine the moment about O due to the force F shown, the magnitude of the force F = 76.0 lbs. Note: Pay attention to the axis. Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 1.90 ft b 2.80 ft с 2.60 ft d 2.30 ft Mo 144 ft-lb = -212 × 1 + xk) ☑+212arrow_forward20 in. PROBLEM 15.206 Rod AB is connected by ball-and-socket joints to collar A and to the 16-in.-diameter disk C. Knowing that disk C rotates counterclockwise at the constant rate ₁ =3 rad/s in the zx plane, determine the velocity of collar A for the position shown. 25 in. B 8 in. Answer: -30 in/s =arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY