
Concept explainers
Periodic inventory by three methods
Pappa’s Appliances uses the periodic inventory system. Details regarding the inventory of appliances at January 1, purchases invoices during the year, and the inventory count at December 31 are summarized as follows:
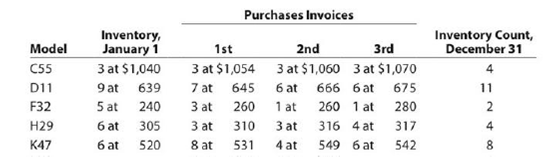
Instructions
1. Determine the cost of the inventory on December 31 by the first-in, first-out method.
Present data in columnar form, using the following headings:
| Model | Quantity | Unit Cost | Total Cost |
If the inventory of a particular model comprises one entire purchase plus a portion of another purchase acquired at a different unit cost, use a separate line for each purchase.
2. Determine the cost of the inventory on December 31 by the last-in, first-out method, following the procedures indicated in (1).
3. Determine the cost of the inventory on December 31 by the weighted average cost method, using the columnar headings indicated in (1).
4. Discuss which method (FIFO or LIFO) would be preferred for income tax purposes in periods of (a) rising prices and (b) declining prices.
(1)
Periodic Inventory System:
Periodic inventory system is a system, in which the inventory is updated in the accounting records on a periodic basis such as at the end of each month, quarter or year. In other words, it is an accounting method which is used to determine the amount of inventory at the end of each accounting period.
First-in-First-Out:
In First-in-First-Out method, the costs of the initially purchased items are considered as cost of goods sold, for the items which are sold first. The value of the ending inventory consists of the recent purchased items.
Last-in-Last-Out:
In Last-in-First-Out method, the costs of last purchased items are considered as the cost of goods sold, for the items which are sold first. The value of the closing stock consists of the initial purchased items.
Weighted-average cost method:
Under Weighted average cost method, the company calculates a new average cost after every purchase is made. It is determined by dividing the cost of goods available for sale by the units on hand.
To determine: value of inventory using first in first out method under periodic inventory system.
Explanation of Solution
The tabular column showing inventory cost is presented as follows:
| Model | Quantity ($) | Unit cost ($) | Total cost ($) |
| C55 | 3 | 1,070 | 3,210 |
| 1 | 1,060 | 1,060 | |
| D11 | 6 | 675 | 4,050 |
| 5 | 666 | 3,330 | |
| F32 | 1 | 280 | 280 |
| 1 | 260 | 260 | |
| H29 | 4 | 317 | 1,268 |
| K47 | 6 | 542 | 3,252 |
| 2 | 549 | 1,098 | |
| S33 | 2 | 232 | 464 |
| X74 | 7 | 39 | 273 |
| Total | 18,545 |
Hence, the ending inventory under First in First out Method is $18,545.
(2)
Explanation of Solution
The tabular column showing inventory cost is presented as follows:
| Model | Quantity ($) | Unit cost ($) | Total cost ($) |
| C55 | 3 | 1,040 | 3,210 |
| 1 | 1,054 | 1,054 | |
| D11 | 9 | 639 | 5,751 |
| 2 | 645 | 1,290 | |
| F32 | 2 | 240 | 480 |
| H29 | 4 | 305 | 1,220 |
| K47 | 6 | 520 | 3,120 |
| 2 | 531 | 1,062 | |
| S33 | 2 | 222 | 444 |
| X74 | 4 | 35 | 140 |
| 3 | 36 | 108 | |
| Total | 17,789 |
Hence, the ending inventory under Last in First out Method is $17,789.
(3)
Explanation of Solution
The tabular column showing inventory cost is presented as follows:
| Model | Quantity ($) | Unit cost ($) | Total cost ($) |
| C55 | 4 | 1,056 (1) | 4,224 |
| D11 | 11 | 654 (2) | 7,194 |
| F32 | 2 | 252 (3) | 504 |
| H29 | 4 | 311 (4) | 1,244 |
| K47 | 8 | 534 (5) | 4,272 |
| S33 | 2 | 227 (6) | 454 |
| X74 | 7 | 37 (7) | 259 |
| 18,151 |
Working notes:
Computation of unit cost for Model C55:
Computation of unit cost for Model D11:
Computation of unit cost for Model F32:
Computation of unit cost for Model H29:
Computation of unit cost for Model K47:
Computation of unit cost for Model S33:
Computation of unit cost for Model X74:
Hence, the ending inventory under weighted average cost Method is $18,151.
(4.a)
To discuss: the method that would be preferred for income tax purposes in the period of rising prices.
Explanation of Solution
During the period of rising prices, the last in first out method will result in lower cost of inventory, the cost of merchandise sold will be higher, and net income would be lower than other two methods. Therefore, the LIFO method would be preferred for the current year because it would effect in lower income tax.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Accounting
- Can you demonstrate the proper approach for solving this financial accounting question with valid techniques?arrow_forwardNavarro Enterprises has a beginning retained earnings balance of $78,000. Net income for the year is $22,000, and cash dividends paid during the year amount to $12,500. What will be the ending retained earnings balance? a. $78,000 b. $87,500 c. $100,000 d. $65,500arrow_forwardGeneral accountingarrow_forward
- I am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardCan you explain the correct approach to solve this financial accounting question?arrow_forwardI am looking for help with this general accounting question using proper accounting standards.arrow_forward
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





