Concept explainers
Consider the following

a. Draw a mechanism using curved arrows.
b. Draw an energy diagram. Label the axes, the reactants, products,
c. Draw the structure of the transition state.
d. What is the rate equation?
e. What happens to the reaction rate in each of the following instances? [1] The leaving group is changed from
(a)
Interpretation: The mechanism of the given reaction is to be drawn by the use of curved arrows.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron rich chemical species that contains negative charge or lone pair of electrons are known as a nucleophile. In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, nucleophile takes the position of leaving group by attacking the electron deficient carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 7.53P
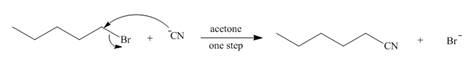
The mechanism of the given reaction is,
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given alkyl halide shows that carbon atom, on which bromine is present, is bonded to one another carbon atom. Hence, the bromine atom is bonded to primary carbon atom and the given alkyl halide is
In

Figure 1
The mechanism of the given reaction is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The energy diagram is to be drawn. The axes, reactants, products,
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The graphical representation of chemical reaction in which x-axis represents energy of the reaction and y-axis represents the reaction coordinate is called energy profile diagram.
Answer to Problem 7.53P
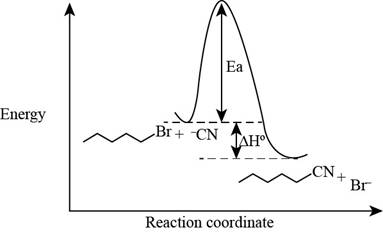
The energy diagram of the given reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
In bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction, formation and breakage of bond takes place simultaneously in the transition state. In the given reaction, breakage of
The energy of products is lower than the energy of reactants in exothermic reaction. Therefore, the energy diagram of the given reaction is,
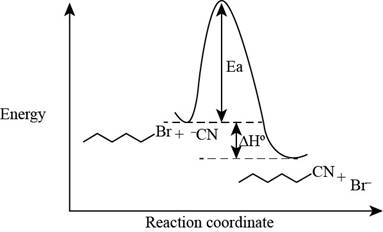
Figure 2
The x-axes of the energy diagram represent the energy of reactants and products and y-axes represent the reaction coordinate.
The energy diagram of the given reaction is shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation: The structure of the transition state is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: In bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction, formation and breakage of bond takes place simultaneously in the transition state. The energy of transition state is more than the energy of reactants and products.
Answer to Problem 7.53P
The structure of the transition state is shown below.
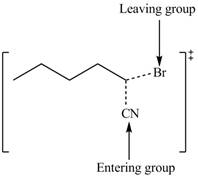
Explanation of Solution
In bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction, formation and breakage of bond takes place simultaneously in the transition state. In the given reaction, breakage of
Therefore, the transition state of the given reaction is,
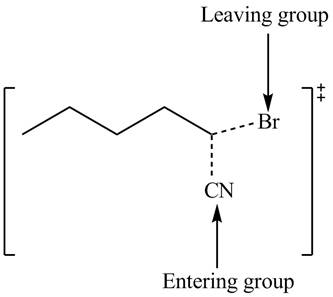
Figure 3
The structure of the transition state is shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation: The rate equation of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The rate of
The rate equation of
Answer to Problem 7.53P
The rate equation of the given reaction is,
Explanation of Solution
The rate of
The rate equation of
The alkyl halide of given reaction is
Therefore, the rate equation of given reaction is,
The rate equation of the given reaction is,
(e)
Interpretation: The change that occurs to the reaction rate in given instances is to be stated.
Concept introduction: The rate of
The rate of
Answer to Problem 7.53P
The change that occurs to the reaction rate in given instances is,
[1] The rate of the reaction will increase.
[2] The rate of the reaction will decrease.
[3] The rate of the reaction will decrease.
[4] The rate of the reaction increases by five times.
[5] The rate of the reaction increases by twenty five times.
Explanation of Solution
[1]
The primary halide undergoes nucleophilic substitution by
[2]
The polar protic solvent favors
[3]
The primary halide undergoes nucleophilic substitution by
[4]
The rate of
The rate of
According the given statement, the concentration of
Therefore, the rate of the reaction increases by five times when the concentration of
[5]
The rate of
The rate of
According the given statement, the concentration of
Therefore, the rate of the reaction increases by twenty five times when the concentration
The change that occurs to the reaction rate in given instances is,
[1] The rate of the reaction will increase.
[2] The rate of the reaction will decrease.
[3] The rate of the reaction will decrease.
[4] The rate of the reaction increases by five times.
[5] The rate of the reaction increases by twenty five times.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
PKG ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
- Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? O ? A . If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. . If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ㅇ 80 F5 F6 A 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Cente FIGarrow_forwardIn methyl orange preparation, if the reaction started with 0.5 mole of sulfanilic acid to form the diazonium salt of this compound and then it converted to methyl orange [0.2 mole]. If the efficiency of the second step was 50%, Calculate: A. Equation(s) of Methyl Orange synthesis: Diazotization and coupling reactions. B. How much diazonium salt was formed in this reaction? C. The efficiency percentage of the diazotization reaction D. Efficiency percentage of the whole reaction.arrow_forwardHand written equations pleasearrow_forward
- Hand written equations pleasearrow_forward> each pair of substrates below, choose the one that will react faster in a substitution reaction, assuming that: 1. the rate of substitution doesn't depend on nucleophile concentration and 2. the products are a roughly 50/50 mixture of enantiomers. Substrate A Substrate B Faster Rate X Ś CI (Choose one) (Choose one) CI Br Explanation Check Br (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Farrow_forwardNMR spectrum of ethyl acetate has signals whose chemical shifts are indicated below. Which hydrogen or set of hydrogens corresponds to the signal at 4.1 ppm? Select the single best answer. The H O HỌC—C—0—CH, CH, 2 A ethyl acetate H NMR: 1.3 ppm, 2.0 ppm, 4.1 ppm Check OA B OC ch B C Save For Later Submit Ass © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center |arrow_forward
- How many signals do you expect in the H NMR spectrum for this molecule? Br Br Write the answer below. Also, in each of the drawing areas below is a copy of the molecule, with Hs shown. In each copy, one of the H atoms is colored red. Highlight in red all other H atoms that would contribute to the same signal as the H already highlighted red Note for advanced students: In this question, any multiplet is counted as one signal. 1 Number of signals in the 'H NMR spectrum. For the molecule in the top drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. Check For the molecule in the bottom drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. O ✓ No additional Hs to color in top molecule ง No additional Hs to color in bottom…arrow_forwardin the kinetics experiment, what were the values calculated? Select all that apply.a) equilibrium constantb) pHc) order of reactiond) rate contstantarrow_forwardtrue or false, given that a 20.00 mL sample of NaOH took 24.15 mL of 0.141 M HCI to reach the endpoint in a titration, the concentration of the NaOH is 1.17 M.arrow_forward
- in the bromothymol blue experiment, pKa was measured. A closely related compound has a Ka of 2.10 x 10-5. What is the pKa?a) 7.1b) 4.7c) 2.0arrow_forwardcalculate the equilibrium concentration of H2 given that K= 0.017 at a constant temperature for this reaction. The inital concentration of HBr is 0.050 M.2HBr(g) ↔ H2(g) + Br2(g)a) 4.48 x 10-2 M b) 5.17 x 10-3 Mc) 1.03 x 10-2 Md) 1.70 x 10-2 Marrow_forwardtrue or falsegiven these two equilibria with their equilibrium constants:H2(g) + CI2(l) ↔ 2HCI(g) K= 0.006 CI2(l) ↔ CI2(g) K= 0.30The equilibrium contstant for the following reaction is 1.8H2(g) + CI2 ↔ 2HCI(g)arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
