
Foundation Design: Principles and Practices (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780133411898
Author: Donald P. Coduto, William A. Kitch, Man-chu Ronald Yeung
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 7, Problem 7.1QPP
List the three types of bearing capacity failures and explain the differences between them.
Expert Solution & Answer
To determine
The list of three types of bearing capacity failures and differences between them.
Explanation of Solution
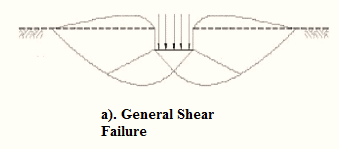
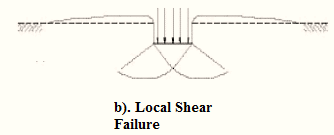
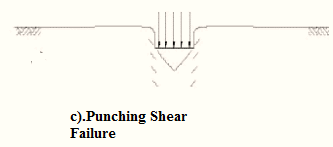
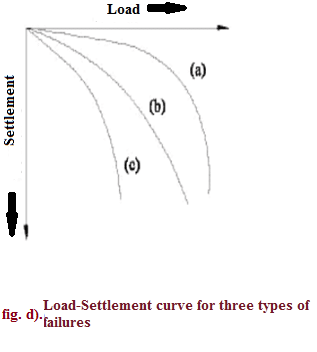
Three types of bearing capacity failures are:
- General shear failure.
- Local shear failure.
- Punching shear failure.
The differences between them are explained in tabular form below:
| Serial Number | General shear failure | Local shear failure | Punching shear failure |
| 1. | The continuous, well-defined failure surface | Not well-defined failure surface, | Failure surface is not well defined, no bulging of ground surface adjacent to the foundation |
| 2. | Sudden failure as shown in the load settlement curve.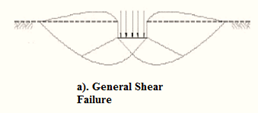 | Not a sudden failure. | Not a sudden failure, failure occurs gradually as depicted in the load-settlement curve. |
| 3. | Dense and stiff clay, incompressible soil | Relatively loose and soft soil | Lose and soft soil, highly compressible soil |
| 4. | Considerable settlement | Lage settlement occurs | |
| 5. | Bulging of failure surfaces at ground occurs | Slight bulging of soil around footing is observed | Shearing in vertical direction around the edge of the footing |
| 3. | Tilting of footing occurs | No tilting | No tilting |
| 7. | Relative density | Relative density | Relative density |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Subscribe now to access step-by-step solutions to millions of textbook problems written by subject matter experts!
schedule07:16
Students have asked these similar questions
Using a relevant image such as a 3D architectural rendering of a warehouse landscape in Edmond.
A simple beam has a span of 10 m and supports a total uniformly distributed load of 12 kN/m.
Properties of W 480×86:
Property
Value
A = 10800 mm²
bf = 180 mm
tf = 15 mm
Ix = 383.13 × 10⁶ mm⁴
tw = 12 mm
d = 480 mm
Questions:
Calculate the maximum shear in the beam in kN.
Calculate the average shear stress in the beam in MPa.
Calculate the maximum shear stress in the beam in MPa.
Given the properties of the wide flange:
Property
Value
d = 530 mm
bf = 210 mm
tw = 18 mm
tf = 16 mm
Question:
Compute the value of rₜ, defined as the radius of gyration of the compression flange plus 1/3 of the compression web area about the y-axis.
Given an existing two-story steel structure with interior columns spaced as shown in Fig.2. The columns are spaced at 18 ft in the North-South direction and at 30 ft in the East-West direction. An interior lower-story column is to be removed by adding newsteel girder as shown in Fig. 4. The floor dead loads and the roof dead loads are 70 psfand 18 psf respectively. The floor live loads and the roof live loads are 50 psf and20 psf respectively. All existing steel materials are ASTM A36 steel (Fy=36 ksi). Newgirder is ASTM A992 steel (Fy= 50 ksi). All columns are W8x31. Use the LRFD Method.Assumptions:1- The loads given include column and beam self weights.2- Existing beam and new girder are simply supported at both ends.3- New girder top flange is laterally braced at mid span and at girder ends only.4- Columns are continuous from foundation to roof and are prevented from sway atfloor level and at roof level in both directions.5- Columns are pin supported at foundation, at floor level,…
Chapter 7 Solutions
Foundation Design: Principles and Practices (3rd Edition)
Ch. 7 - List the three types of bearing capacity failures...Ch. 7 - A 1.2 m square, 0.4 m deep spread footing is...Ch. 7 - A 5 ft wide, 8 ft long, 2 ft deep spread footing...Ch. 7 - A column carrying a vertical downward unfactored...Ch. 7 - A column carrying a vertical downward ultimate...Ch. 7 - A 120 ft diameter cylindrical tank with an empty...Ch. 7 - A 1.5 m wide, 2.5 m long, 0.5 m deep spread...Ch. 7 - A 5 ft wide, 8 ft long, 2 ft deep spread footing...Ch. 7 - A bearing wall carries a total unfactored load 220...Ch. 7 - After the footing in Problem 7.9 was built, the...
Ch. 7 - A bearing wall carries a factored ultimate...Ch. 7 - A 5 ft wide, 8 ft long, 3 ft deep footing supports...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.13QPPCh. 7 - A spread footing supported on a sandy soil has...Ch. 7 - A certain column carries a vertical downward load...Ch. 7 - A building column carries a factored ultimate...Ch. 7 - A 3 ft square footing is founded at a depth of 2.5...Ch. 7 - A building column carries factored ultimate loads...Ch. 7 - Develop a spread sheet to compute allowable total...Ch. 7 - A certain column carries a vertical downward load...Ch. 7 - Repeat Problem 7.20 using LRFD assuming the...Ch. 7 - Conduct a bearing capacity analysis on the Fargo...Ch. 7 - Three columns, A, B, and C, are collinear, 500 mm...Ch. 7 - Two columns, A and B, are to be built 6 ft 0 in...Ch. 7 - In May 1970, a 70 ft tall, 20 ft diameter concrete...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Explain how each of the following types of integrity constraints is enforced in the SQL CREATE TABLE commands: ...
Modern Database Management
In Exercises 41 through 46, identify the errors. Dim9WAsDouble9W=2*9WIstoutput.Items.Add(9W)
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
2-1 List the five types of measurements that form the
basis of traditional ptane surveying-
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Use the following tables for your answers to questions 3.7 through 3.51 : PET_OWNER (OwnerID, OwnerLasst Name, ...
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Why must the number of teeth on the cutter be known when calculating milling machine table feed, in in./min?
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Suppose a class has a field named description. The fields data type is String. How would you indicate the field...
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Determine the bending moment at support A for the beam shown using the slope-deflection method. Use the sign convention defined in the chapter. a. 232.9 k-ft b. -182.1 k-ft c. 182.1 k-ft d. -232.9 k-ftarrow_forwardWhat is the shear and normal stresses of Point J and Point K?arrow_forwardWhat are the states of stress (magnitude and tension/compression of the normal stresses and shear stress) at Point J and Point K?arrow_forward
- Consider, M people (aka pax) who want to travel by car from O to D. They all start working at D at Q (e.g., Q-8am). If a person departs at time t, assume the time needed to go from O to D is given by c(t)=A+Bx(t), where x(t) is the flow of people departing at time t [car/unit of time]. In addition, a is the penalty for being early at work (E(t) is how early the person arrived when departing at time t), and ẞ is the penalty for being late at work (L(t) is how late the person arrived when departing at time t). Assume 0 < a < 1 < ß. Further assume the departure time choice problem under the equilibrium conditions. Prove that the arrival time of people who depart when most of the M people start their trips is equal to Q.arrow_forwarda. A b. A 3. Sketch normal depth, critical depth and the water surface profile. Assume at A and B the water is flowing at normal depth. Label and Identify all curves (i.e., M1, S2, etc.) Yn > Ye Уп Ye Уп> Ус yarrow_forward2. Design a trapezoidal ditch to carry Q = 1000 cfs. The ditch will be a lined channel, gravel bottom with sides shown below on a slope of S = 0.009. The side slopes of the 20-ft wide ditch will be 1 vertical to 3 horizontal. a) Determine the normal depth of flow (yn) using the Normal value for Manning's n. b) If freeboard requirements are 25% of the normal depth, how deep should the ditch be constructed? c) Classify the slope. T b Уп Z 1 Yn + FBarrow_forwardP15.45 WP A stainless steel pipe (Figure P15.45) with an outside diameter of 2.375 in. and a wall thickness of 0.109 in. is subjected to a bending moment M = 50 lb ft and an internal pressure of 180 psi. Determine the absolute maximum shear stress on the outer surface of the pipe. M FIGURE P15.45 Marrow_forward10.72 What power must the pump supply to the system to pump the oil from the lower reservoir to the upper reservoir at a rate of 0.3 m³/s? Sketch the HGL and the EGL for the system. p=940 kg/m³ v = 10-5 m²/s Elevation 100 m Elevation 112 m L= 150 m Oil Steel pipe D = 30 cm Problem 10.72arrow_forwardL / 83° 28° $75°E M 202° Q2: The scanning process was completed from point J to point N. The direction of the straight line was LM and the angles of deviation are shown in the figure below. Find the direction of the remaining sides? Narrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning
Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305081550
Author:Braja M. Das
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305086272
Author:William P. Spence, Eva Kultermann
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305635180
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305970939
Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning