
Reconstruct Missing Data
A tornado struck the only manufacturing plant of Toledo Farm Implements (TFI) on June 1. All work-in-process inventory was destroyed, but a few records were salvaged from the wreckage and from the company’s headquarters. If acceptable documentation is provided, the loss will be covered by insurance. The insurable value of work-in-process inventory consists of direct materials, direct labor, and applied
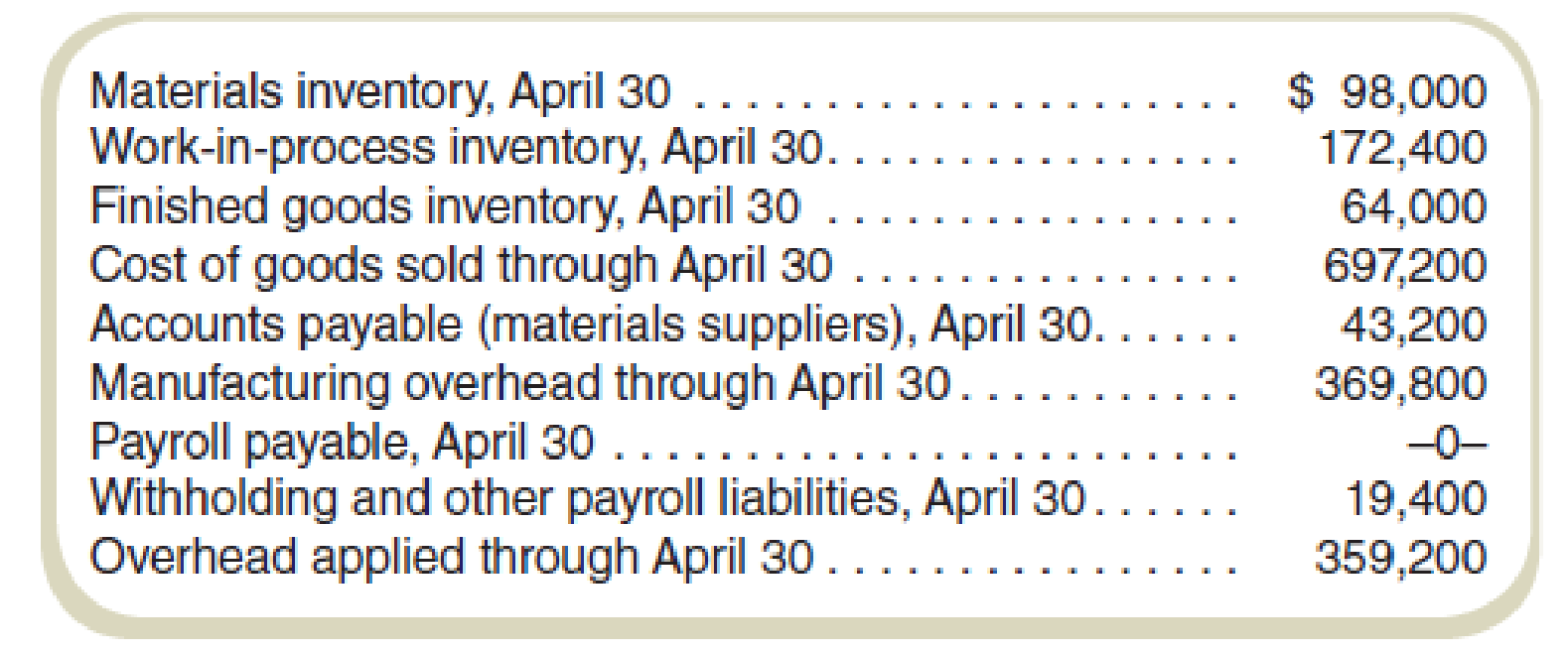
The following information about the plant appears on the April financial statements at the company’s downtown headquarters:
A count of the inventories on hand May 31 shows the following:

The accounts payable clerk tells you that outstanding bills to suppliers totaled $100,200 and that cash payments of $75,800 were made to them during the month. She informs you that the payroll costs last month for the manufacturing section included $164,800, of which $29,400 was indirect labor.
At the end of May, the following balances were available from the main office:

Recall that each month there is only one requisition for indirect materials. Among the fragments of paper, you located the following information, which you have neatly typed for your records:
From scrap found under desk: indirect materials → $4,172
You also learn that the overhead during the month was overapplied by $2,400.
Required
Determine the cost of the work-in-process inventory lost in the disaster.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF COST ACCOUNTING
- What is the asset turnover of this financial accounting question?arrow_forwardWhat is its average inventory of this financial accounting question?arrow_forwardThe underapplication of overhead will result in Group of answer choices understatement of net income. overstatement of cost of goods sold. understatement of cost of goods sold. overvalued finished goods inventory.arrow_forward
- Business Its Legal Ethical & Global EnvironmentAccountingISBN:9781305224414Author:JENNINGSPublisher:Cengage
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub

