
Concept explainers
Cost Flows through Accounts
Brighton Services repairs locomotive engines. It employs 100 full-time workers at $20 per hour. Despite operating at capacity, last year’s performance was a great disappointment to the managers. In total, 10 jobs were accepted and completed, incurring the following total costs:

Of the $1,040,000 manufacturing
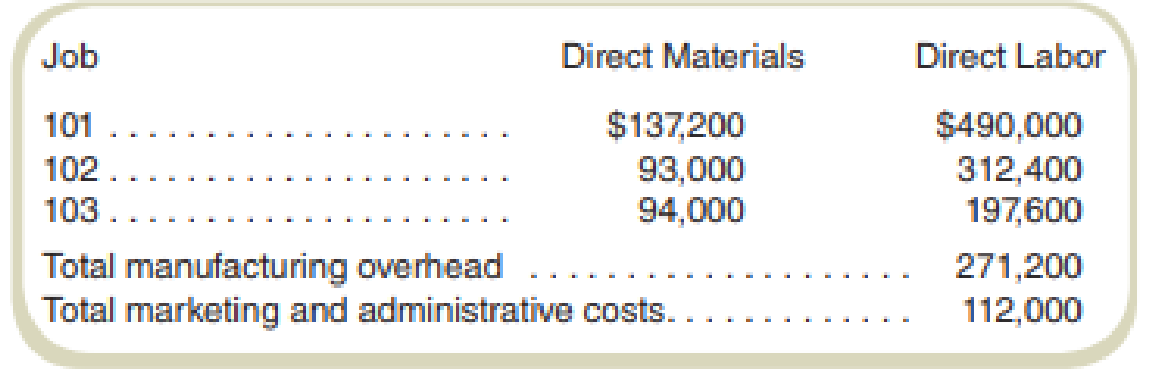
This year, Brighton Services expects to operate at the same activity level as last year, and overhead costs and the wage rate are not expected to change. For the first quarter of this year, Brighton Services completed two jobs and was beginning the third (Job 103). The costs incurred follow:
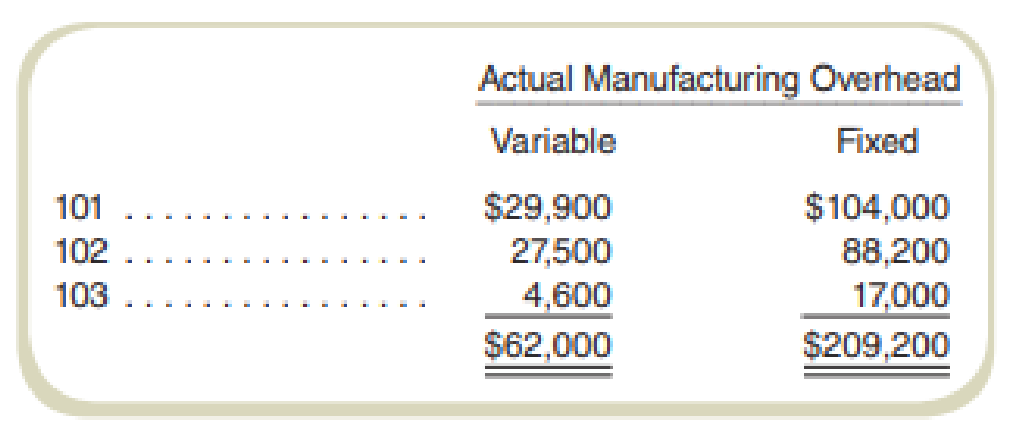
You are a consultant associated with Lodi Consultants, which Brighton Services has asked for help. Lodi’s senior partner has examined Brighton Services’s accounts and has decided to divide actual factory overhead by job into fixed and variable portions as follows:
In the first quarter of this year, 40 percent of marketing and administrative cost was variable and 60 percent was fixed. You are told that Jobs 101 and 102 were sold for $850,000 and $550,000, respectively. All over- or underapplied overhead for the quarter is written off to Cost of Goods Sold.
Required
- a. Present in T-accounts the actual
manufacturing cost flows for the three jobs in the first quarter of this year. - b. Using last year’s overhead costs and direct labor-hours as this year’s estimate, calculate predetermined overhead rates per direct labor-hour for variable and fixed overhead.
- c. Present in T-accounts the normal manufacturing cost flows for the three jobs in the first quarter of this year. Use the overhead rates derived in requirement (b).
- d. Prepare income statements for the first quarter of this year under the following costing systems:
- (1) Actual.
- (2) Normal.
a.
Compute in T-accounts: the actual manufacturing cost flows for the three jobs in the first quarter of this year.
Explanation of Solution
T-accounts in job costing: The ledger accounts are also termed as T-accounts which are prepared after the recording of the journal entry of the transactions. The balances of raw materials, work-in-process, finished goods inventory and overheads from the journal book are transferred to the respective T-accounts.
T-account of materials inventory:
| Materials inventory | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Amount | Date | Particulars | Amount |
| $ 137,200 | |||||
| $ 93,000 | |||||
| $ 94,000 | |||||
Table: (1)
T-account of wages payable:
| Wages payable | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Amount | Date | Particulars | Amount |
| $ 490,000 | |||||
| $ 312,400 | |||||
| $ 197,600 | |||||
Table: (2)
T-account of variable manufacturing overhead:
| Variable manufacturing overhead | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Amount | Date | Particulars | Amount |
| $ 62,000 | $ 29,900 | ||||
| $ 27,500 | |||||
| $ 4,600 | |||||
Table: (3)
T-account of fixed manufacturing overhead:
| Fixed manufacturing overhead | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Amount | Date | Particulars | Amount |
| $ 209,200 | $ 104,000 | ||||
| $ 88,200 | |||||
| $ 17,000 | |||||
Table: (4)
T-account of work-in-process inventory:
| Work-in-process inventory | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Amount | Date | Particulars | Amount |
| $ 324,200 | $ 761,100 | ||||
| $ 1,000,000 | $ 521,100 | ||||
| $ 62,000 | |||||
| $ 209,200 | |||||
Table: (5)
T-account of finished goods inventory:
| Finished goods inventory | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Amount | Date | Particulars | Amount |
| $ 761,100 | |||||
| $ 521,100 | $ 1,282,200 | ||||
Table: (6)
T-account of the cost of goods sold:
| Cost of goods sold | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Amount | Date | Particulars | Amount |
| $ 1,282,200 | |||||
Table: (7)
b.
Calculate predetermined overhead rates per direct labor-hour for variable and fixed overhead by using last year’s overhead costs and direct labor-hours.
Explanation of Solution
Predetermined overhead rate: The predetermined overhead rate is the rate computed for applying manufacturing overheads to the work-in-process inventory. This rate can be computed by dividing the total amount of manufacturing overheads by the base of allocation. The formula for calculating the predetermined overhead rate is:
Compute the predetermined variable overhead rate:
Compute the predetermined fixed overhead rate:
Working note 1:
Compute the total direct labor-hours:
Working note 2:
Compute the variable manufacturing overhead:
Working note 3:
Compute the fixed manufacturing overhead:
c.
Present in T-accounts the normal manufacturing cost flows for the three jobs in the first quarter of this year by using the overhead rates derived as per the previous part.
Explanation of Solution
T-accounts in job costing: The ledger accounts are also termed as T-accounts which are prepared after the recording of the journal entry of the transactions. The balances of raw materials, work-in-process, finished goods inventory and overheads from the journal book are transferred to the respective T-accounts.
T-account of materials inventory:
| Materials inventory | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Amount | Date | Particulars | Amount |
| $ 137,200 | |||||
| $ 93,000 | |||||
| $ 94,000 | |||||
Table: (8)
T-account of wages payable:
| Wages payable | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Amount | Date | Particulars | Amount |
| $ 490,000 | |||||
| $ 312,400 | |||||
| $ 197,600 | |||||
Table: (9)
T-account of variable manufacturing overhead:
| Variable manufacturing overhead | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Amount | Date | Particulars | Amount |
| $ 62,000 | $ 38,220 | ||||
| $ 16,000 | $ 24,367 | ||||
| $ 15,413 | |||||
Table: (10)
T-account of fixed manufacturing overhead:
| Fixed manufacturing overhead | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Amount | Date | Particulars | Amount |
| $ 182,000 | $ 89,180 | ||||
| $ 56,857 | |||||
| $ 35,963 | |||||
| $ 27,200 | |||||
Table: (11)
T-account of work-in-process inventory:
| Work-in-process inventory | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Amount | Date | Particulars | Amount |
| $ 324,200 | $ 754,600 | ||||
| $ 1,000,000 | $ 486,624 | ||||
| $ 78,000 | |||||
| $ 182,000 | |||||
Table: (12)
T-account of finished goods inventory:
| Finished goods inventory | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Amount | Date | Particulars | Amount |
| $ 754,600 | |||||
| $ 486,624 | $ 1,241,224 | ||||
Table: (13)
T-account of the cost of goods sold:
| Cost of goods sold | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Amount | Date | Particulars | Amount |
| $ 1,241,224 | |||||
Table: (14)
T-account of under-or over-applied overhead
| Under-or over-applied overhead | |||||
| Date | Particulars | Amount | Date | Particulars | Amount |
| $ 27,200 | $ 16,000 | ||||
Table: (15)
d.
Prepare the income statement for the first quarter of this year using actual and normal systems.
Explanation of Solution
Normal system of costing: Under normal costing, the cost of a job is determined by using the actual direct material, and the labor cost by adding overhead applied using a predetermined rate and an actual allocation base.
Actual system of costing: The cost of a job is determined by using the actual direct material, and the labor cost by adding overhead applied using an actual overhead rate and an actual allocation base under actual costing.
Income statement using actual system:
| Particulars | Amount |
| Sales Revenue | $ 1,400,000 |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | ($ 1,282,200) |
| Gross margin | $ 117,800 |
| Less: (Under-) Over applied overhead | $ 0 |
| Marketing and administrative costs | ($ 112,000) |
| Operating profit (loss) | $ 5,800 |
Income statement using normal system:
| Particulars | Normal |
| Sales Revenue | $ 1,400,000 |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | ($ 1,241,224) |
| Gross margin | $ 158,776 |
| Less: (Under-) Over applied overhead | $ 11,200 |
| Marketing and administrative costs | ($ 112,000) |
| Operating profit (loss) | $ 35,576 |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF...(LL)-W/ACCESS>CUSTOM<
- The underapplication of overhead will result in Group of answer choices understatement of net income. overstatement of cost of goods sold. understatement of cost of goods sold. overvalued finished goods inventory.arrow_forwardchoose best answer financial accountingarrow_forwardWhat is the couple marriage penalty or benefit?arrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College



