
(a)
Interpretation: The mistake in the mechanism of indicated reaction should be pointed out and correction should be proposed.

Concept introduction:Carbocation formation is relatively slower than acid-base reactions. Carbocations generated from
Unimolecular substitution or
A general

(b)
Interpretation: The mistake in the mechanism of indicated reaction should be pointed out and correction should be proposed.
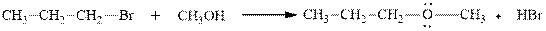
Concept introduction:Carbocation formation is relatively slower than acid-base reactions. Carbocations generated from alkyl halides have two fates; they can be either trapped by nucleophiles to give substitution product or may deprotonate to yield a small amount of alkene.
Unimolecular substitution or
A general

(c)
Interpretation: The mistake in the mechanism of indicated reaction should be pointed out and correction should be proposed.
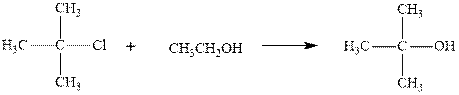
Concept introduction: Carbocation formation is relatively slower than acid-base reactions. Carbocations generated from alkyl halides have two fates; they can be either trapped by nucleophiles to give substitution product or may deprotonate to yield a small amount of alkene.
Unimolecular substitution or
A general

Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 7 Solutions
EBK STUDY GUIDE/SOLUTIONS MANUAL FOR OR
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: Explanation Check IN NaBH3CN H+ ? Click and drag to start drawing a structure. D 5 C +arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: H3O+ + ? • Draw all the reasonable products in the drawing area below. If there are no products, because no reaction will occur, check the box under the drawing area. • Include both major and minor products, if some of the products will be more common than others. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds if you need to distinguish between enantiomers. No reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. dmarrow_forwardIarrow_forward
- Draw the anti-Markovnikov product of the hydration of this alkene. this problem. Note for advanced students: draw only one product, and don't worry about showing any stereochemistry. Drawing dash and wedge bonds has been disabled for esc esc ☐ Explanation Check F1 1 2 F2 # 3 F3 + $ 14 × 1. BH THE BH3 2. H O NaOH '2 2' Click and drag to start drawing a structure. F4 Q W E R A S D % 905 LL F5 F6 F7 © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility < & 6 7 27 8 T Y U G H I F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 9 0 J K L P + // command option Z X C V B N M H H rol option commandarrow_forwardAG/F-2° V 3. Before proceeding with this problem you may want to glance at p. 466 of your textbook where various oxo-phosphorus derivatives and their oxidation states are summarized. Shown below are Latimer diagrams for phosphorus at pH values at 0 and 14: -0.93 +0.38 -0.50 -0.51 -0.06 H3PO4 →H4P206 →H3PO3 →→H3PO₂ → P → PH3 Acidic solution Basic solution -0.28 -0.50 3--1.12 -1.57 -2.05 -0.89 PO HPO H₂PO₂ →P → PH3 -1.73 a) Under acidic conditions, H3PO4 can be reduced into H3PO3 directly (-0.28V), or via the formation and reduction of H4P206 (-0.93/+0.38V). Calculate the values of AG's for both processes; comment. (3 points) 0.5 PH P 0.0 -0.5 -1.0- -1.5- -2.0 H.PO, -2.3+ -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 2 H,PO, b) Frost diagram for phosphorus under acidic conditions is shown. Identify possible disproportionation and comproportionation processes; write out chemical equations describing them. (2 points) H,PO 4 S Oxidation stale, Narrow_forward4. For the following complexes, draw the structures and give a d-electron count of the metal: a) Tris(acetylacetonato)iron(III) b) Hexabromoplatinate(2-) c) Potassium diamminetetrabromocobaltate(III) (6 points)arrow_forward
- 2. Calculate the overall formation constant for [Fe(CN)6]³, given that the overall formation constant for [Fe(CN)6] 4 is ~1032, and that: Fe3+ (aq) + e = Fe²+ (aq) E° = +0.77 V [Fe(CN)6]³ (aq) + e¯ = [Fe(CN)6] (aq) E° = +0.36 V (4 points)arrow_forward5. Consider the compounds shown below as ligands in coordination chemistry and identify their denticity; comment on their ability to form chelate complexes. (6 points) N N A B N N N IN N Carrow_forward1. Use standard reduction potentials to rationalize quantitatively why: (6 points) (a) Al liberates H2 from dilute HCl, but Ag does not; (b) Cl2 liberates Br2 from aqueous KBr solution, but does not liberate C12 from aqueous KCl solution; c) a method of growing Ag crystals is to immerse a zinc foil in an aqueous solution of AgNO3.arrow_forward
- What would be the best choices for the missing reagents 1 and 3 in this synthesis? 1 1. PPh3 2. n-BuLi 3 2 • Draw the missing reagents in the drawing area below. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. • Do not draw the missing reagent 2. If you draw 1 correctly, we'll know what it is. • Note: if one of your reagents needs to contain a halogen, use bromine. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant R in this organic reaction? N N H3O+ +R + • Draw the structure of R in the drawing area below. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds if it's necessary to draw one particular enantiomer. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. fmarrow_forwardThe product on the right-hand side of this reaction can be prepared from two organic reactants, under the conditions shown above and below the arrow. Draw 1 and 2 below, in any arrangement you like. 1+2 NaBH3CN H+ N Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 5arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

