
Concept explainers
Take your medicine: Medication used to treat a certain condition is administered by syringe. The target dose in a particular application is 10 milligrams. Because of the variations in the syringe, in reading the scale: and in mixing the fluid suspension, the actual dose administered is
- What is the
probability that the dose administered is between 9 and 11.5 milligrams? - Find the 98th percentile of the administered dose.
- If a clinical overdose is defined as a dose larger than 15 milligrams, what is the probability that a patient will receive an overdose?
(a)
To find: the probability that the dose administered is between
Answer to Problem 4RE
The required answer is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
A normal population has mean
standard deviation
Required Calculations:
It is asked in the question to find
Now,
Using normal table
Calculation:
To compute the proportion of the population that is between
1. Click CaIc, then select Probability distributions and then go to Normal.
2. Select the Cumulative option.
3. Enter
4. Enter
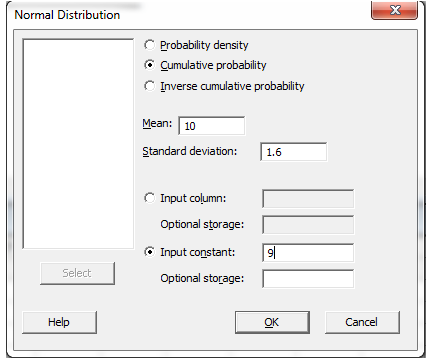
5. Click Ok. The final output is given below.
Cumulative Distribution function
Normal with mean
Similarly, compute the probability when
Cumulative distribution function.
Normal with mean
The required probability that
The required answer is
(b)
To find: the
Answer to Problem 4RE
The
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The actual dose administered is normally distributed with mean
standard deviation
Calculation:
To compute the
1. Click on Insert function.
2. Select NORMINV
3. Enter
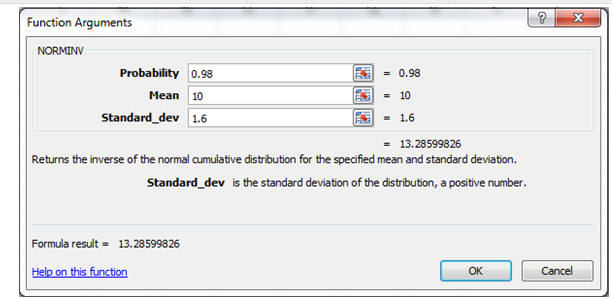
The above output shows that the
The required answer is
(C)
To compute: the probability that the dose administered is greater than
Answer to Problem 4RE
The probability that the dose administered is greater than
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
A normal population has mean
standard deviation
Required calculations:
it is asked in the question to find
Using normal table
Calculation steps:
Compute the probability that the dose administered is greater than
Cumulative Distribution Function
Normal with mean
The required probability is,
The probability that the dose administered is greater than
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Elementary Statistics
- 19. Let X be a non-negative random variable. Show that lim nE (IX >n)) = 0. E lim (x)-0. = >arrow_forward(c) Utilize Fubini's Theorem to demonstrate that E(X)= = (1- F(x))dx.arrow_forward(c) Describe the positive and negative parts of a random variable. How is the integral defined for a general random variable using these components?arrow_forward
- 26. (a) Provide an example where X, X but E(X,) does not converge to E(X).arrow_forward(b) Demonstrate that if X and Y are independent, then it follows that E(XY) E(X)E(Y);arrow_forward(d) Under what conditions do we say that a random variable X is integrable, specifically when (i) X is a non-negative random variable and (ii) when X is a general random variable?arrow_forward
 Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill

