
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The preparation method for the given compound has to be given by taking ethyne as starting material.
Concept Introduction:
Acid Catalysed addition of water: When water is added to alkyne in the presence of an acid, the product formed will be an enol. Enol contains a double bond and an
If a carbonyl group is bonded to two alkyl groups, it is called as a
Conversion of terminal
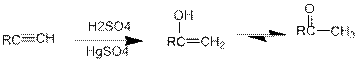
(b)
Interpretation:
The preparation method for the given compound has to be given by taking ethyne as starting material.
Concept Introduction:
Deprotonation: The reaction in which proton is removed from the compound using reagents is known as deprotonation.
Different reagents are used for the deprotonation and one of the common reagent is sodium amide.
Lindlar catalyst: The catalyst is used for the hydrogenation of alkynes in a syn manner. This means both hydrogen are added on the same side across the triple bond and the product obtained will be a cis product.
Sodium in liquid ammonia: The catalyst is used for the formation of trans
(c)
Interpretation:
The preparation method for the given compound has to be given by taking ethyne as starting material.
Concept Introduction:
Deprotonation: The reaction in which proton is removed from the compound using reagents is known as deprotonation.
Different reagents are used for the deprotonation and one of the common reagent is sodium amide.
Lindlar catalyst: The catalyst is used for the hydrogenation of alkynes in a syn manner. This means both hydrogen are added on the same side across the triple bond and the product obtained will be a cis product.
Sodium in liquid ammonia: The catalyst is used for the formation of trans alkenes from alkynes. Because of its more reactivity towards triple bonds, the reaction will stop at the formation of alkenes.
Acid Catalysed addition of water: When water is added to alkyne in the presence of an acid, the product formed will be an enol. Enol contains a double bond and an
If a carbonyl group is bonded to two alkyl groups, it is called as a ketone. The enol formed in the acid catalysed addition of water will be easily converted into a ketone.
Conversion of terminal alkynes into enol: If we want to convert terminal alkyne into an enol, the presence of mercuric ion as a catalyst should be needed and the catalyst will increase the rate of the reaction.
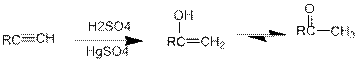
(d)
Interpretation:
The preparation method for the given compound has to be given by taking ethyne as starting material.
Concept Introduction:
Deprotonation: The reaction in which proton is removed from the compound using reagents is known as deprotonation.
Different reagents are used for the deprotonation and one of the common reagent is sodium amide.
Lindlar catalyst: The catalyst is used for the hydrogenation of alkynes in a syn manner. This means both hydrogen are added on the same side across the triple bond and the product obtained will be a cis product.
Sodium in liquid ammonia: The catalyst is used for the formation of trans alkenes from alkynes. Because of its more reactivity towards triple bonds, the reaction will stop at the formation of alkenes.
(e)
Interpretation:
The preparation method for the given compound has to be given by taking ethyne as starting material.
Concept Introduction:
Deprotonation: The reaction in which proton is removed from the compound using reagents is known as deprotonation.
Different reagents are used for the deprotonation and one of the common reagent is sodium amide.
Lindlar catalyst: The catalyst is used for the hydrogenation of alkynes in a syn manner. This means both hydrogen are added on the same side across the triple bond and the product obtained will be a cis product.
Sodium in liquid ammonia: The catalyst is used for the formation of trans alkenes from alkynes. Because of its more reactivity towards triple bonds, the reaction will stop at the formation of alkenes.
(f)
Interpretation:
The preparation method for the given compound has to be given by taking ethyne as starting material.
Concept Introduction:
Deprotonation: The reaction in which proton is removed from the compound using reagents is known as deprotonation.
Different reagents are used for the deprotonation and one of the common reagent is sodium amide.
Lindlar catalyst: The catalyst is used for the hydrogenation of alkynes in a syn manner. This means both hydrogen are added on the same side across the triple bond and the product obtained will be a cis product.
Sodium in liquid ammonia: The catalyst is used for the formation of trans alkenes from alkynes. Because of its more reactivity towards triple bonds, the reaction will stop at the formation of alkenes.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Organic Chemistry; Organic Chemistry Study Guide A Format: Kit/package/shrinkwrap
- lighting discharges in the atmosphere catalyze the conversion of nitrogen to nitric oxide. How many grams of nitrogen would be required to make 25.0 g of nitric oxide in this way ?arrow_forwardThe electron of a hydrogen atom is excited to the 4d orbital. Calculate the energy of the emitted photon if the electron were to move to each of the following orbitals: (a) 1s; (b) 2p; (c) 2s; (d) 4s. (e) Suppose the outermost electron of a potassium atom were excited to a 4d orbital and then moved to each of these same orbitals. Describe qualitatively the differences that would be found between the emission spectra of potassium and hydrogen (do not perform calculations). Explain your answer.arrow_forwardImagine a four-dimensional world. In it, atoms would have one s orbital and four p orbitals in a given shell. (a) Describe the shape of the Periodic Table of the first 24 elements. (b) What elements would be the first two noble gases (use the names from our world that correspond to the atomic numbers).arrow_forward
- The electron affinity of thulium was measured by a technique called laser photodetachment electron spectroscopy. In this technique, a gaseous beam of anions of an element is bombarded with photons from a laser. The photons knock electrons off some of the anions, and the energies of the emitted electrons are detected. The incident radiation had a wavelength of 1064 nm, and the emitted electrons had an energy of 0.137 eV. Although the analysis is more complicated, we can obtain an estimate of the electron affinity from the energy difference between the photons and the emitted electrons. What is the electron affinity of thulium in electron volts and in kilojoules per mole?arrow_forwardBe sure to answer all parts. The following alkyne is treated with 03 followed by H₂O. Part 1: How many different compounds are formed in this process? 1 Part 2 out of 2 Draw the product of the reaction. draw structure ...arrow_forwardMany fireworks use magnesium to burn, which releases a significant amount of energy. The heat released causes the oxide to glow, emitting white light. The color of this light can be changed by including nitrates and chlorides of elements that emit in the visible region of their spectra. One such compound is barium nitrate, which produces a yellow-green light. Excited barium ions generate light with wavelengths of 487 nm, 524 nm, 543 nm, and 578 nm. For each case, calculate: (a) the change in energy (in electron volts) of a barium atom and (b) the molar change in energy (in kilojoules per second).arrow_forward
- Clouds of hot, luminous interstellar hydrogen gas can be seen in some parts of the galaxy. In some hydrogen atoms, electrons are excited to quantum levels with n = 100 or higher. (a) Calculate the wavelength observed on Earth if the electrons fall from the level with n = 100 to one with n = 2. (b) In what series would this transition be found? (c) Some of these high-energy electrons fall into intermediate states, such as n = 90. Would the wavelengths of a transition from the state with n = 100 to one with n = 90 be longer or shorter than those in the Balmer series? Explain your answer.arrow_forwardIn the spectroscopic technique known as photoelectron spectroscopy (PES), ultraviolet radiation is directed at an atom or molecule. Electrons are ejected from the valence shell and their kinetic energies are measured. Since the energy of the incident ultraviolet photons is known and the kinetic energy of the ejected electron is measured, the ionization energy, I, can be deduced because total energy is conserved. (a) Show that the velocity, v, of the ejected electron and the frequency, n, of the incident radiation are related by hv = I + (1/2)mv^2? (b) Use this relation to calculate the ionization energy of a rubidium atom, knowing that light of wavelength 58.4 nm produces electrons with a velocity of 2,450 km/s Recall that 1 J = 1 kg.m^2/s^2arrow_forwardI) In Millikan's experiment, each droplet observed by the technicians contained an even number of electrons. If they had been unaware of this limitation, how would it have affected their report of an electron's charge?II) Millikan measured the charge of an electron in electrostatic units, esu. The data he collected included the following series of charges found on oil drops: 9.60 X 10^-10 esu, 1.92 X 10^-9 esu; 2.40 X 10^-9 esu; 2.88 X 10^-9 esu; and 4.80 X 10^-9 esu. (a) From this series, find the probable charge of the electron in electrostatic units. (b) Estimate the number of electrons in an oil drop with a charge of 6.72 X 10^-9 esu. The actual charge (in Coulombs) of an electron is 1.602 X 10^-19 C. What is the relationship between esu and Coulombs?arrow_forward
- my ccc edu - Search X Quick Access X D2L Homepage - Spring 2025 x N Netflix X Dimensional Analysis - A x+ pp.aktiv.com Q ☆ X Question 59 of 70 The volume of 1 unit of plasma is 200.0 mL If the recommended dosage for adult patients is 10.0 mL per kg of body mass, how many units are needed for a patient with a body mass of 80.0 kg ? 80.0 kg 10.0 DAL 1 units X X 4.00 units 1 1 Jeg 200.0 DAL L 1 units X 200.0 mL = 4.00 units ADD FACTOR *( ) DELETE ANSWER RESET D 200.0 2.00 1.60 × 10³ 80.0 4.00 0.0400 0.250 10.0 8.00 & mL mL/kg kg units/mL L unit Q Search delete prt sc 111 110 19arrow_forwardIdentify the starting material in the following reaction. Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. draw structure ... [1] 0 3 C10H18 [2] CH3SCH3 Harrow_forwardIn an equilibrium mixture of the formation of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen, it is found that PNH3 = 0.147 atm, PN2 = 1.41 atm and Pн2 = 6.00 atm. Evaluate Kp and Kc at 500 °C. 2 NH3 (g) N2 (g) + 3 H₂ (g) K₂ = (PN2)(PH2)³ = (1.41) (6.00)³ = 1.41 x 104arrow_forward

 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning




