Problem 1RQ: Review Question 7.1 Assuming that Earths orbit around the Sun is circular, what information do you... Problem 2RQ: Review Question 7.2 A system can possess energy but it cannot possess work. Why?
Problem 3RQ: Review Question 7.3 When we use the work-energy equation, how do we incorporate the force that Earth... Problem 4RQ: Review Question 7.4 If the magnitude of the force exerted by a spring on an object is kx, why is it... Problem 5RQ: Review Question 7.5 Why, when friction cannot be neglected, is it useful to include both surfaces in... Problem 6RQ: Review Question 7.6 What would change in the solution to the problem in Example 7.8 if we did not... Problem 7RQ: Review Question 7.7 Imagine that a collision occurs. You measure the masses of the two objects... Problem 8RQ: Review Question 7.8 Toyota says that the power of their Prius car is 121 hp. What does this number... Problem 9RQ: Review Question 7.9 In this section you read that the gravitational potential energy of two large... Problem 1MCQ: In which of the following is positive work done by a person on a suitcase? a. The person holds a... Problem 2MCQ: 2. Which answer best represents the system’s change in energy for the following process? The system... Problem 3MCQ: An Atwood machine is shown in Figure Q7.3. As the blocks are released and block 1 moves downward,... Problem 4MCQ Problem 5MCQ: 5. Three processes are described below. Choose one process in which there is work done on the... Problem 6MCQ: 6. Choose which statement describes a process in which an external force does negative work on the... Problem 7MCQ: 7. Which example(s) below involve(s) zero physics work? Choose all that apply.
a. A person holds a... Problem 8MCQ: 8. Estimate the change in gravitational potential energy when you rise from bed to a standing... Problem 9MCQ: What does it mean if object 1 does +10 J of work on object 2? a. Object 1 exerts a 10-N force on... Problem 10MCQ: You pull on a spring, which obeys Hookes law, in two steps. In step 1, you extend it by distance xs.... Problem 11MCQ: The graph in Figure Q7.11 shows the time dependence of the vertical displacement of a lead ball with... Problem 12MCQ: 12. A 1400-kg car is traveling on a level road at a constant speed of 60 mi/h. The drag force... Problem 13MCQ Problem 14MCQ: Two clay balls are moving toward each other. The balls have equal kinetic energies (K1=K2), but ball... Problem 15CQ: 15. Is energy a physical phenomenon, a model, or a physical quantity? Explain your answer.
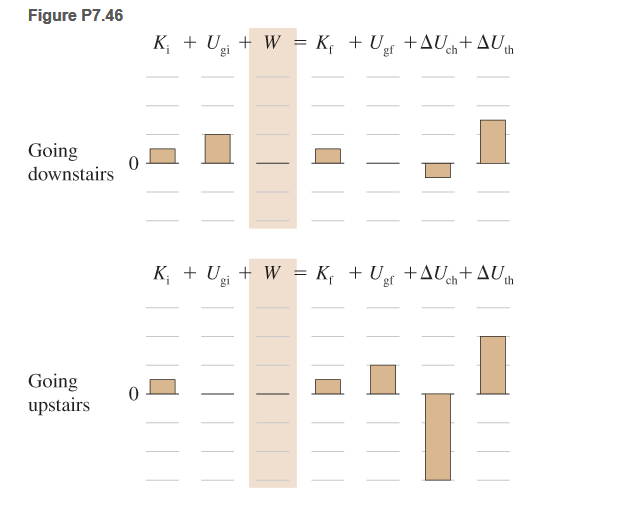
Problem 16CQ: 16. Your friend thinks that the escape speed should be greater for more massive objects than for... Problem 17CQ: Suggest how you can measure the following quantities: the power of a motor, the kinetic energy of a... Problem 18CQ: How can satellites stay in orbit without any jet propulsion system? Explain using work-energy ideas. Problem 19CQ: Why does the Moon have no atmosphere, but Earth does? Problem 20CQ: What will happen to Earth if our Sun becomes a black hole? Problem 21CQ: 21. In the equation , the gravitational potential energy is directly proportional to the distance of... Problem 22CQ: 22. You push a small cart by exerting a constant force F along a table. After you push the cart a... Problem 1P: 1. Jay fills a wagon with sand (about 20 kg) and pulls it with a rope 30 m along the beach. He holds... Problem 2P: 2. You have a 15-kg suitcase and (a) slowly lift it 0.80 m upward, (b) hold it at rest to test... Problem 3P: * You use a rope to slowly pull a sled and its passenger 50 m up a 20 incline, exerting a 150-N... Problem 4P: A rope attached to a truck pulls a 180-kg motorcycle at 9.0 m/s. The rope exerts a 400-N force on... Problem 5P: 5. You lift a 25-kg child 0.80 m, slowly carry him 10 m to the playroom, and finally set him back... Problem 6P: A truck runs into a pile of sand, moving 0.80 m as it slows to a stop. The magnitude of the work... Problem 7P: 7. A 0.50-kg block is placed in a straight gutter that allows the block to move only along the... Problem 8P: s up a smooth incline, which makes an angle with the horizontal. (a) Derive an expression for the... Problem 9P: 9. ** It is a windy day. You are moving a 20-kg box at a constant speed over 10 m by pulling a rope... Problem 10P: A 5.0-kg rabbit and a 12-kg Irish setter have the same kinetic energy. If the setter is running at... Problem 11P Problem 12P: * A pickup truck (2268 kg) and a compact car (1100 kg) have the same momentum. (a) What is the ratio... Problem 13P: * When does the kinetic energy of a car change more: when the car accelerates from 0 to 10 m/s or... Problem 14P: * When exiting the highway, a 1100-kg car is traveling at 22 m/s. The cars kinetic energy decreases... Problem 15P Problem 16P: 16. * Flea jump flea pushes off a surface by extending its rear legs for a distance of slightly... Problem 17P: * Roller coaster ride A roller coaster car drops a maximum vertical distance of 35.4 m. (a)... Problem 18P: 18. * BIO EST Heart pumps blood The heart does about 1 J of work while pumping blood into the aorta... Problem 19P: 19. * Wind energy Air circulates across Earth in regular patterns. A tropical air current called the... Problem 20P: 20. * BIO Bone break The tibia bone in the lower leg of an adult human will break if the compressive... Problem 21P: 21. * BIO EST Climbing Mt. Everest In 1953 Sir Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay made the first... Problem 22P: 22. A door spring is difficult to stretch. (a) What maximum force do you need to exert on a relaxed... Problem 23P: * A moving car has 40,000 J of kinetic energy while moving at a speed of 7.0 m/s. A spring-loaded... Problem 24P: 24. * The force required to stretch a slingshot by different amounts is shown in the graph in Figure... Problem 25P: Jim is driving a 2268-kg pickup truck at 20 m/s and releases his foot from the accelerator pedal.... Problem 26P: 26. * A car skids 18 m on a level road while trying to stop before hitting a stopped car in front of... Problem 27P: s mass is m. An average friction force of magnitude f opposes her motion. She starts down the slide... Problem 28P Problem 29P Problem 30P: 30. In a popular new hockey game, the players use small launchers with springs to move the 0.0030-kg... Problem 31P: 31. The top of a descending ski slope is 50 m higher than the bottom of the slope. A 60-kg skier... Problem 32P: * If 20% of the gravitational potential energy change of the skier in the previous problem is... Problem 33P Problem 34P: 34. A driver loses control of a car, drives off an embankment, and lands in a canyon 6.0 m below.... Problem 35P: * You are pulling a box so it moves at increasing speed. Compare the work you need to do to... Problem 36P: s speed increases from zero to 4.0 m/s in a vertical distance of 6.0 m. What is the force that the... Problem 37P: 37. ** EST Hit by a hailstone A 0.030-kg hailstone the size of a golf ball (4.3 cm in diameter) is... Problem 38P: 38. * BIO Froghopper jump Froghoppers may be the insect jumping champs. These 6-mm-long bugs can... Problem 39P: 39. * Bar chart Jeopardy 1 Describe in words and with a sketch a process that is consistent with the... Problem 40P: * Bar chart Jeopardy 2 Describe in words and with a sketch a process that is consistent with the... Problem 41P: 41. * Equation Jeopardy 1 Construct a qualitative work-energy bar chart for a process that is... Problem 42P: * Equation Jeopardy 2 Construct a qualitative work-energy bar chart for a process that is consistent... Problem 43P Problem 44P: 44. * Evaluation 2 Your friend provides a solution to the following problem. Evaluate her solution.... Problem 45P: 45. A crab climbs up a vertical rock with a constant speed. Students Iris and Alden represent this... Problem 46P: 46 * Work-energy bar charts for a person going downstairs and upstairs are shown in Figure P7.46 .... Problem 47P Problem 48P: * A 1060-kg car moving west at 16 m/s collides with and locks onto a 1830-kg stationary car. (a)... Problem 49P: * You fire an 80-g arrow so that it is moving at 80 m/s when it hits and embeds in a 10-kg block... Problem 50P: 50. * You fire a 50-g arrow that moves at an unknown speed. It hits and embeds in a 350-g block that... Problem 51P: * To confirm the results of Problem 7.50, you try a new experiment. The 50-g arrow is launched in an... Problem 52P: 52. * Somebody tells you that Figure P7.52 shows a displacement-versus-time graph of two carts on a... Problem 54P: 54. A roofing shingle elevator is lifting a 10.0-kg package to the top of a building at constant... Problem 55P: 55. (a) What is the power involved in lifting a 1.0-kg object 1.0 m in 1.0 s? (b) While lifting a... Problem 56P: * A fire engine must lift 30 kg of water a vertical distance of 20 m each second. What is the amount... Problem 57P: * BIO Internal energy change while biking You set your stationary bike on a high 80-N friction-like... Problem 58P: * Climbing Mt. Mitchell An 82-kg hiker climbs to the summit of Mount Mitchell in western North... Problem 59P: * BIO EST Sears stair climb The fastest time for the Sears Tower (now Willis Tower) stair climb (103... Problem 60P: * BIO EST Exercising so you can eat ice cream You curl a 5.5-kg (12 lb) dumbbell that is hanging... Problem 61P: 61. ** BIO Salmon move upstream In the past, salmon would swim more than 1130 km (700 mi) to spawn... Problem 62P: * EST Estimate the maximum horsepower of the process of raising your body mass as fast as possible... Problem 63P Problem 64P: At what distance from Earth is the gravitational potential energy of a spaceship- Earth system... Problem 65P:
65. * Possible escape of different air molecule types (a) Determine the ratio of escape speeds from... Problem 66P: Determine the escape speed for a rocket to leave Earths Moon. Problem 67P: Determine the escape speed for an object to leave the solar system if it starts at Earths distance... Problem 68P: If the Sun were to become a black hole, how much would it increase the gravitational potential... Problem 69P: * A satellite moves in elliptical orbit around Earth, which is one of the foci of the elliptical... Problem 70P: 70. * Determine the maximum radius Earth's Moon would have to have in order for it to be a black... Problem 71GP: 71. You throw a clay ball vertically upward. The ball hits the ceiling and sticks to it. Let the... Problem 72GP Problem 73GP Problem 74GP: 74 * EST A “gravity force car” is powered by the force exerted by Earth on an object of mass M. The... Problem 75GP: * Loop the loop You are given a loop raceway for your Hot Wheels cars (as shown in Figure P7.75).... Problem 76GP: 76. ** Atwood machine Two blocks of masses hang at the ends of a string that passes over a very... Problem 77GP: andm2 are connected with a string that passes over a very light pulley (see Figure P7.77). Friction... Problem 78GP: of all species became extinct, ending the reign of dinosaurs and opening the way for mammals to... Problem 79GP: s cradle is a toy that consists of several metal balls touching each other and suspended on strings... Problem 81GP: 81. ** Six Flags roller coaster A loop-the-loop on the Six Flags Shockwave roller coaster has a 10-m... Problem 82GP: ** Designing a ride You are asked to help design a new type of loop-the-loop ride. Instead of... Problem 83RPP: BIO Metabolic rate Energy for our activities is provided by the chemical energy of the foods we eat.... Problem 84RPP: BIO Metabolic rate Energy for our activities is provided by the chemical energy of the foods we eat.... Problem 85RPP: BIO Metabolic rate Energy for our activities is provided by the chemical energy of the foods we eat.... Problem 86RPP: BIO Metabolic rate Energy for our activities is provided by the chemical energy of the foods we eat.... Problem 87RPP: BIO Metabolic rate Energy for our activities is provided by the chemical energy of the foods we eat.... Problem 89RPP:
BIO Kangaroo hopping Hopping is an efficient method of locomotion for the kangaroo (see Figure... Problem 90RPP: BIO Kangaroo hopping Hopping is an efficient method of locomotion for the kangaroo (see Figure 7.18... Problem 91RPP: BIO Kangaroo hopping Hopping is an efficient method of locomotion for the kangaroo (see Figure... Problem 92RPP: BIO Kangaroo hopping Hopping is an efficient method of locomotion for the kangaroo (see Figure... Problem 93RPP: BIO Kangaroo hopping Hopping is an efficient method of locomotion for the kangaroo (see Figure... Problem 94RPP: BIO Kangaroo hopping Hopping is an efficient method of locomotion for the kangaroo (see Figure... format_list_bulleted


 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning




