
PHYSICS F/SCI.+ENGINEERS W/MOD.PHYSICS
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780321992277
Author: GIANCOLI
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 7, Problem 38P
(II) If the hill in Example 7–2 (Fig. 7–4) was not an even slope hut rather an irregular curve as in Fig. 7–23, show that the same result would be obtained as in Example 7–2: namely, that the work done by gravity depends only on the height of the hill and not on its shape or the path taken.
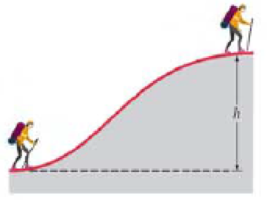
FIGURE 7-23
Problem 36.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule03:40
Students have asked these similar questions
If a proton is located on the x-axis in some coordinate system at x0 = -3.2 x 10-5 meters, what is the x-component of the Electric Field due to this proton at a position x = +3.2 x 10-5 meters and on the x axis as the y-axis is 0 giving a number of Newtons/Coulomb?
Consider a single square loop of wire of area A carrying a current I in a uniform magnetic field
of strength B. The field is pointing directly up the page in the plane of the page. The loop is
oriented so that the plane of the loop is perpendicular to the plane of the page (this means that the
normal vector for the loop is always in the plane of the page!). In the illustrations below the
magnetic field is shown in red and the current through the current loop is shown in blue. The
loop starts out in orientation (i) and rotates clockwise, through
orientations (ii) through (viii)
before returning to (i).
(i)
Ø I N - - I N -
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
(vii)
(viii)
a) [3 points] For each of the eight configurations, draw in the magnetic dipole moment vector
μ of the current loop and indicate whether the torque on the dipole due to the magnetic field
is clockwise (CW), counterclockwise (CCW), or zero. In which two orientations will the
loop experience the maximum magnitude of torque?
[Hint: Use the…
Please help with calculating the impusle, thanks!
Having calculated the impact and rebound velocities of the ping pong ball and the tennis ball calculate the rebounding impulse:
1.Measure the weight of the balls and determine their mass.
Tennis ball: 0.57 kg Ping Pong Ball: 0.00246 kg
The impulse, I, is equal to the change in momentum, Pf-Pi. Note the sign change, i.e., going down is negative and up is positive. The unit for momentum is kg-m/s. The change is momentum, impulse, is often givens the equivalent unit of N-S, Newton-Second
Chapter 7 Solutions
PHYSICS F/SCI.+ENGINEERS W/MOD.PHYSICS
Ch. 7.1 - A box is dragged a distance d across a floor by a...Ch. 7.1 - Return to the Chapter-Opening Question, page 163,...Ch. 7.4 - (a) Make a guess: will the work needed to...Ch. 7.4 - Can kinetic energy ever be negative?Ch. 7.4 - Prob. 1EECh. 7 - In what ways is the word work as used in everyday...Ch. 7 - A woman swimming upstream is not moving with...Ch. 7 - Can a centripetal force ever do work on an object?...Ch. 7 - Why is it tiring to push hard against a solid wall...Ch. 7 - Does the scalar product of two vectors depend on...
Ch. 7 - Can a dot product ever he negative? If yes, under...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7QCh. 7 - Does the dot product of two vectors have direction...Ch. 7 - Can the normal force on an object ever do work?...Ch. 7 - You have two springs that are identical except...Ch. 7 - Prob. 11QCh. 7 - In Example 710, it was stated that the block...Ch. 7 - Does the net work done on a particle depend on the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 2MCQCh. 7 - Prob. 3MCQCh. 7 - Prob. 5MCQCh. 7 - Prob. 7MCQCh. 7 - Prob. 8MCQCh. 7 - Prob. 9MCQCh. 7 - Prob. 10MCQCh. 7 - Prob. 12MCQCh. 7 - Prob. 13MCQCh. 7 - Prob. 14MCQCh. 7 - (I) How much work is done by the gravitational...Ch. 7 - (I) How high will a 1.85-kg rock go if thrown...Ch. 7 - (I) A 75.0-kg firefighter climbs a flight of...Ch. 7 - (I) A hammerhead with a mass of 2.0 kg is allowed...Ch. 7 - Prob. 5PCh. 7 - Prob. 6PCh. 7 - Prob. 7PCh. 7 - Prob. 8PCh. 7 - (II) Estimate the work you do to mow a lawn 10 m...Ch. 7 - Prob. 10PCh. 7 - (II) A lever such as that shown in Fig. 720 can be...Ch. 7 - Prob. 12PCh. 7 - Prob. 13PCh. 7 - Prob. 14PCh. 7 - Prob. 15PCh. 7 - Prob. 16PCh. 7 - Prob. 17PCh. 7 - Prob. 18PCh. 7 - (I) For any vector V=Vxi+Vyj+Vzk show that...Ch. 7 - Prob. 20PCh. 7 - Prob. 21PCh. 7 - Prob. 22PCh. 7 - Prob. 23PCh. 7 - (II) A constant force F=(2.0i+4.0j)N acts on an...Ch. 7 - Prob. 25PCh. 7 - Prob. 26PCh. 7 - (II) Show that if two nonparallel vectors have the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 28PCh. 7 - Prob. 29PCh. 7 - Prob. 30PCh. 7 - Prob. 31PCh. 7 - Prob. 32PCh. 7 - Prob. 33PCh. 7 - Prob. 34PCh. 7 - Prob. 35PCh. 7 - Prob. 36PCh. 7 - Prob. 37PCh. 7 - (II) If the hill in Example 72 (Fig. 74) was not...Ch. 7 - (II) The net force exerted on a particle acts in...Ch. 7 - Prob. 40PCh. 7 - (II) The force on a particle, acting along the x...Ch. 7 - Prob. 42PCh. 7 - Prob. 43PCh. 7 - (II) At the top of a pole vault, and athlete...Ch. 7 - Prob. 45PCh. 7 - Prob. 46PCh. 7 - (II) If it requires 5.0 J of work to stretch a...Ch. 7 - (II) An object, moving along the circumference of...Ch. 7 - Prob. 49PCh. 7 - Prob. 50PCh. 7 - Prob. 51PCh. 7 - Prob. 52PCh. 7 - (III) A 3.0-m-long steel chain is stretched out...Ch. 7 - (I) At room temperature, an oxygen molecule, with...Ch. 7 - (I) (a) If the kinetic energy of a particle is...Ch. 7 - Prob. 56PCh. 7 - Prob. 57PCh. 7 - Prob. 58PCh. 7 - Prob. 59PCh. 7 - (II) An 85-g arrow is fired from a bow whose...Ch. 7 - (II) If the speed of a car is increased by 50%, by...Ch. 7 - Prob. 62PCh. 7 - Prob. 63PCh. 7 - Prob. 64PCh. 7 - Prob. 65PCh. 7 - (II) (a) How much work is done by the horizontal...Ch. 7 - Prob. 67PCh. 7 - Prob. 68PCh. 7 - (II) A train is moving along a track with constant...Ch. 7 - Prob. 70PCh. 7 - Prob. 71PCh. 7 - Prob. 72PCh. 7 - Prob. 73PCh. 7 - Prob. 74GPCh. 7 - Prob. 75GPCh. 7 - Prob. 76GPCh. 7 - Prob. 77GPCh. 7 - Prob. 78GPCh. 7 - A varying force is given by F = Aekx, where x is...Ch. 7 - Prob. 80GPCh. 7 - A force F=(10.0i+9.0j+12.0k)kNacts on a small...Ch. 7 - Prob. 82GPCh. 7 - Prob. 83GPCh. 7 - Prob. 84GPCh. 7 - (III) We usually neglect the mass of a spring if...Ch. 7 - Prob. 86GPCh. 7 - Prob. 87GPCh. 7 - Prob. 88GPCh. 7 - Prob. 89GPCh. 7 - Prob. 90GPCh. 7 - Prob. 91GPCh. 7 - Assume a cyclist of weight mg can exert a force on...Ch. 7 - A car passenger buckles himself in with a seat...Ch. 7 - A simple pendulum consists of a small object of...Ch. 7 - Prob. 95GPCh. 7 - A small mass m hangs at rest from a vertical rope...Ch. 7 - Prob. 97GPCh. 7 - Prob. 98GPCh. 7 - Stretchable ropes ate used to safely arrest the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 100GP
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Heat lamps are commonly used to maintain foods at about 50C for as long as 12 hours in cafeteria serving lines....
Microbiology: An Introduction
Albinism in humans is inherited as a simple recessive trait. For the following families, determine the genotype...
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. In which of the following objects does...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
If someone at the other end of a room smokes a cigarette, you may breathe in some smoke. The movement of smoke ...
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
4. Three groups of nonvascular plants are _______, ______, and _______. Three groups of seedless vascular plant...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
If a compound has a molecular ion with an odd-numbered mass, then the compound contains an odd number of nitrog...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 5. Three blocks, each with mass m, are connected by strings and are pulled to the right along the surface of a frictionless table with a constant force of magnitude F. The tensions in the strings connecting the masses are T1 and T2 as shown. m T1 T2 F m m How does the magnitude of tension T₁ compare to F? A) T₁ = F B) T₁ = (1/2)F C) T₁ = (1/3)F D) T₁ = 2F E) T₁ = 3Farrow_forwardUsing Coulombs Law, what is the magnitude of the electrical force between two protons located 1 meter apart from each other in Newtons?arrow_forwardCalculate the magnitude of the gravitational force between 2 protons located 1 meter apart from each other in Newtons using Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation.arrow_forward
- If the metal sphere on the Van de Graff has a charge of 0.14 Coulombs and the person has a mass of 62 kg, how much excess charge would the person need in order to levitate at a distance 25 cm from the center of the charged metal sphere if there is a distance 25 cm from the person to the sphere using Coulomb's Law to calculate the electrical force. Give your answer as the number of Coulombs (with no unit label, as usual).arrow_forwardA balloon is rubbed on a sweater, giving the balloon a negative charge by adding an extra 3.9 x 107 electrons compared to its neutral state. What is the magnitude of the net charge on the balloon, in Coulombs?arrow_forwardA ping pong ball and a tennis ball are dropped and there is a very small gap between them when the tennis ball hits the floor. Indicate the directions of the momentums of the ping pong ball and the tennis ball after the tennis ball collides with the floor, but before the balls collide with each other. (Drawing a diagram may be helpful.)arrow_forward
- Describe how the momentum of a single ball changes as it free falls from a height of approximately 1 m, collides with a hard floor, and rebounds.arrow_forwardIf the answer is 2.8, -2.8 or -8.4, it is not CORRECTarrow_forwardThree blocks, light connecting ropes, and a light frictionless pulley comprise a system, as shown in the figure. An external force of magnitude P is applied downward on block A, causing block A to accelerate downward at a constant 2.5 m/s2. The tension in the rope connecting block B and block C is equal to 60 N. (a) What is the magnitude of the force P? (b) What is the mass of block C?arrow_forward
- Current Attempt in Progress In the figure what is the net electric potential at point P due to the four particles if V = 0 at infinity, q = 2.12 fC, and d = 1.75 cm? d Number MI Units +qarrow_forwardCurrent Attempt in Progress In the figure what is the net electric potential at point P due to the four particles if V = 0 at infinity, q = 2.12 fC, and d = 1.75 cm? d Number MI Units +qarrow_forwardA 0.500 kg sphere moving with a velocity given by (2.00î – 2.60ĵ + 1.00k) m/s strikes another sphere of mass 1.50 kg moving with an initial velocity of (−1.00î + 2.00ĵ – 3.20k) m/s. (a) The velocity of the 0.500 kg sphere after the collision is (-0.90î + 3.00ĵ − 8.00k) m/s. Find the final velocity of the 1.50 kg sphere. R = m/s Identify the kind of collision (elastic, inelastic, or perfectly inelastic). ○ elastic O inelastic O perfectly inelastic (b) Now assume the velocity of the 0.500 kg sphere after the collision is (-0.250 + 0.850ĵ - 2.15k) m/s. Find the final velocity of the 1.50 kg sphere. ✓ = m/s Identify the kind of collision. O elastic O inelastic O perfectly inelastic (c) Take the velocity of the 0.500 kg sphere after the collision as (−1.00ỉ + 3.40] + ak) m/s. Find the value of a and the velocity of the 1.50 kg sphere after an elastic collision. (Two values of a are possible, a positive value and a negative value. Report each with their corresponding final velocities.) a…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College
Mechanical work done (GCSE Physics); Author: Dr de Bruin's Classroom;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OapgRhYDMvw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY