
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Based on the structure given, the different types of stereoisomers for each of the conditions given are to be identified.
Concept introduction:
A chiral carbon atom is attached to four different atoms or groups of atoms. The number of stereoisomers is determined by using the formula
Stereoisomers arise from chiral centers as well as the arrangement of atoms or groups attached to the double bonded carbon atoms.
The pair of isomers designated
Enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images of each other.
Stereoisomers that are not mirror images are diastereomers.
Answer to Problem 35P
Solution:
a) The number of stereoisomers represented by the given constitution is
b) If the substituents on the five-membered ring are cis to each other, then there are four stereoisomers represented by the given constitution.
c) If the butenyl side chain has the Z configuration of its double bond, the given constitutional isomer has four possible stereoisomers.
d) Stereochemically accurate representations of all the stereoisomers are as follows:
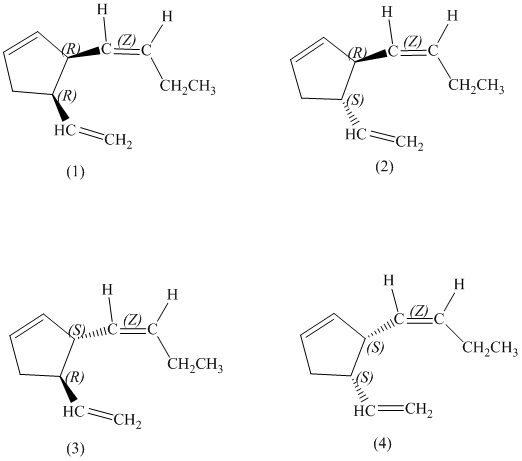
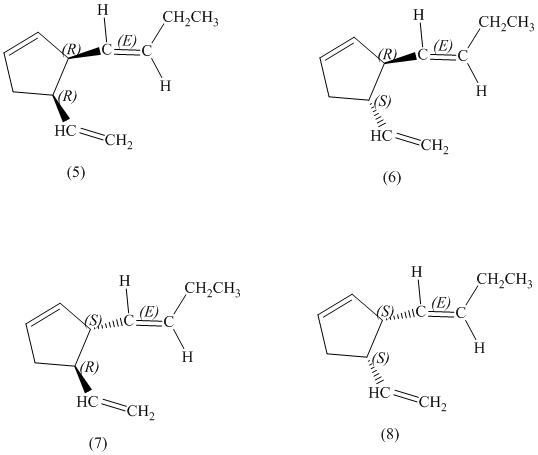
e) The pairs of enantiomers are as follows:
The pairs of diastereomers are as follows:
Explanation of Solution
a)
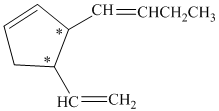
In the given structure, there are two chiral carbon atoms indicated by
Also, the double bond of butenyl side chain can form E and Z isomers, so the total number of possible stereoisomers will be:
Therefore, the number of stereoisomers represented by the given constitution is
b)
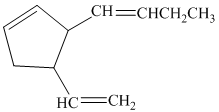
So, if the substituents on the five-membered ring are cis to each other, then the double bond in the butenyl side chain can be in the E or Z form. Thus, there are
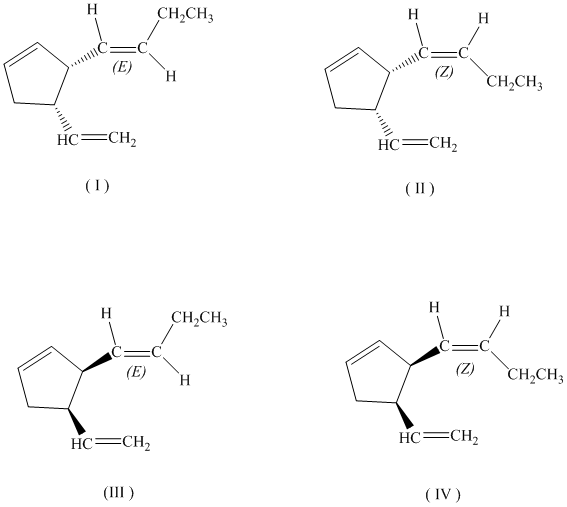
c)

If the butenyl side chain has the Z configuration of its double bond, the two substituents on the ring can be oriented in four different ways. The number of possible stereoisomers is
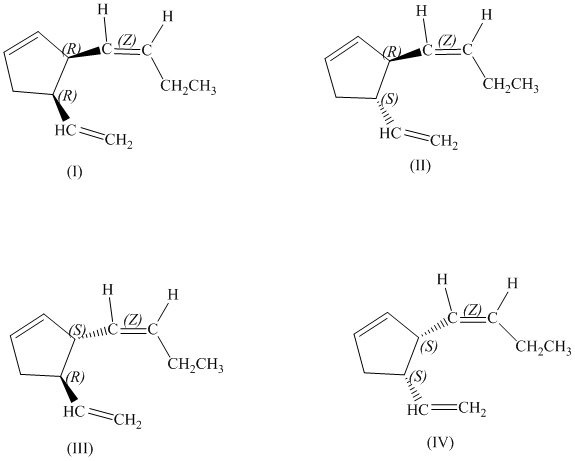
d)

There are total
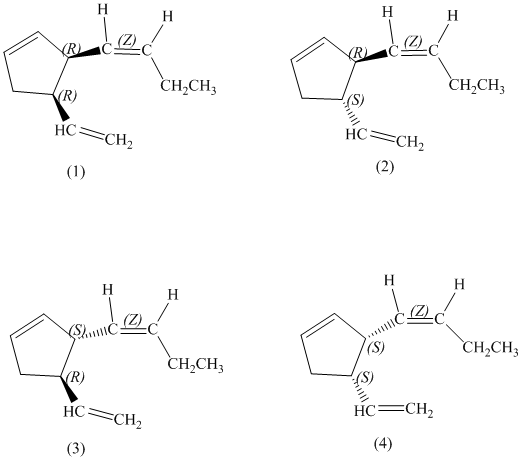
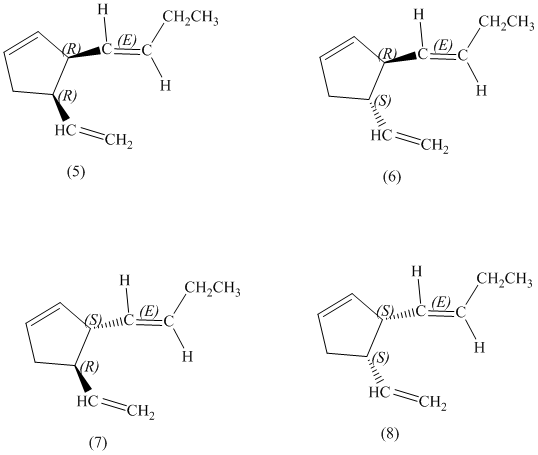
e)
Enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. Diastereomers are the stereoisomers which are not mirror images.
The pairs of enantiomers are as follows:
The pairs of diastereomers are as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-W/STUD.SOLN.MAN.
- Determine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forward
- Can I please get help with identifying these?arrow_forward4. Calculate the pH of a 0.10 M acetic acid (CH3COOH) solution if the Ka of acetic acid = 1.8 x 10-5arrow_forwardDraw the Zaitsev product of the dehydration of this alcohol. + I X 5 OH ざ~ TSOH Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

