
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series in Finance, Insurance, and Real Estate)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780077861759
Author: Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan Professor
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 7, Problem 25QP
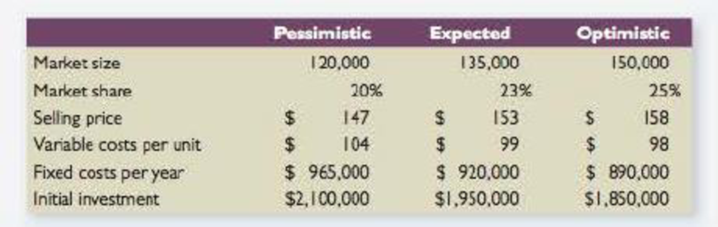
Scenario Analysis You are the financial analyst for a tennis racket manufacturer. The company is considering using a graphitelike material in its tennis rackets. The company has estimated the information in the following table about the market for a racket with the new material. The company expects to sell the racket for six years. The equipment required for the project has no salvage value. The required return for projects of this type is 13 percent, and the company has a 40 percent tax rate. Should you recommend the project?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
<
When you purchased your car, you took out a 5-year annual-payment loan with an interest rate of 5% per year. The annual payment on the car is $5,200. You have just made a payment and have now decided to
pay off the loan by repaying the outstanding balance. What is the payoff amount for the following scenarios?
a. You have owned the car for 1 year (so there are 4 years left on the loan)?
b. You have owned the car for 4 years (so there is 1 year left on the loan)?
a. You have owned the car for 1 year (so there are 4 years left on the loan)?
The payoff if there are 4 years left on the loan is $
(Round to the nearest cent.)
b. You have owned the car for 4 years (so there is 1 year left on the loan)?
The payoff if there is 1 year left on the loan is $
(Round to the nearest cent.)
Victoria Exports (Canada). A Canadian exporter, Victoria Exports, will be receiving six payments of €13,800, ranging from now to 12 months in the future. Since the company keeps cash balances in both Canadian dollars
and U.S. dollars, it can choose which currency to exchange the euros for at the end of the various periods. Which currency appears to offer the better rates in the forward market? (Click on the icon to import the table into
a spreadsheet.)
Period
Days Forward
spot
1 month
C$/euro
1.3347
1.3370
US$/euro
1.3219
1.3224
m
2 months
3 months
1.3392
30
60
1.3229
90
1.3235
180
1.3438
12 months
360
1.3464
1.3239
1.3269
6 months
1.3416
Calculate the forward premium, the Canadian dollar proceeds, and the difference from the spot rate proceeds in the C$/Euro forward market below: (Round the forward premium to three decimal places and the Canadian
dollar amounts to the nearest cent.)
Days
Forward Premium
C$ Proceeds of
Difference
Period
Forward
C$/euro
on the C$/euro
€13,800
Over Spot…
identify the primary sources of financing, both traditional and alternative, accessible to companies seeking sources of funding. To do so, you should:
Collect and curate data and documentary resources from various sources (magazine articles, newspapers, online content, working papers from various institutions, activity reports, performance reports, legal regulations, speeches, appearances, press conferences, etc.).
Analyze the documentary content you have previously curated and collected. During your analysis, consider the context, location, timing, and target audience of the texts.
Reference Article: One Park Financial. (2022). Best alternative business loans and financing for entrepreneurs. https://www.oneparkfinancial.com/blog/alternative-business-funding
Questions:
Identify and summarize the traditional financial avenues available to businesses.
What are the most innovative financing options they could find?
Open-ended question: if you were in the opposite position, as an…
Chapter 7 Solutions
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series in Finance, Insurance, and Real Estate)
Ch. 7 - Forecasting Risk What is forecasting risk? In...Ch. 7 - Sensitivity Analysis and Scenario Analysis What is...Ch. 7 - Prob. 3CQCh. 7 - Break-Even Point As a shareholder of a firm that...Ch. 7 - Prob. 5CQCh. 7 - Real Options Why does traditional NPV analysis...Ch. 7 - Real Options The Mango Republic has just...Ch. 7 - Prob. 8CQCh. 7 - Prob. 9CQCh. 7 - Project Analysis You are discussing a project...
Ch. 7 - Sensitivity Analysis and Break-Even Point We are...Ch. 7 - Prob. 2QPCh. 7 - Prob. 3QPCh. 7 - Prob. 4QPCh. 7 - Prob. 5QPCh. 7 - Decision Trees Ang Electronics. Inc., has...Ch. 7 - Decision Trees The manager for a growing firm is...Ch. 7 - Prob. 8QPCh. 7 - Prob. 9QPCh. 7 - Financial Break-Even Niko has purchased a brand...Ch. 7 - Prob. 11QPCh. 7 - Prob. 12QPCh. 7 - Project Analysis You are considering a new product...Ch. 7 - Project Analysis McGilla Golf has decided to sell...Ch. 7 - Prob. 17QPCh. 7 - Prob. 18QPCh. 7 - Prob. 19QPCh. 7 - Prob. 20QPCh. 7 - Prob. 21QPCh. 7 - Option to Wait Hickock Mining is evaluating when...Ch. 7 - Abandonment Decisions Allied Products, Inc., is...Ch. 7 - Prob. 24QPCh. 7 - Scenario Analysis You are the financial analyst...Ch. 7 - Scenario Analysis Consider a project to supply...Ch. 7 - Sensitivity Analysis In Problem 26, suppose youre...Ch. 7 - Prob. 28QPCh. 7 - Prob. 29QPCh. 7 - Financial Break-Even The Cornchopper Company is...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- XYZ stock price and dividend history are as follows: Beginning-of- $ 130 Dividend Paid at Year Year Price Year-End 2021 $ 2 2022 2023 153 2 2024 128 133 2 2 An investor buys five shares of XYZ at the beginning of 2021, buys another two shares at the beginning of 2022, sells one share at the beginning of 2023, and sells all six remaining shares at the beginning of 2024. Required: a. What are the arithmetic and geometric average time-weighted rates of return for the investor? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places. Arithmetic time-weighted average returns Geometric time-weighted average returns % % b-1. Prepare a chart of cash flows for the four dates corresponding to the turns of the year for January 1, 2021, to January 1, 2024. Note: Negative amounts should be indicated by a minus sign. Date 01/01/2021 01/01/2022 Cash Flow 01/01/2023 01/01/2024 b-2. What is the dollar-weighted rate of return? (Hint. If your calculator cannot calculate…arrow_forwardConsider the following two banks: Bank 1 has assets composed solely of a 10-year, 11.50 percent coupon, $1.5 million loan with a 11.50 percent yield to maturity. It is financed with a 10-year, 10 percent coupon, $1.5 million CD with a 10 percent yield to maturity. Bank 2 has assets composed solely of a 7-year, 11.50 percent, zero-coupon bond with a current value of $1,108,283.85 and a maturity value of $2,374,515.87. It is financed with a 10-year, 5.75 percent coupon, $1,500,000 face value CD with a yield to maturity of 10 percent. All securities except the zero-coupon bond pay interest annually. a. If interest rates rise by 1 percent (100 basis points), what is the difference in the value of the assets and liabilities of each bank? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Negative amounts should be indicated by a minus sign. Enter the answers in dollars, not millions of dollars. Round your answers to 2 decimal places. (e.g., 32.16) Before Interest Asset Value After Interest…arrow_forwardTIME TO REACH A FINANCIAL GOAL You have $42,180.53 in a brokerage account, and you plan to deposit an additional $5,000 at the end of every future year until your account totals $250,000. You expect to earn 12% annually on the account. How many years will it take to reach your goal? Round UP to the nearest year. (Example 5.01 years = 6 years) Your answer should include numerical value only.arrow_forward
- You plan to retire in 30 years. • In 50 years, you want to give your daughter a $500,000 gift. • You will receive an inheritance of $200,000 in 25 years. • You think you will want $50,000 per year when you retire for 30 years (the first withdrawal will come one year after retirement). • You will begin saving an amount to meet your retirement goals one year from today. Required: • If you think you can make 9% on your investments, how much will you need to save each year for the next 30 years to meet your retirement goals?arrow_forwardAn initial $3300 investment was worth $3820 after two years and six months. What quarterly compounded nominal rate of return did the investment earn? (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your final answer to 2 decimal places.) Nominal rate of return % compounded quarterly.arrow_forwardSuppose your firm is considering investing in a project with the cash flows shown below, that the required rate of return on projects of this risk class is 9 percent, and that the maximum allowable payback and discounted payback statistics for the project are 2.0 and 3.0 years, respectively.arrow_forward
- Please don't use Ai solutionarrow_forwardng Equipment is worth $998,454. It is expected to produce regular cash flows of $78,377 per year for 20 years and a special cash flow of $34,800 in 20 years. The cost of capital is X percent per year and the first regular cash flow will be produced in 1 year. What is X? Input instructions: Input your answer as the number that appears before the percentage sign. For example, enter 9.86 for 9.86% (do not enter .0986 or 9.86%). Round your answer to at least 2 decimal places. percentarrow_forward3 years ago, you invested $6,700. In 5 years, you expect to have $12,201. If you expect to earn the same annual return after 5 years from today as the annual return implied from the past and expected values given in the problem, then in how many years from today do you expect to have $25,254?arrow_forward
- 4 years ago, you invested $3,600. In 2 years, you expect to have $7,201. If you expect to earn the same annual return after 2 years from today as the annual return implied from the past and expected values given in the problem, then in how many years from today do you expect to have $10,022? Input instructions: Round your answer to at least 2 decimal places. yearsarrow_forwardSince ROE can sometimes be boosted artificially through financial leverage, do you think it would be more beneficial for investors to rely on a combination of ROE and other financial health indicators, such as the debt-to-equity ratio or interest coverage ratio, when assessing a stock's long-term potential?arrow_forwardGiven that Merck and Pfizer both face revenue risks from patent expirations, how do you think financial managers at these companies should adjust their capital structure to maintain stability and investor confidence?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College

Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...
Accounting
ISBN:9781305970663
Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. Mowen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:9781337514835
Author:MOYER
Publisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Excel Applications for Accounting Principles
Accounting
ISBN:9781111581565
Author:Gaylord N. Smith
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395083
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:9781947172609
Author:OpenStax
Publisher:OpenStax College
Capital Budgeting Introduction & Calculations Step-by-Step -PV, FV, NPV, IRR, Payback, Simple R of R; Author: Accounting Step by Step;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hyBw-NnAkHY;License: Standard Youtube License