
Concept explainers
a.
Indicate the event that affects the
a.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: Income statement is a financial statement that shows the net income or net loss by deducting the expenses from the revenues and vice versa.
Balance Sheet: Balance sheet summarizes the assets, the liabilities, and the
Statement of cash flows: The financial statement that shows the changes in cash flows from operating, investing, and financing activities is referred to as statement of cash flows.
Indicate the event that affects the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows and also indicate whether the increases (+), decreases (-), or does not affect (NA) for each element of the financial statements as follows:
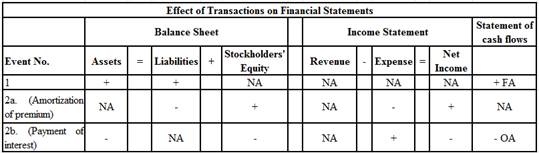
Table (1)
b.
Ascertain the carrying value (face value less discount or plus premium) of the bond liability as of December 31, 2018.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Bonds: Bonds are a kind of interest bearing notes payable, usually issued by companies, universities and governmental organizations. It is a debt instrument used for the purpose of raising fund of the corporations or governmental agencies. If selling price of the bond is equal to its face value, it is called as par on bond. If selling price of the bond is lesser than the face value, it is known as discount on bond. If selling price of the bond is greater than the face value, it is known as premium on bond.
Straight-line amortization bond:
Ascertain the carrying value (face value less discount or plus premium) of the bond liability as of December 31, 2018:
| Particulars | $ |
| Bonds payable | 200,000 |
| Add: Premium on bonds payable | 3,600 |
| Carrying value of the bond at December 31, Year 1 | 203,600 |
Table (2)
Therefore, the carrying value of the bond at December 31, 2018 is $203,600.
Working notes:
Calculate the premium rate.
Calculate the value of premium.
Calculate bond premium amortized during 2018.
Calculate the premium on bonds payable at the end of 2018.
c.
Calculate the amount of interest expense reported on the 2018 income statement.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the interest expense reported on the 2018 income statement.
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Interest expense | 12,000 |
| Less: Bond premium amortized during 2018 | 400 |
| Interest expense paid in 2018 | 11,600 |
Table (3)
Therefore, the interest expense reported on the 2018 income statement is $11,600.
Working note:
Calculate the value of interest expense
d.
Ascertain the carrying value of the bond liability as of December 31, 2019.
d.
Explanation of Solution
Ascertain the carrying value of the bond liability as of December 31, 2019.
| Particulars | $ |
| Bonds payable | 200,000 |
| Add: Premium on bonds payable | 3,200 |
| Carrying value of the bond at December 31, Year 2 | 203,200 |
Table (4)
Therefore, the carrying value of the bond liability as of December 31, 2019 is $203,200.
Working note:
Calculate bond premium amortized during 2018.
Calculate the premium on bonds payable at the end of the 2019.
e.
Calculate the amount of interest expense reported on the 2019 income statement.
e.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the interest expense reported on the 2018 income statement.
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Interest expense | 12,000 |
| Less: Bond premium amortized during 2019 | 400 |
| Interest expense paid in 2019 | 11,600 |
Table (5)
Therefore, the interest expense reported on the 2019 income statement is $11,600.
Working note:
Calculate the value of interest expense
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
SURVEY OF ACCOUNT.(LL)-W/ACCESS>CUSTOM<
- A new production equipment with a purchase price of $125,000, freight costs of $12,500, setup costs of $8,500, and testing fees of $4,000, would have a cost basis of what?arrow_forwardPlease explain the solution to this general accounting problem using the correct accounting principles.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- Vampire Co. reports total sales of $610,000. Variable costs are 58% of sales, and fixed costs are $135,000. What is the contribution margin ratio?(a) 42% (b) 46% (c) 40% (d) 44% (e) 48%arrow_forwardI need guidance with this general accounting problem using the right accounting principles.arrow_forwardAt the beginning of the year, Evergreen Corporation has assets of $250,000 and equity of $180,000. During the year, assets increase by $90,000, and liabilities increase by $40,000. What is the equity at the end of the year?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781285866307Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781285866307Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305653535Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Corporate Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305653535Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Accounting (Text Only)AccountingISBN:9781285743615Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Accounting (Text Only)AccountingISBN:9781285743615Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





