
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The term “acid” should be defined by giving an example.
Concept Introduction:
The chemical properties of an acid and a base are different from each other because both are chemically opposite. Acid and base reacts with each other to form water and salt. The reaction is known as neutralization reaction. In aqueous solution, acid gives hydrogen ion/s 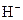 and base gives hydroxide ion/s
and base gives hydroxide ion/s 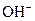 these positive and negative ions combined to form H2O and affect the concentration of aqueous solution.
these positive and negative ions combined to form H2O and affect the concentration of aqueous solution.
(a)
Answer to Problem 1RQ
Solution:
A compound that gives H+ ion/s in the aqueous solution and turns litmus indicator dye to red is termed as an acid. For example: Hydrogen chloride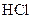
Explanation of Solution
An acid is a compound with some particular properties such as sour in taste and its reaction with base results in the formation of salt and water. It turns litmus indicator dye to red. On reaction with metals, hydrogen gas H2 is released. They also produce H+ ion/s in aqueous solution.
Example of an acid is hydrogen chloride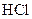 It is a strong acid and completely dissociates into H+ and
It is a strong acid and completely dissociates into H+ and 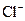 ions in the aqueous solution.
ions in the aqueous solution.
Hydrogen chloride is an acid because it gives H+ ion in the aqueous solution. Also, it turns litmus indicator dye to red. On reaction with metals such as zinc and iron it produces H2 gas.
(b)
Interpretation:
The term “base” should be defined by giving an example.
Concept Introduction:
The chemical properties of an acid and a base are different from each other because both are chemically opposite. Acid and base reacts with each other to form water and salt. The reaction is known as neutralization reaction. In aqueous solution, acid gives hydrogen ion/s 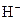 and base gives hydroxide ion/s
and base gives hydroxide ion/s 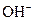 these positive and negative ions combined to form H2O and affect the concentration of aqueous solution.
these positive and negative ions combined to form H2O and affect the concentration of aqueous solution.
(b)
Answer to Problem 1RQ
Solution:
A compound that gives OH- ion/s in the aqueous solution and turns litmus indicator dye to blue is termed as a base. For example: Sodium hydroxide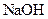
Explanation of Solution
A base is a compound with some particular properties such as bitter in taste and its reaction with acid results in the formation of salt and water. It turns litmus indicator dye to blue. It feels slippery on the skin. It produces OH- ion/s in the aqueous solution.
Example of a base is sodium hydroxide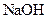 It is a strong base and completely dissociates into Na+ and
It is a strong base and completely dissociates into Na+ and 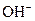 ions in the aqueous solution.
ions in the aqueous solution.
Sodium hydroxide is a base because it produces OH- ion in the aqueous solution. Also, it turns litmus indicator dye to blue. It reacts with acid to form salt and water.
(c)
Interpretation:
The term “salt” should be defined by giving an example.
Concept Introduction:
The chemical properties of an acid and a base are different from each other because both are chemically opposite. Acid and base reacts with each other to form water and salt. The reaction is known as neutralization reaction. In aqueous solution, acid gives hydrogen ion/s 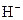 and base gives hydroxide ion/s
and base gives hydroxide ion/s 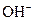 these positive and negative ions combined to form H2O and affect the concentration of aqueous solution.
these positive and negative ions combined to form H2O and affect the concentration of aqueous solution.
(c)
Answer to Problem 1RQ
Solution:
Salt is defined as an ionic compound formed from the reaction of an acid and a base. For example: sodium chloride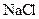 which is formed from the reaction of
which is formed from the reaction of 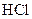 and
and 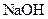 as follows:
as follows:
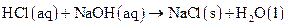
Explanation of Solution
If an acid reacts with a base, salt is formed. It is an ionic compound because it is made up of ions of acid and base. A salt is formed from neutralization reaction of an acid and a base therefore, it is neutral in nature.
For example: Sodium chloride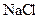 which is formed from the reaction of
which is formed from the reaction of 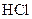 and
and 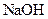 as follows:
as follows:
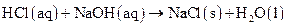
Thus, salt is an ionic compound such as sodium chloride which is formed from the reaction of 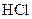 (acid) and
(acid) and 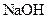 (base).
(base).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Chemistry For Changing Times (14th Edition)
- For the condensation reaction between Alamine and histamine, please help me write the amididation reaction mechanism. Then write the three letter code for the product of the reaction, then write the one letter code for the product of the reaction. arrow_forwardHow to draw the reaction mechasnism belowarrow_forwardName the following molecules with IUpacarrow_forward
- What is the molecular orbital for cyclopropenyl anion and is it aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic?arrow_forwardUsing the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid and its impact on the protein.arrow_forwardHow to get the predicted product of this reaction belowarrow_forward
- Please help me fill out the chart then using the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Then using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid.arrow_forwardWrite the Esterification reaction mechanism for acetic acid, and one propanol to make propanol ethanoate (molecule that gives peas its odor in flavor)arrow_forwardProvide solutionsarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





