
Concept explainers
Program plan:
- Declare a variable file of ifstream type to read the input from the file.
- Declare a variable letter of type char to store the letter read from the file.
- Declare 6 variables upperCounter, lowerCounter, blank, digit, punctuation, allElseCounter of type int to store the counter of each type.
- Declare a variable inFile of type String to store the name of the file read from the user.
- A do- while loop is used to read letters from the file and to increment the each type of counter.
- A switch is used to check for each type of letters and to increment the counter inside do-while loop.
Program description:
The main purpose of the program is to summarize all the contents of the file in a table with details of each type of character scanned.
Explanation of Solution
Program:
//inclusion of header files
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cctype>
//using namespace
using namespace std;
//main function
int main()
{
ifstream file; //fstream input
char letter;
// Declaration and Initialization of variables
int upperCounter = 0; // counter for uppercase letters
int lowerCounter = 0; // counter for lowercase letters
int blank = 0; // counter for blanks
int digit = 0; //counter for digits
int punctuation = 0; //counter for punctuation
int allElseCounter = 0; //counter for Remaining counters
//Declare variable to store filename
string inFile;
cout<<"Enter the filename to be processed" << endl;
cin>>inFile;
//open the file
file.open(inFile.c_str());
//if file doesn’t get opened
if (!file)
{
cout<< "Filename doesn’t exist." << endl;
return 1;
}
//else read the characters
file.get(letter); // Input one letter
do
// process each letter
{
if (isupper(letter))
upperCounter++;
else if (islower(letter))
lowerCounter++;
else if (isdigit(letter))
digit++;
else
switch (letter)
{
case ' ' : blank++;
break;
case '.' :
case '?' :
case '!' : punctuation++;
break;
default : allElseCounter++;
break;
}
file.get(letter);
} while (file);
// Calculate total
float total = upperCounter + lowerCounter + blank + digit + punctuation + allElseCounter;
cout<<"Summary of letters: "<< inFile << endl;
// Letters of each type
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(3)<<"Percentage of uppercase letters:"<<upperCounter / total* 100<<endl;
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(3)<< "Percentage of lowercase letters:" << lowerCounter / total * 100 << endl;
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(3)<< "Percentage of blanks: "<< blank / total * 100 << endl;
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(3)<< "Percentage of digits: "<< digit / total * 100 << endl;
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(3)<< "Percentage of end-of-sentence: "<< "punctuation "<< punctuation / total * 100 << endl;
return 0;
}
Explanation:
In this program, first of all, the user is asked to enter the filename which needs to be processed. After entering the filename, all the characters of it are scanned to get a summary table of each type of letters. Each letter is scanned for uppercase letters, lowercase letters, for digits, blanks, and for any puctuations. Each type counter get incremented if the letter scanned is of that type. For example, if the letter scanned is of uppercase then the counter for uppercase letters will get incremented and so on. In the end, complete summary of all types of letters is printed on the screen with the filename which is scanned as shown in the output.
Output:
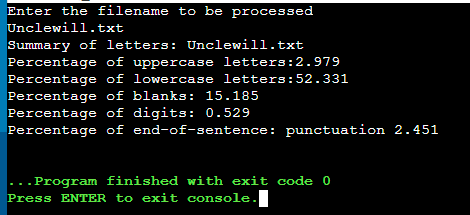
Contents of the file Unclewill.txt:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Programming and Problem Solving With C++
- using r language a continuous random variable X has density function f(x)=1/4x^3e^-(pi/2)^4,x>=0 derive the probability inverse transformation F^(-1)x where F(x) is the cdf of the random variable Xarrow_forwardusing r language in an accelerated failure test, components are operated under extreme conditions so that a substantial number will fail in a rather short time. in such a test involving two types of microships 600 chips manufactured by an existing process were tested and 125 of them failed then 800 chips manufactured by a new process were tested and 130 of them failed what is the 90%confidence interval for the difference between the proportions of failure for chips manufactured by two processes? using r languagearrow_forwardI want a picture of the tools and the pictures used Cisco Packet Tracer Smart Home Automation:o Connect a temperature sensor and a fan to a home gateway.o Configure the home gateway so that the fan is activated when the temperature exceedsa set threshold (e.g., 30°C).2. WiFi Network Configuration:o Set up a wireless LAN with a unique SSID.o Enable WPA2 encryption to secure the WiFi network.o Implement MAC address filtering to allow only specific clients to connect.3. WLC Configuration:o Deploy at least two wireless access points connected to a Wireless LAN Controller(WLC).o Configure the WLC to manage the APs, broadcast the configured SSID, and applyconsistent security settings across all APs.arrow_forward
- A. What will be printed executing the code above?B. What is the simplest way to set a variable of the class Full_Date to January 26 2020?C. Are there any empty constructors in this class Full_Date?a. If there is(are) in which code line(s)?b. If there is not, how would an empty constructor be? (create the code lines for it)D. Can the command std::cout << d1.m << std::endl; be included after line 28 withoutcausing an error?a. If it can, what will be printed?b. If it cannot, how could this command be fixed?arrow_forwardCisco Packet Tracer Smart Home Automation:o Connect a temperature sensor and a fan to a home gateway.o Configure the home gateway so that the fan is activated when the temperature exceedsa set threshold (e.g., 30°C).2. WiFi Network Configuration:o Set up a wireless LAN with a unique SSID.o Enable WPA2 encryption to secure the WiFi network.o Implement MAC address filtering to allow only specific clients to connect.3. WLC Configuration:o Deploy at least two wireless access points connected to a Wireless LAN Controller(WLC).o Configure the WLC to manage the APs, broadcast the configured SSID, and applyconsistent security settings across all APs.arrow_forwardTransform the TM below that accepts words over the alphabet Σ= {a, b} with an even number of a's and b's in order that the output tape head is positioned over the first letter of the input, if the word is accepted, and all letters a should be replaced by the letter x. For example, for the input aabbaa the tape and head at the end should be: [x]xbbxx z/z,R b/b,R F ① a/a,R b/b,R a/a, R a/a,R b/b.R K a/a,R L b/b,Rarrow_forward
- Given the C++ code below, create a TM that performs the same operation, i.e., given an input over the alphabet Σ= {a, b} it prints the number of letters b in binary. 1 #include 2 #include 3 4- int main() { std::cout > str; for (char c : str) { if (c == 'b') count++; 5 std::string str; 6 int count = 0; 7 char buffer [1000]; 8 9 10 11- 12 13 14 } 15 16- 17 18 19 } 20 21 22} std::string binary while (count > 0) { binary = std::to_string(count % 2) + binary; count /= 2; std::cout << binary << std::endl; return 0;arrow_forwardConsidering the CFG described below, answer the following questions. Σ = {a, b} • NT = {S} Productions: P1 S⇒aSa P2 P3 SbSb S⇒ a P4 S⇒ b A. List one sequence of productions that can accept the word abaaaba; B. Give three 5-letter words that can be accepted by this CFG; C. Create a Pushdown automaton capable of accepting the language accepted by this CFG.arrow_forwardGiven the FSA below, answer the following questions. b 1 3 a a b b с 2 A. Write a RegEx that is equivalent to this FSA as it is; B. Write a RegEx that is equivalent to this FSA removing the states and edges corresponding to the letter c. Note: To both items feel free to use any method you want, including analyzing which words are accepted by the FSA, to generate your RegEx.arrow_forward
- 3) Finite State Automata Given the FSA below, answer the following questions. a b a b 0 1 2 b b 3 A. Give three 4-letter words that can be accepted by this FSA; B. Give three 4-letter words that cannot be accepted by this FSA; C. How could you describe the words accepted by this FSA? D. Is this FSA deterministic or non-deterministic?arrow_forwardConsidering the TM below, answer the following questions. a/x,R €/E,L €/E,R €/E,L x/E,R c/c,R b/E.L c/c,L x/x,R I J K L M F b/E.L D A. Give three 4-letter words that can be accepted by this TM; B. Give three 4-letter words that cannot be accepted by this TM; C. How could you describe the words accepted by this TM? D. What is the alphabet of the language accepted by this TM?arrow_forwardWhat is the generator? Explain motor generator motorarrow_forward
 C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage LearningProgramming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage
Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage LearningProgramming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage Programming with Microsoft Visual Basic 2017Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102124Author:Diane ZakPublisher:Cengage Learning
Programming with Microsoft Visual Basic 2017Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102124Author:Diane ZakPublisher:Cengage Learning





