
Concept explainers
To state: The three main components of the immune system and match the given terms with the organs.
Introduction: A complex network of cells, tissues, and organs, which works together to protect the body and fight against pathogens or foreign substances are collectively known as the immune system.
Answer to Problem 1P
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 shows the parts of the immune system.
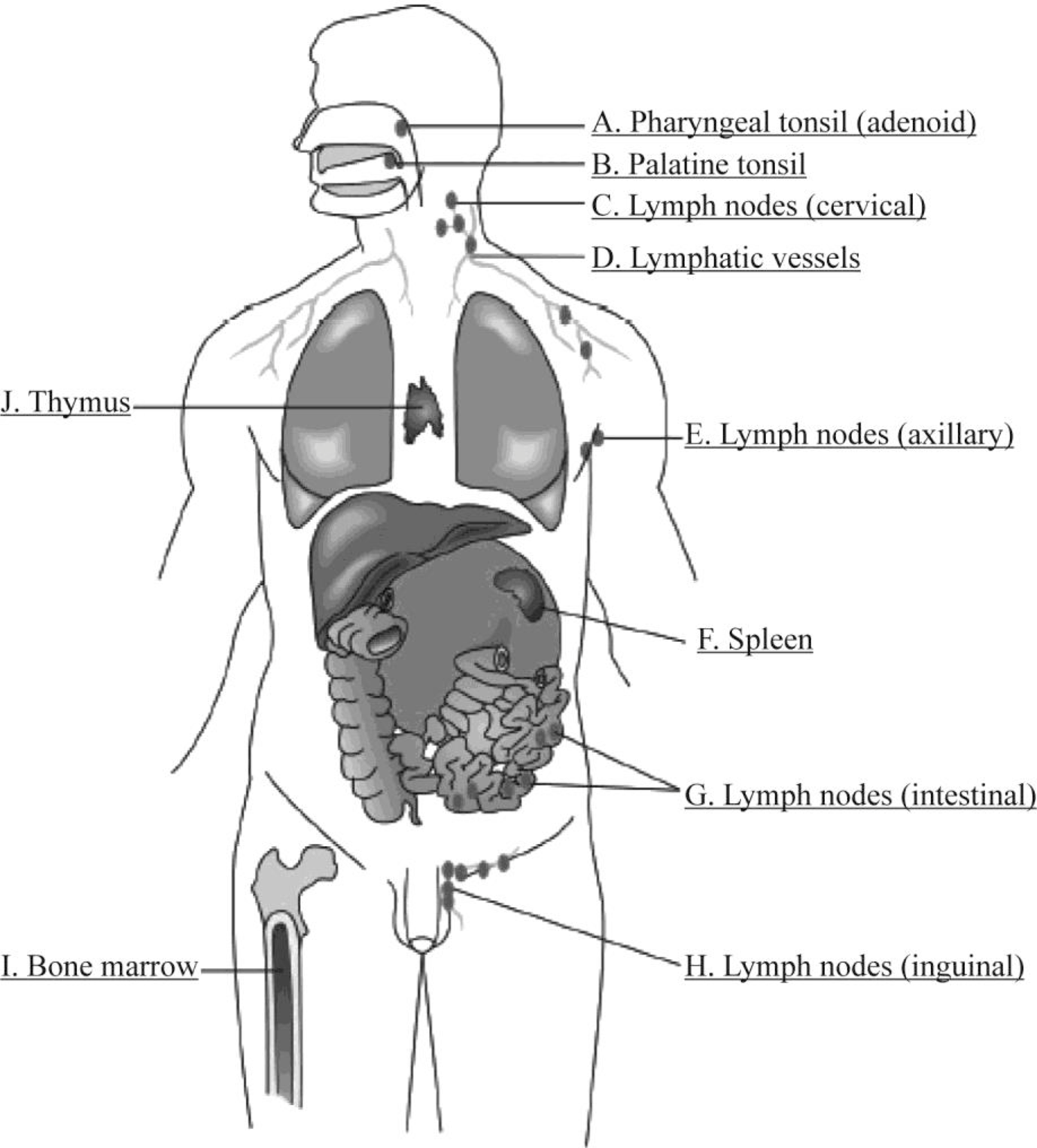
Fig.1: structures involved in immune system
Explanation of Solution
The three main components of the immune system are as follows:
- Lymphoid tissues (lymph nodes, tonsils, spleen, intestinal lymphoid tissue, and lymphatic circulation).
- Immune cells (macrophages and lymphocytes).
- Tissues concerned with immune cell development (bone marrow and thymus gland).
- A. Pharyngeal tonsil (adenoid)
The patch of lymphatic tissues present in the throat that is located behind the nasal cavity, in the roof of the nasopharynx is known as adenoids. It is also known as pharyngeal tonsil or nasopharyngeal tonsil. It functions by trapping the germs that enter through the nose and mouth.
- B. Palatine tonsil
Palatine tonsil is one among the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues that is located at the entrance of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory tract. It will protect the body from the exogenous material that enters through the mucosal sites. Palatine tonsils are located on the left and right sides at the back of the throat. They are occasionally called as faucial tonsils.
- C. Lymph nodes (cervical)
The lymph nodes are the secondary lymphoid organs present in the immune system. The lymph nodes are small glands that are situated throughout the body and are linked with the help of lymphatic vessels. These organs are the main sites of B and T lymphocytes. These organs act as a defense system. Cervical nodes are a group of lymph nodes, which are found in the neck region. Out of 800 lymph nodes, the neck region contains 300 lymph nodes. These lymph nodes can lead to various pathological conditions such as infection, tumors, and inflammation.
- D. Lymphatic vessels
The vessels of the lymphatic system reach most parts of the body and collect and return the interstitial body fluids with the blood. It comprises a fluid called lymph that contains waste products and cellular debris collected from the interstitial spaces of tissues. This fluid is taken to the secondary lymphoid organ called as lymph nodes.
- E. Lymph nodes (axillary)
Axillary nodes are located at the armpit (axillary) region of the body. These nodes are responsible for the lymphatic drainage of a large part of the human structure. They mainly perform the filtration and conduction of lymph from the upper back, pectoral region, and upper back.
- F. Spleen
The spleen is the secondary lymphoid organ. It is an organ that is present in the upper left part of the abdomen. It can serve as filters for the blood. The spleen can also help to fight against the bacteria causing meningitis and pneumonia.
- G. Lymph nodes (intestinal)
The intestinal lymph node also called as mesenteric nodes are present in the intestinal region. These types of nodes help to fight against the diseases in our body.
- H. Lymph nodes (inguinal)
Inguinal lymph nodes are the lymph nodes present in the groin (inguinal) region. These nodes are usually located below the inguinal ligament, which runs from the ilium's anterior superior iliac spine to the pubic bone's pubic tubercle. It is mainly classified as superficial lymph node and deep lymph node.
- I. Bone marrow
The spongy tissue called the bone marrow is present in the center of bones. This organ is an important site for the production of blood cells (hematopoiesis). It is the major site where B lymphocytes mature.
- J. Thymus
The thymus is the primary lymphoid organ. It is situated in the neck of vertebrates. Two identical lobes are found in the thymus. They are located in the anterior superior mediastinum, behind the sternum and in front of the heart. The thymus plays a fundamental role in the mechanism of immunity against infections. Before birth, they are the final site for the development of lymphocytes. It secretes hormones after birth, which facilitates the formation of mature T-lymphocytes. These T-lymphocytes help to attack the foreign cells and act as regulators for the immune system.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Professions
- what causes a variation in vital signs and how can we make adjustments?arrow_forwardAnalyze the traits that define a profession that nursing has attained?arrow_forwardHello, Can you help me please with the next case: Assessment (Recognizing Cues) Which client information is relevant? What client data is most important? Which client information is of immediate concern? Consider signs and symptoms, lab work, client statements, H & P, and others. Consider subjective and objective data. Analysis (Analyzing Cues) Which client conditions are consistent with the cues? Do the cues support a particular client condition? What cues are a cause for concern? What other information would help to establish the significance of a cue? Analysis (Prioritizing Hypotheses) What explanations are most likely? What is the most serious explanation? What is the priority order for safe and effective care? In order of priority, identify the top 3 client conditions. Thank you in advnce!arrow_forward
- Adult Case 1: Day 2—Questions 1. Write the Day 2 PN bag using a 2-in-1 formulation. 2. Would you increase dextrose to goal? 3. Would you add/continue ILE on Day 2? Why or why not? If so, what amount? 4. Assess and determine electrolyte additives. Assess calcium–phosphate compatibility. 5. What other additives would you include in the Day 2 PN? 6. Are there any additional interventions you would make? 7. What follow-up laboratory test results might be important to obtain for tomorrow morning?arrow_forwardAnalyze the traits that define a profession that nursing has attained?arrow_forwardEvaluate ways nursing has failed to attain its status as a profession?arrow_forward
- Discuss the difference between an occupation and a profession?arrow_forward1. Write goal PN macronutrients using a 2-in-1 formulation. 2. What consideration for amino acid concentration needs to be assessed? 3. Would you start this patient on goal dextrose for Day 1? 4. Would you add ILE on Day 1? Why or why not? If so, what amount? 5. Assess and determine electrolyte additives. Assess calcium–phosphate compatibility. 6. What other additives would you include in the Day 1 PN?arrow_forwardWhat impact do regulatory and accreditation standards have on the risk management process within health care organizations? Why do you think it’s important to understand how regulatory and accreditation standards affect risk management? Provide examples.arrow_forward
- you are a school nurse. in the last2 weeks, 9 cases of head lice have been reported in four different classrooms. The potential for spread is high, and both parents and teachers are growing anxious. compose a memo for distribution to the teachers. your goals are to inform, reassure, and direct future inqueries.arrow_forwardasked but not answers yet Language of Medicine 13th edition chapter 1 sections A-E exercise with answers onlyarrow_forwardwhat are the different types of assessments in the nursing process and when are they performed?arrow_forward
 Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC.
Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC. Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders
Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer,
Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer, Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science
Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders
Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning





