
Concept explainers
Complete this summary map of photosynthesis.
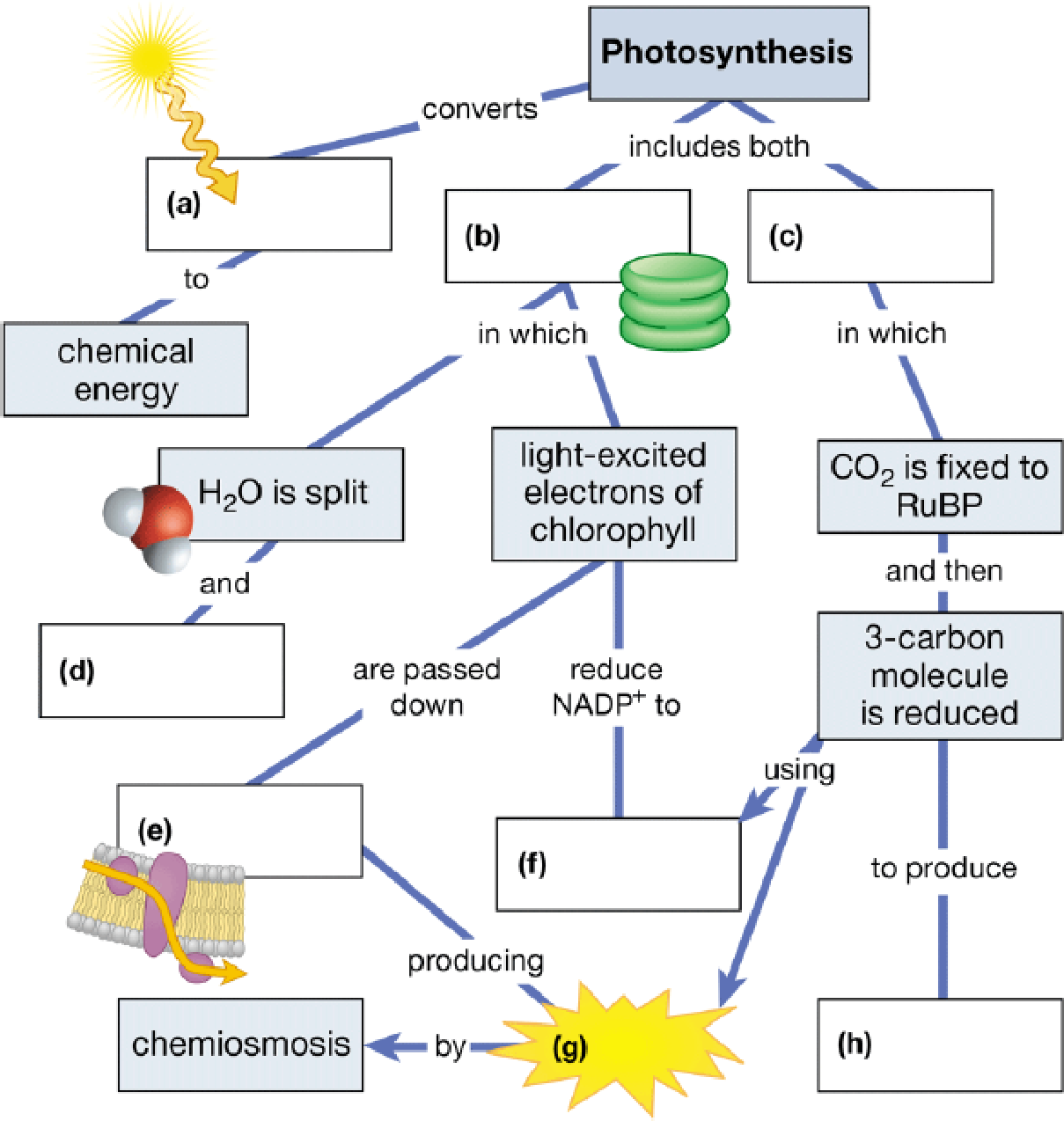
To complete: The connect map to summarize the major steps in photosynthesis.
Concept introduction: Photosynthesis is a vital process in primary producers, plants. Plants use light energy and carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and produce sugars that are stored in various parts of the plants. The most edible ones are consumed by the primary consumers. Several compounds are converted and recycled in the process of photosynthesis. Several reactions of photosynthesis take place in the chloroplast of the plant cell, which contains the green pigment chlorophyll.
Answer to Problem 1CC
The Fig.1 shows all the key processes in photosynthesis.
Pictorial representation:
The Fig. 1shows the summary of all the processes involved in photosynthesis.
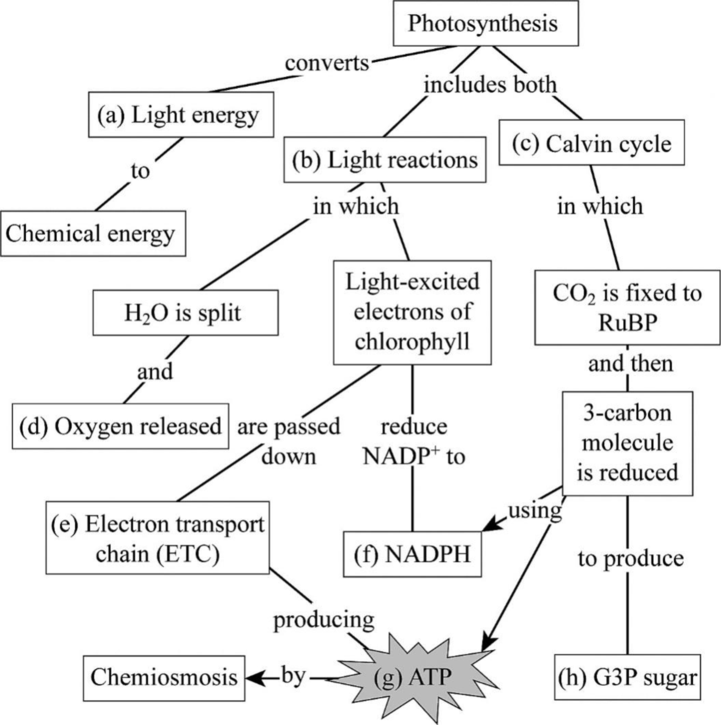
Fig 1: Summary of various steps in photosynthesis.
Explanation of Solution
(a)
Correct answer: Light energy
In the process of photosynthesis, photons from light energy are converted into chemical energy. In the visible spectrum of light, the red and blue wavelengths are used to initiate the reactions of photosynthesis. The light energy is used up to break the water molecule by the process called photolysis of water, which is the first step in photosynthesis.
Hence, the correct answer is light energy.
(b)
Correct answer: Light reactions
Photosynthesis includes two reactions, namely, light-dependent and light-independent reactions. Light reactions are those that are dependent on the incident light energy on the chloroplast. Light reactions include two sub steps. One reaction is the photolysis of water where light energy is used up to break the water molecules to produce an oxygen molecule and protons. The second reaction is where these protons and the energy released during photolysis of water are used up to excite the electrons in the chlorophyll.
Hence, the correct answer is light reactions.
(c)
Correct answer: Calvin cycle
The CBB (Calvin–Benson–Bassham) cycle or Calvin’s cycle is a series of reactions that take place in the stroma of the chloroplast. The Calvin’s cycle is a light-independent reaction, which is also known as the dark reaction. In the Calvin’s cycle, the atmospheric carbondioxide is fixed with ribulose1, 5-bisphosphate to produce two 3-carbon compounds. One of the two 3-carbon compounds is reduced to form another sugar.
Hence, the correct answer is the Calvin cycle
(d)
Correct answer: Oxygen released
During one of the light reactions, that is, photolysis of water, the light energy is used up to break two molecules of water to produce one molecule of oxygen, 4 electrons, and 4 protons (H+). The oxygen molecule then escapes the chloroplast and is released into the atmosphere.
Hence, the correct answer is oxygen released
(e)
Correct answer: Electrontransportchain(ETC)
During the second light reaction of photosynthesis, the electrons released from photolysis of water are passed on through the photosystem II and photosystem I and are then sent to the electron transport chain. In the electron transport chain, the protons released during photolysis of water are used by F0-F1 ATP synthase to produce ATP.
Hence, the correct answer is the electron transport chain (ETC)
(f)
Correct answer: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH)
During the second light reaction of photosynthesis, the electrons released from photolysis of water are passed on through the photosystem II and photosystem I, which at the end of photosystem II reduce NAD+ to NADPH. This NADPH is then used up during the hexose monophosphate pathway to produce several sugars, and it is also used during the Calvin’s cycle to produce sugars.
Hence, the correct answer is NADPH
(g)
Correct answer: ATP
The electrons released from photolysis of water are passed on through the photosystem II and then from the photosystem to the electron transport chain. In the electron transport chain, the protons released during photolysis of water are used by F0-F1 ATP synthase present on the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast to produce ATP. This ATP is used up along with NADPH to produce several sugars in the Calvin’s cycle.
Hence, the correct answer is ATP
(h)
Correct answer: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P)(sugar)
During the Calvin’s cycle, the NADPH and ATP produced during the light reactions and F0-F1 ATP synthase, respectively, are used up to reduce ribulose 1.5-bisphosphate to produce two molecules of G3P. For every 3 molecules of carbondioxide entering the Calvin’s cycle, one G3P is produced. Few G3Ps are sent for the production of 6-carbon sugars and others are recycled back to produce ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate.
Hence, the correct answer is G3P (sugar)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
- 12. Calculate the area of a circle which has a radius of 1200 μm. Give your answer in mm² in scientific notation with the correct number of significant figures.arrow_forwardDescribe the image quality of the B.megaterium at 1000X before adding oil? What does adding oil do to the quality of the image?arrow_forwardWhich of the follwowing cells from this lab do you expect to have a nucleus and why or why not? Ceratium, Bacillus megaterium and Cheek epithelial cells?arrow_forward
- 14. If you determine there to be debris on your ocular lens, explain what is the best way to clean it off without damaging the lens?arrow_forward11. Write a simple formula for converting mm to μm when the number of mm's is known. Use the variable X to represent the number of mm's in your formula.arrow_forward13. When a smear containing cells is dried, the cells shrink due to the loss of water. What technique could you use to visualize and measure living cells without heat-fixing them? Hint: you did this technique in part I.arrow_forward
- 10. Write a simple formula for converting μm to mm when the number of μm's are known. Use the variable X to represent the number of um's in your formula.arrow_forward8. How many μm² is in one cm²; express the result in scientific notation. Show your calculations. 1 cm = 10 mm; 1 mm = 1000 μmarrow_forwardFind the dental formula and enter it in the following format: I3/3 C1/1 P4/4 M2/3 = 42 (this is not the correct number, just the correct format) Please be aware: the upper jaw is intact (all teeth are present). The bottom jaw/mandible is not intact. The front teeth should include 6 total rectangular teeth (3 on each side) and 2 total large triangular teeth (1 on each side).arrow_forward
- Answer iarrow_forwardAnswerarrow_forwardcalculate the questions showing the solution including variables,unit and equations all the questiosn below using the data a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forward
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning





