
Habicht Company was formed in 2018 to produce a single product. The production and sales for the next 4 years were as follows:
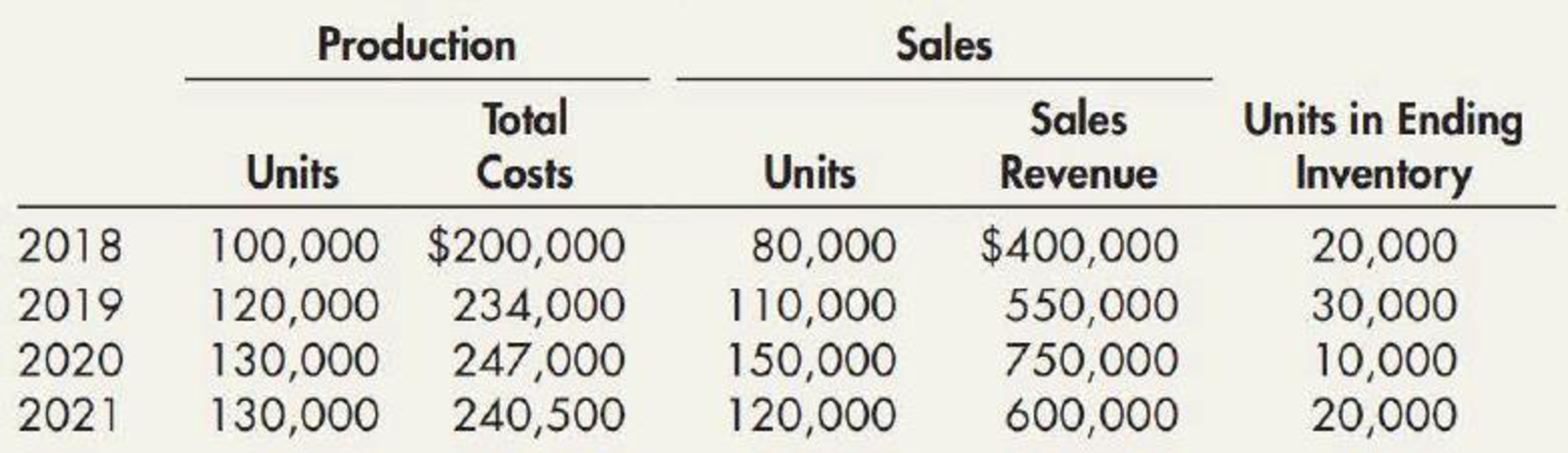
Required:
- 1. Determine the gross profit for each year under each of the following periodic inventory methods:
- a. FIFO
- b. LIFO
- c. Average cost (Round unit costs to 3 decimal places.)
- 2. Next Level Explain whether the company’s return on assets (net income divided by average total assets) would be higher under FIFO or LIFO.
1.
Ascertain the gross profit under the periodic inventory system for each year as per the inventory cashflow methods.
Explanation of Solution
First-in-First-Out (FIFO): In this method, items purchased initially are sold first. So, the value of the ending inventory consists the recent cost for the remaining unsold items.
Last-in-First-Out (LIFO): In this method, items purchased recently are sold first. So, the value of the ending inventory consists the initial cost for the remaining unsold items.
- a) Calculate the gross profit for the four years under FIFO method:
| Particulars | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 |
| Amount ($) | Amount ($) | Amount ($) | Amount ($) | |
| Net sales | $400,000 | $550,000 | $750,000 | $600,000 |
| Cost of goods sold | ||||
| Beginning inventory | $ 0 | $ 40,000 | $ 58,500 | $ 19,000 |
| Add: Production | $ 200,000 | $ 234,000 | $ 247,000 | $ 240,500 |
| Goods available for sale | $ 200,000 | $ 274,000 | $ 305,500 | $ 259,500 |
| Less: Ending inventory | (1) $ 40,000 | (2) $ 58,500 | (3) $ 19,000 | (4) $ 37,000 |
| Cost of goods sold | $ 160,000 | $ 215,500 | $ 286,500 | $ 222,500 |
| Gross Margin | $ 240,000 | $ 334,500 | $ 463,500 | $ 377,500 |
Table (1)
Working Note (1):
Ending inventory for 2018 is $40,000
Working Note (2):
Ending inventory for 2019 is $58,500
Working Note (3):
Ending inventory for 2020 is $19,000
Working Note (4):
Ending inventory for 2021 is $37,000
- b) Calculate the gross profit for the four years under LIFO method:
| Particulars | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 |
| Amount ($) | Amount ($) | Amount ($) | Amount ($) | |
| Net sales | $400,000 | $550,000 | $750,000 | $600,000 |
| Cost of goods sold | ||||
| Beginning inventory | $ 0 | $ 40,000 | $ 59,500 | $ 20,000 |
| Add: Production | $ 200,000 | $ 234,000 | $ 247,000 | $ 240,500 |
| Goods available for sale | $ 200,000 | $ 274,000 | $ 306,500 | $ 260,500 |
| Less: Ending inventory | (5) $ 40,000 | (6) $ 59,500 | (7) $ 20,000 | (8) $ 38,500 |
| Cost of goods sold | $ 160,000 | $ 214,500 | $ 286,500 | $ 222,000 |
| Gross Margin | $ 240,000 | $ 335,500 | $ 463,500 | $ 378,000 |
Table (2)
Working Note (5):
Ending inventory for 2018 is $40,000
Working Note (6):
Ending inventory for 2019 is $59,500
Working Note (7):
Ending inventory for 2020 is $20,000
Working Note (8):
Ending inventory for 2021 is $38,500
- a) Calculate the gross profit for the four years under Average cost method:
Compute the cost of goods sold for average cost method:
| Year | Beginning inventory | Production | Goods available for sale | Average Unit | |||
| Units | Cost | Units | Cost | Units | Cost | Cost | |
| 2018 | 0 | $ 0 | 100,000 | $ 200,000 | 100,000 | $ 200,000 | $ 2.00 |
| 2019 | 20,000 | $ 40,000 | 120,000 | $ 234,000 | 140,000 | $ 274,000 | $ 1.957 |
| 2020 | 30,000 | $ 58,710 | 130,000 | $ 247,000 | 160,000 | $ 305,710 | $ 1.911 |
| 2021 | 10,000 | $ 19,110 | 130,000 | $ 240,500 | 140,000 | $ 259,610 | $ 1.854 |
Table (3)
| Year | Ending inventory | Cost of goods sold | ||
| Units | Cost | Units | Cost | |
| 2018 | 20,000 | $ 40,000 | 80,000 | $ 160,000 |
| 2019 | 30,000 | $ 58,710 | 110,000 | $ 215,290 |
| 2020 | 10,000 | $ 19,110 | 150,000 | $ 286,600 |
| 2021 | 20,000 | $ 37,080 | 120,000 | $ 222,530 |
Table (4)
Calculate the gross profit for the four years under Average cost method
| Particulars | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 |
| Amount ($) | Amount ($) | Amount ($) | Amount ($) | |
| Net sales | $400,000 | $550,000 | $750,000 | $600,000 |
| Cost of goods sold | ||||
| Beginning inventory | $ 0 | $ 40,000 | $ 58,710 | $ 19,110 |
| Add: Production | $ 200,000 | $ 234,000 | $ 247,000 | $ 240,500 |
| Goods available for sale | $ 200,000 | $ 274,000 | $ 305,710 | $ 259,610 |
| Less: Ending inventory | $ 40,000 | $ 58,710 | $ 19,110 | $ 37,080 |
| Cost of goods sold | $ 160,000 | $ 215,290 | $ 286,600 | $ 222,530 |
| Gross Margin | $ 240,000 | $ 334,710 | $ 463,400 | $ 377,470 |
Table (5)
2.
Identify would return on asset would be greater under FIFO and LIFO.
Explanation of Solution
The net income and assets are higher under the FIFO method. There is a difference in the net income under both the methods.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting and Analysis (Looseleaf)
- Cuneo Companys income statements for the last 3 years are as follows: Refer to the information for Cuneo Company above. Required: 1. Prepare a common-size income statement for Year 1 by expressing each line item as a percentage of sales revenue. (Note: Round percentages to the nearest tenth of a percent.) 2. Prepare a common-size income statement for Year 2 by expressing each line item as a percentage of sales revenue. (Note: Round percentages to the nearest tenth of a percent.) 3. Prepare a common-size income statement for Year 3 by expressing each line item as a percentage of sales revenue. (Note: Round percentages to the nearest tenth of a percent.)arrow_forwardAssume your company uses the periodic inventory costing method, and the inventory count left out an entire warehouse of goods that were in stock at the end of the year, with a cost value of $222,000. How will this affect your net income in the current year? How will it affect next years net income?arrow_forwardSundahl Companys income statements for the past 2 years are as follows: Refer to the information for Sundahl Company above. Required: 1. Prepare a common-size income statement for Year 1 by expressing each line item as a percentage of sales revenue. (Note: Round percentages to the nearest tenth of a percent.) 2. Prepare a common-size income statement for Year 2 by expressing each line item as a percentage of sales revenue. (Note: Round percentages to the nearest tenth of a percent.)arrow_forward
- Fava Company began operations in 2018 and used the LIFO inventory method for both financial reporting and income taxes. At the beginning of 2019, the anticipated cost trends in the industry had changed, so that it adopted the FIFO method for both financial reporting and income taxes. Fava reported revenues of 300,000 and 270,000 in 2019 and 2018, respectively. Fava reported expenses (excluding income tax expense) of 125,000 and 120,000 in 2019 and 2018, which included cost of goods sold of 55,000 and 45,000, respectively. An analysis indicates that the FIFO cost of goods sold would have been lower by 8,000 in 2018. The tax rate is 21%. Fava has a simple capital structure with 15,000 shares of common stock outstanding during 2018 and 2019. It paid no dividends in either year. Required: 1. Prepare the journal entry to reflect the change. 2. At the end of 2019, prepare the comparative income statements for 2019 and 2018. Notes to the financial statements are not necessary. 3. At the end of 2019, prepare the comparative retained earnings statements for 2019 and 2018.arrow_forwardLast year, Nikkola Company had net sales of 2,299,500,000 and cost of goods sold of 1,755,000,000. Nikkola had the following balances: Refer to the information for Nikkola Company above. Required: Note: Round answers to one decimal place. 1. Calculate the average inventory. 2. Calculate the inventory turnover ratio. 3. Calculate the inventory turnover in days. 4. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Based on these ratios, does Nikkola appear to be performing well or poorly?arrow_forwardCuneo Companys income statements for the last 3 years are as follows: Refer to the information for Cuneo Company above. Required: 1. Prepare a common-size income statement for Year 2 by expressing each line item for Year 2 as a percentage of that same line item from Year 1. (Note: Round percentages to the nearest tenth of a percent.) 2. Prepare a common-size income statement for Year 3 by expressing each line item for Year 3 as a percentage of that same line item from Year 1. (Note: Round percentages to the nearest tenth of a percent.)arrow_forward
- Use the following hypothetical data for Walgreens in Years 11 and 12 to project revenues, cost of goods sold, and inventory for Year +1. Assume that Walgreenss Year +1 revenue growth rate, gross profit margin, and inventory turnover will be identical to Year 12. Project the average inventory balance in Year +1 and use it to compute the implied ending inventory balance.arrow_forwardOlson Company adopted the dollar-value LIFO method for inventory valuation at the beginning of 2015. The following information about the inventory at the end of each year is available from Olsons records: Required: 1. Calculate the dollar-value LIFO inventory at the end of each year. 2. Prepare the appropriate disclosures for the 2021 annual report if Olson uses current cost internally and LIFO for financial reporting.arrow_forwardQuestion: Capital Technologies Inc. began 2020 with inventory of $20,000. During the year, Capital purchased inventory costing $100,000 and sold goods for $140,000, with all transactions on account. Capital ended the year with inventory of $30,000. Use the data in exercise to do the following for Capital Technologies Inc.: 1. Post to the Inventory and Cost of Goods Sold accounts. 2. Compute cost of goods sold by the cost-of-goods-sold model. 3. Prepare the December 2020 income statement of Capital Technologies Inc. through gross profit. (Please explain how to get the amount for Sales Revenue, I did not understand)arrow_forward
- Use the following information relating to Clover Company to calculate (a) the inventory turnover ratio, (b) gross margin, and (c) the number of days’ sales in inventory ratio, for years 2022 and 2023. Assume a year has 365 days. Do not round intermediate calculations and round your final answers to 3 decimal places. Sales Cost ofGoods Sold AverageInventory Year 2021 $250,000 $187,500 $26,000 Year 2022 295,000 221,250 30,000 Year 2023 323,000 252,250 35,000 InventoryTurnover GrossMargin Days' Salesin Inventory Year 2022 fill in the blank 1 $fill in the blank 2 fill in the blank 3 Year 2023 fill in the blank 4 $fill in the blank 5 fill in the blank 6arrow_forwardPlease give correct Answersarrow_forwardVikrambahiarrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning




