
The work done by the force is to be estimated.
Answer to Problem 14P
The work done by the force on the particle is 7.04J
Explanation of Solution
Given
It is given that the particle is moving along the axis with x=0 and x=4 and the graph is given below −
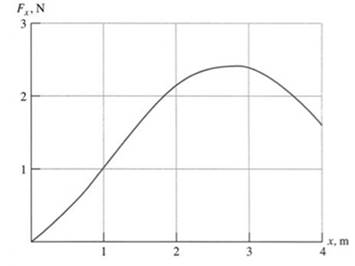
Formula used:
The following formula will be used to calculate the net work done by the force on the particle −
Calculation:
The total area under the given curve of the graph is representing the work done by the force on the particle. It is represented as −
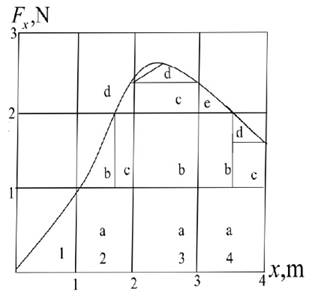
The final work done will be the summation of the area of triangle and rectangle under the curve −
Area of portion (1) =
Area of portion 2(a) = Area of rectangle
Area of portion 2(b) = Area of triangle
Area of portion 2(c) = Area of rectangle
Area of portion 2(d) = Area of triangle
Area of portion 3(a) = Area of rectangle
Area of portion 3(b) = Area of rectangle
Area of portion 3(c) = Area of rectangle
Area of portion 3(d) = Area of triangle
Area of portion 4(a) = Area of rectangle
Area of portion 4(b) = Area of rectangle
Area of portion 4(c) = Area of rectangle
Area of portion 4(d) = Area of triangle
Area of portion 4(e) = Area of triangle
Now, the work done by the force on the particle can be given as −
Conclusion: It can be concluded that the work done by the force on particle is 7.04J.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Physics Fundamentals
- 3. Four identical small masses are connected in a flat perfect square. Rank the relative rotational inertias (IA, IB, IC) about the three axes of rotation shown. Axes A and B are in the plane of the square, and axis C is perpendicular to the plane, through mass m1. ΙΑ IB m2 m1 m3 Ic m4 (a) IAarrow_forwardConsider the circuit shown in the figure below. (Assume L = 5.20 m and R2 = 440 Ω.) (a) When the switch is in position a, for what value of R1 will the circuit have a time constant of 15.4 µs? (b) What is the current in the inductor at the instant the switch is thrown to position b?arrow_forwardCan someone helparrow_forwardCan someone help mearrow_forwardA particle in a box between x=0 and x=6 has the wavefunction Psi(x)=A sin(2πx). How muchenergy is required for the electron to make a transition to Psi(x)= A’ sin(7π x/3). Draw anapproximate graph for the wavefunction. Find A and A'arrow_forwardA proton is moving with 10^8 m/s speed. Find the De Broglie wavelength associated with theproton and the frequency of that wave.arrow_forwardFind the wavelength of the photon if a (Li--) electron makes a transition from n=4 to n=3. Findthe Bohr radius for each state.arrow_forwardA photon with wavelength 3000 nm hits a stationary electron. After the collision electron isscattered to 60 degrees. Find the wavelength and frequency of the scattered photon.arrow_forwardA metal has threshold frequency 10^15. Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of the ejectedelectron if a laser beam with wavelength 1.5 10^-7 m is projected on the metal.arrow_forwardDetermine the direction of the vector V, B, or ♬ that is missing from the pair of vectors shown in each scenario. Here, u is the velocity vector of a moving positive charge, B is a constant and uniform magnetic field, and F is the resulting force on the moving charge. 1. 2. 3. B OB F 4. ↑F F 5. 怔 ↑ ↑F Answer Bank 6. ↑ TE Farrow_forwardTwo point charges (+9.80 nC and -9.80 nC) are located 8.00 cm apart. Let U=0 when all of the charges are separated by infinite distances. What is the potential energy if a third point charge q=-4.20 nC is placed at point b? 8.00 cm 8.00 cm 4.00 +4.00 +4.00- cm cm cm HJarrow_forward! Required information Two chloride ions and two sodium ions are in water, the "effective charge" on the chloride ions (CI¯) is −2.00 × 10-21 C and that of the sodium ions (Na+) is +2.00 x 10-21 C. (The effective charge is a way to account for the partial shielding due to nearby water molecules.) Assume that all four ions are coplanar. CT Na+ Na+ 30.0° 45.0% с сг L. where a = 0.300 nm, b = 0.710 nm, and c = 0.620 nm. What is the direction of electric force on the chloride ion in the lower right-hand corner in the diagram? Enter the angle in degrees where positive indicates above the negative x-axis and negative indicates below the positive x-axis.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College





