
Concept explainers
Absorption Costing Approach to Cost-Plus Pricing LO6—8
Martin Company uses the absorption costing approach to cost-plus pricing. It is considering the introduction of a new product. To determine a selling price, the company has gathered the following information:
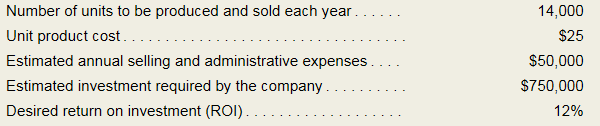
Required:
- Compute the markup percentage on absorption cost required to achieve the desired ROL.
- Compute the selling price per unit.
Concept Introduction:
Costing is a process of calculation of the cost of the product or service manufactured or provided by an organization. There are two methods of costing; absorption costing and variable costing.
As per nature, costs can be divided into three categories, i.e., variable costs, fixed costs, and mixed costs.
Requirement-1:
The markup percentage.
Answer to Problem 6A.1E
The markup percentage is 25.71%.
Explanation of Solution
The markup percentage is calculated as follows:
| Number of units (A) | $ 14,000 |
| Unit product cost (B) | $ 25 |
| Total absorption product cost (C) = (A*B) | $ 350,000 |
| Selling and admn expenses (D) | $ 50,000 |
| Total Cost (E) = (C+D) | $ 400,000 |
| Amount of investment (F) | $ 750,000 |
| Desired return on investment (G) | 12% |
| Desired markup (H) = (F*G) | $ 90,000 |
| Markup % (I) = (H/C) | 25.71% |
Concept Introduction:
Costing is a process of calculation of the cost of the product or service manufactured or provided by an organization. There are two methods of costing; absorption costing and variable costing.
As per nature, costs can be divided into three categories, i.e., variable costs, fixed costs, and mixed costs.
Requirement-2:
The selling price per unit.
Answer to Problem 6A.1E
The selling price per unit is $35.
Explanation of Solution
The selling price per unit is calculated as follows:
| Number of units (A) | $ 14,000 |
| Unit product cost (B) | $ 25 |
| Total absorption product cost (C) = (A*B) | $ 350,000 |
| Selling and admn expenses (D) | $ 50,000 |
| Total Cost (E) = (C+D) | $ 400,000 |
| Amount of investment (F) | $ 750,000 |
| Desired return on investment (G) | 12% |
| Desired markup (H) = (F*G) | $ 90,000 |
| Markup % (I) = (H/C) | 25.71% |
| Tota cost per unit (J) = (E/A) | $ 28.57 |
| Markup per unit (K) = (H/A) | $ 6.43 |
| Selling price (J+K) | $ 35.00 |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6A Solutions
MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING(LL)-W/CONNECT >C<
- The industrial enterprise "HUANG S.A." purchased a sorting and packaging machine from a foreign company on 1/4/2017 at a cost of €500,000. The useful life of the machine was estimated by the Management at ten (10) years, while the residual value was estimated at zero. For the transportation of the machine from abroad to the company's factory, the amount of €20,000 was paid on 15/4/2017. As the insurance coverage of the machine during transportation was the responsibility of the selling company, HUANG S.A. proceeded to insure the machine from 16/4/2017 to 15/4/2018, paying the amount of €1,200. The delivery took place on 15/4/2017. As adequate ventilation of the multifunction device is essential for its proper operation, the company fitted an air duct on the multifunction device. The cost of the air duct amounted to €2,000 and was paid on 20/4/2017. On 25/4/2017, an external electrician was paid €5,000 for the electrical connection of the device. The company also paid €5,000 to an…arrow_forwardNO AI ANSWERarrow_forwardGive me Answerarrow_forward
- WW Office Solutions implemented a new supply requisition system. Departments must submit requests by Thursday for next week, maintain minimum 20% buffer stock, and obtain supervisor approval for urgent orders. From 85 total requisitions last month, 65 followed timeline, 72 maintained proper buffer, and 58 met both conditions. What is the compliance rate? Financial Accounting problemarrow_forwardansarrow_forwardWW Office Solutions implemented a new supply requisition system. Departments must submit requests by Thursday for next week, maintain minimum 20% buffer stock, and obtain supervisor approval for urgent orders. From 85 total requisitions last month, 65 followed timeline, 72 maintained proper buffer, and 58 met both conditions. What is the compliance rate? Problem related general Accountarrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning


