
Concept explainers
i.
To make a tree diagram to show all the different possible outcomes.
i.
Answer to Problem 6E
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Three coins are flipped.
Calculation:
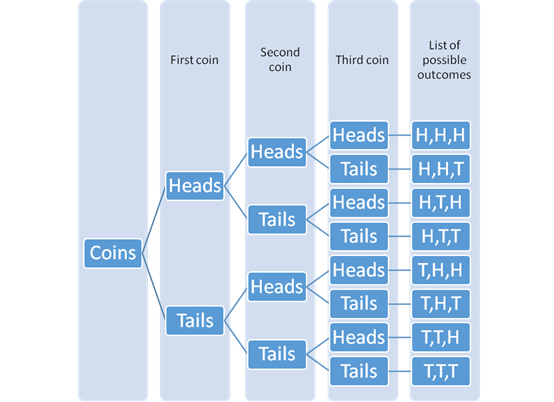
The tree diagram with the possible outcomes can be drawn as:
The different possible outcomes are HHH,HHT,HTH,HTT,THH,THT,TTH,TTT.
ii.
To find how many different possible outcomes are there.
ii.
Answer to Problem 6E
There are total of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Three coins are flipped.
Calculation:
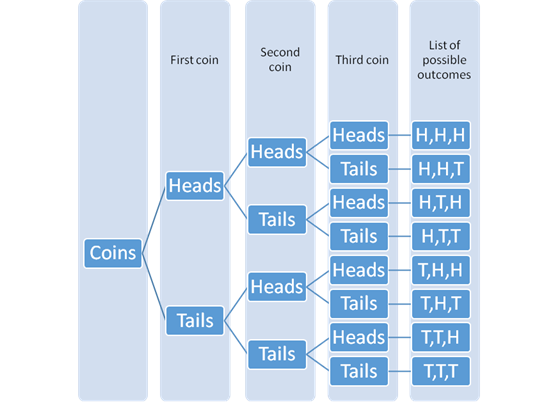
The tree diagram with the possible outcomes can be drawn as:
As conclude from the tree diagram there are total of
HHH, HHT, HTH, HTT, THH, THT, TTH, TTT.
Hence,
There are total of
iii.
The find favorable outcomes.
iii.
Answer to Problem 6E
There are
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Three coins are flipped.
Calculation:
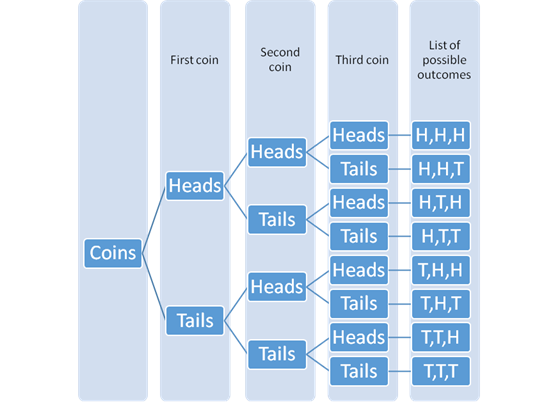
The tree diagram with the possible outcomes can be drawn as:
As from the tree diagram,
The favorable outcomes which shows all three coins heads or all three coins tails is HHH and TTT.
Hence,
There are
iv.
To find the probability.
iv.
Answer to Problem 6E
The probability of getting all three coins heads or all three coins tails is
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Three coins are flipped.
Calculation:
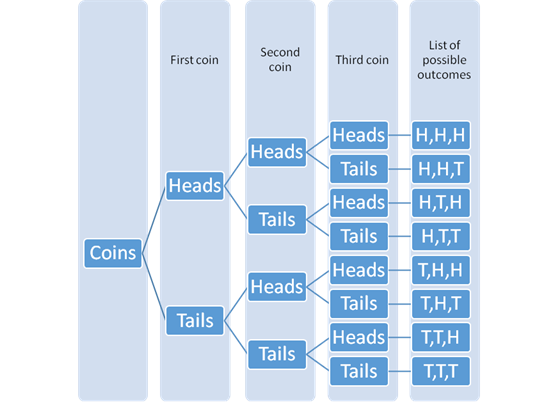
The tree diagram with the possible outcomes can be drawn as:
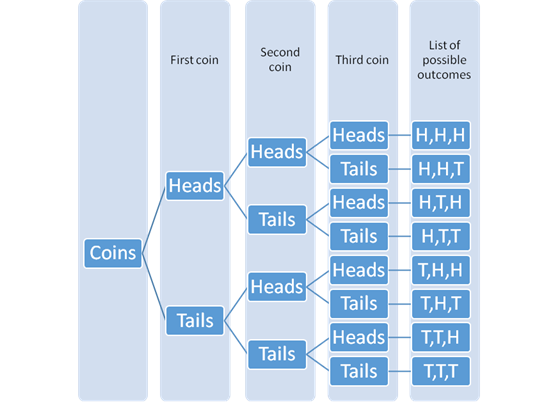
The probability of getting all three coins heads or all three coins tails is:
Hence,
The probability of getting all three coins heads or all three coins tails is
Chapter 6 Solutions
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Common Core Practice Workbook
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- Safari File Edit View History Bookmarks Window Help Ο Ω OV O mA 0 mW ర Fri Apr 4 1 222 tv A F9 F10 DII 4 F6 F7 F8 7 29 8 00 W E R T Y U S D பட 9 O G H J K E F11 + 11 F12 O P } [arrow_forwardSo confused. Step by step instructions pleasearrow_forwardIn simplest terms, Sketch the graph of the parabola. Then, determine its equation. opens downward, vertex is (- 4, 7), passes through point (0, - 39)arrow_forward
- In simplest way, For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. a) y = x 2 + 16 x + 39 b) y = 5 x2 - 50 x - 120arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step Write each quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = - 4( x + 6)2 + 36arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. 1) y = - 2 x2 - 28 x + 64 2) y = 6 x2 + 36 x - 42arrow_forward
- Write each relation in standard form a)y = 5(x + 10)2 + 7 b)y = 9(x - 8)2 - 4arrow_forwardIn simplest form and step by step Write the quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = 3(x - 1)2 - 147arrow_forwardStep by step instructions The path of a soccer ball can be modelled by the relation h = - 0.1 d 2 + 0.5 d + 0.6, where h is the ball’s height and d is the horizontal distance from the kicker. a) Find the zeros of the relation.arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





