
EBK MATHEMATICS FOR MACHINE TECHNOLOGY
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780100548169
Author: SMITH
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 66, Problem 17A
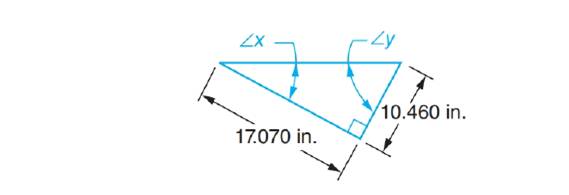
Solve the following exercises. Compute angles to the nearer minute in triangles with customary unit sides. Compute angles to the nearer hundredth degree in triangles with metric unit sides.
a. Determine
b. Determine
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please help with detailed way to find answer. Thank you
Please help with as much detail as possible. Thanks
Page
of 2
ZOOM
+
1) a) Answer the following questions by circling TRUE or FALSE (No explanation or
work required).
[1 0
0
i) A = 0 2
6
is invertible.
(TRUE FALSE)
LO -4-12]
ii) We can use the transpose of the cofactor matrix to find the inverse of a matrix.
(TRUE FALSE)
=
iii) If A 2, and A is a 5x5 square matrix, |2A] = 64. (TRUE FALSE)
iv) Every vector space must contain two trivial subspaces. (TRUE FALSE)
v) The set of all integers with standard operations is a vector space.
(TRUE FALSE)
b) Write v as a linear combination of the vectors in the set S, if possible, where
v=(1,-4), and S={(1,2),(1,-1)}.
2) a) Solve the following system of linear equations using Cramer's Rule and check
the correctness of your answer.
4xyz
1
2x + 2y + 3z = 10
5x-2y-2z = -1
b) Find the adjoint of the following matrix A. Then use the adjoint to find the inverse
of A if possible, and check the correctness of your answer.
A
=
c) Determine whether the following points are collinear. Why or why not? If not,…
Chapter 66 Solutions
EBK MATHEMATICS FOR MACHINE TECHNOLOGY
Ch. 66 - If cos 3518', write the cofunction of the...Ch. 66 - If sinA=0.3617 , determine the value of angle A in...Ch. 66 - Find the volume to the nearest tenth cubic...Ch. 66 - Prob. 4ACh. 66 - Prob. 5ACh. 66 - Prob. 6ACh. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute angles to...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute angles to...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute angles to...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute angles to...
Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute angles to...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute angles to...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute angles to...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute angles to...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute angles to...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute angles to...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute angles to...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute angles to...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute the sides...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute the sides...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute the sides...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute the sides...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute the sides...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute the sides...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute the sides...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute the sides...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute the sides...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute the sides...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute the sides...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. Compute the sides...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. For triangles...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. For triangles...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. For triangles...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. For triangles...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. For triangles...Ch. 66 - Solve the following exercises. For triangles...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please help with 4e) thanksarrow_forwardPage of 2 Zoom Name: _______________Project Wacko-pediaWacko-podia is an Internet encyclopedia (OK, I admit I made Wacko-podia up for this project, anyway)that uses an automated system based on logic to determine whether a new entry will be entered intheir website. Unfortunately, sometimes inaccurate information can get entered because the statementhas a “True” truth value even if there is incorrect information in part of the statement. For eachstatement below, determine if the entry will get past the automated system or will be labeled with a“False” truth value and end up being returned to the sender.Notes:1. You may need to look up some information in an almanac or other trustworthy onlinereference.2. Work must be shown to receive credit.Statement A: The capital of Pennsylvania is Pittsburgh or the capital of Kentucky is Frankfort.p: Truth Value of p:q: Truth Value of q:Translation of compound statement into symbols:Work:Conclusion: Entered __?…arrow_forwardPlease help with 18 d) with as much detail. Thanksarrow_forward
- Please help with 18 c) with as much detail. Thanksarrow_forwardPage of 2 ZOOM + 1) a) Answer the following questions by circling TRUE or FALSE (No explanation or work required). [1 0 0 i) A = 0 2 6 is invertible. (TRUE FALSE) LO -4-12] ii) We can use the transpose of the cofactor matrix to find the inverse of a matrix. (TRUE FALSE) = iii) If A 2, and A is a 5x5 square matrix, |2A] = 64. (TRUE FALSE) iv) Every vector space must contain two trivial subspaces. (TRUE FALSE) v) The set of all integers with standard operations is a vector space. (TRUE FALSE) b) Write v as a linear combination of the vectors in the set S, if possible, where v=(1,-4), and S={(1,2),(1,-1)}. 2) a) Solve the following system of linear equations using Cramer's Rule and check the correctness of your answer. 4xyz 1 2x + 2y + 3z = 10 5x-2y-2z = -1 b) Find the adjoint of the following matrix A. Then use the adjoint to find the inverse of A if possible, and check the correctness of your answer. A = c) Determine whether the following points are collinear. Why or why not? If not,…arrow_forwardFigure B is a scaled copy of Figure A what is the scale factor from Figure A to Figure Barrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answer Plzarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answerarrow_forwardRadioShack sells Samsung and Lenovo tablets. When five Samsung tablets and eight Lenovo tablets are sold, RadioShack makes a profit of more than $1,920.00. The total cost of purchasing a Samsung and a Lenovo tablet cannot exceed $375.00. The total revenue made from the sale of nine Lenovo tablets and two Samsung is no more than $2,610. At no point in time, RadioShack's stock on either tablet will fall below 5 units. a. Derive five (5) linear inequalities to represent the above information. b. Using the same Cartesian Plane to represent each of the above linear inequalities from part a. above, solve the system of linear inequalities. Ensure that all work is clearly stated. c. Hence, label the solution from part b. above with a capital S.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781337798310
Author:Peterson, John.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,
The Law of Cosines; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3wGQMyaWoLA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Law of Sines and Law of Cosines (4 Examples); Author: Mario's Math Tutoring;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T--nPHdS1Vo;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY