
Representing Colors Colors for computer monitors are often described using ordered triples. One model, called the RGB system, uses red, green, and blue to generate all colors. The figure describes the relationships of these colors in this system. Red is (1, 0, 0), green is (0, 1, 0), and blue is (0, 0, 1). Since equal amounts of red and green combine to form yellow, yellow is represented by (1, 1, 0). Similarly, magenta (a deep reddish purple) is a mixture of blue and red and is represented by (1, 0, 1).
Cyan is (0, 1, 1), since it is a mixture of blue and green.
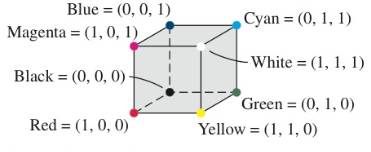
Another color model uses cyan, magenta, and yellow. Referred to as the CMY model, it is used in the four-color printing process for textbooks like this one. In this system, cyan is (1, 0, 0), magenta is (0, 1, 0), and yellow is (0, 0, 1).
In the CMY model, red is created by mixing magenta and yellow. Thus, red is (0, 1, 1) in this system. To convert ordered triples in the RGB model to ordered triples in the CMY model, we can use the following matrix equation. In both of these systems, color intensities vary between 0 and I. (Sources: I. Kerlow, The Art of 3-D Computer Animation and Imaging; R. Wolff.)
2. In the RGB model, rust is (0.552, 0.168, 0.066). Use the matrix equation to determine the mixture of cyan, magenta, and yellow that makes rust in the CMY model.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Mylab Math With Pearson Etext -- 18 Week Standalone Access Card -- For Precalculus With Modeling & Visualization
- 20 2. Let A = = [ -2 0 1 3 ] and B = 2 3 -1 2 For each of the following, calculate the product or indicate why it is undefined: (a) AB (b) BAarrow_forwardAnswer the number questions with the following answers +/- 2 sqrt(2) +/- i sqrt(6) (-3 +/-3 i sqrt(3))/4 +/-1 +/- sqrt(6) +/- 2/3 sqrt(3) 4 -3 +/- 3 i sqrt(3)arrow_forward1 Matching 10 points Factor and Solve 1)x3-216 0, x = {6,[B]} 2) 16x3 = 54 x-[3/2,[D]] 3)x4x2-42 0 x= [ +/-isqrt(7), [F] } 4)x+3-13-9x x=[+/-1.[H]] 5)x38x2+16x=0, x = {0,[K}} 6) 2x6-10x-48x2-0 x-[0, [M], +/-isqrt(3)) 7) 3x+2x²-8 x = {+/-i sqrt(2), {Q}} 8) 5x³-3x²+32x=2x+18 x = {3/5, [S]} [B] [D] [F] [H] [K] [M] [Q] +/-2 sqrt(2) +/- i sqrt(6) (-3+/-3 i sqrt(3))/4 +/- 1 +/-sqrt(6) +/- 2/3 sqrt(3) 4 -3 +/- 3 i sqrt(3) [S]arrow_forward
- The only problems I need help with ae the last 8 ones, Thanksarrow_forwardGraph without using the calculator y-1 = | x+4 |arrow_forward9:43 AS く Akbar © Printed in the United States 15) Scale: 1 cmal unit on both axes .ill 64% The graph above shows a straight line QT intersecting the y-axis at T. i State the co-ordinates of T. ii Calculate the gradient of QT 16) iii Determine the equation of QT. A (-1, 9) ||| i L Г (5 marks)arrow_forward
 Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage

