
To find: the indicated probability for a randomly selected x-value from the distribution using the standard normal table.
Given information:
The probability to be found is:
It is given that the distribution is normal and has mean
Concept Used:
Standard
The standard normal distribution is the normal distribution with mean 0 and standard deviation1. The formula below can be used to transform x-values from a normal distribution with mean
The z-value for a particular x-value is called the z-score for the x-value and is the number of standard deviations the x-value lies above or below the mean
Standard Normal Table
If z is a randomly selected value from a standard normal distribution, the table below can be used to find the probability that z is less than or equal to some given value.
| Standard Normal Table | ||||||||||
| z | .0 | .1 | .2 | .3 | .4 | .5 | .6 | .7 | .8 | .9 |
| -3 | .0013 | .0010 | .0007 | .0005 | .0003 | .0002 | .0002 | .0001 | .0001 | .0000+ |
| -2 | .0228 | .0179 | .0139 | .0107 | .0082 | .0062 | .0047 | .0035 | .0026 | .0019 |
| -1 | .1587 | .1357 | .1151 | .0968 | .0808 | .0668 | .0548 | .0446 | .0359 | .0287 |
| -0 | .5000 | .4602 | .4207 | .3821 | .3446 | .3085 | .2743 | .2420 | .2119 | .1841 |
| 0 | .5000 | .5398 | .5793 | .6179 | .6554 | .6915 | .7257 | .7580 | .7881 | .8159 |
| 1 | .8413 | .8643 | .8849 | .9032 | .9192 | .9332 | .9452 | .9554 | .9641 | .9713 |
| 2 | .9772 | .9821 | .9861 | .9893 | .9918 | .9938 | .9953 | .9965 | .9974 | .9981 |
| 3 | .9987 | .9990 | .9993 | .9995 | .9997 | .9998 | .9998 | .9999 | .9999 | 1.0000- |
Explanation:
Now, to find
So, first step is to find
For that, first find the z-score corresponding to the x-value of 65.
So,
Now, to find this value, find the intersection point where row 0 and column .1 intersects.
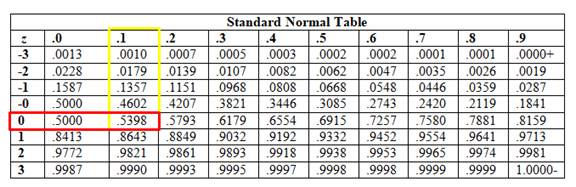
The table shows that:
Next step is to find
First step is to find the z-score corresponding to the x-value of 45.
So,
Now, to find this value, find the intersection point where row -2 and column .7 intersects.
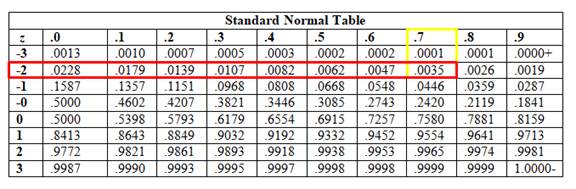
The table shows that:
So, the required probability is:
Chapter 6 Solutions
Algebra 2: New York Edition (holt Mcdougal Larson Algebra 2)
- The only problems I need help with ae the last 8 ones, Thanksarrow_forwardGraph without using the calculator y-1 = | x+4 |arrow_forward9:43 AS く Akbar © Printed in the United States 15) Scale: 1 cmal unit on both axes .ill 64% The graph above shows a straight line QT intersecting the y-axis at T. i State the co-ordinates of T. ii Calculate the gradient of QT 16) iii Determine the equation of QT. A (-1, 9) ||| i L Г (5 marks)arrow_forward
- Pls help.arrow_forwardSolve the system of equation for y using Cramer's rule. Hint: The determinant of the coefficient matrix is -23. - 5x + y − z = −7 2x-y-2z = 6 3x+2z-7arrow_forwarderic pez Xte in z= Therefore, we have (x, y, z)=(3.0000, 83.6.1 Exercise Gauss-Seidel iteration with Start with (x, y, z) = (0, 0, 0). Use the convergent Jacobi i Tol=10 to solve the following systems: 1. 5x-y+z = 10 2x-8y-z=11 -x+y+4z=3 iteration (x Assi 2 Assi 3. 4. x-5y-z=-8 4x-y- z=13 2x - y-6z=-2 4x y + z = 7 4x-8y + z = -21 -2x+ y +5z = 15 4x + y - z=13 2x - y-6z=-2 x-5y- z=-8 realme Shot on realme C30 2025.01.31 22:35 farrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





