
Concept explainers
School days: The following table presents the numbers of students enrolled in grades 1 through 8 in public schools in the United States.
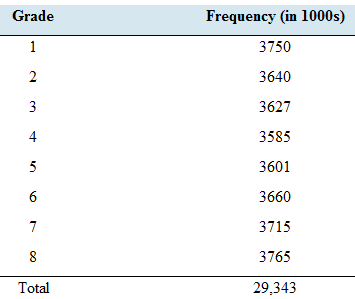
Consider these students to be a population. Let X be the grade of a student randomly chosen from this population.
Construct the
Find the probability that the student is in fourth grade.
Find the probability that the student is seventh or eighth grade.
Compute the
Compute the standard
a.
To construct: The probability distribution of the given random variable.
Explanation of Solution
The enrollment of students from grade
Calculation:
The random variable
To calculate the probability of each value of the random variable, the frequency should be divided by the total number of individuals according to the formula,
As an example,
The all calculation can be expressed in a table as follows. Because both values in the numerator and the denominator is in thousands, in the division those are cancelled out.
The probability distribution can be constructed by the first and third columns of the above table.
b.
To find: The probability to a selected student is from grade four.
Answer to Problem 49E
The probability that the student is in fourth grade is found to be
Explanation of Solution
The probability distribution for the grade of
Calculation:
When a student is fin grade four, the random variable
The relevant probability is calculated in a precious part as,
Conclusion:
The probability of
c.
To find: The probability to a selected student is in grade seven or eight.
Answer to Problem 49E
The probability that the student is seventh or eighth grade is found to be
Explanation of Solution
The probability distribution for the grade of
Calculation:
Same student cannot enroll to two different grades. Hence, being a grade seven student and being a grade eight student are two mutually exclusive events.
Therefore, the probability for this combination can be written as,
By the addition rule, this probability should be equal to
The total probability can be determined as,
Conclusion:
The probability of
d.
To find: The mean of grade of the student.
Answer to Problem 49E
The mean is found to be,
Explanation of Solution
The probability distribution for the grade of
Calculation:
The mean of a random variable, or equivalently the expected value is given by the sum of the product of the values and the corresponding probabilities.
Here, for each value of
Conclusion:
The mean is found to be
e.
To find: The standard deviation of
Answer to Problem 49E
The standard deviation is found to be,
Explanation of Solution
The probability distribution for the grade of
Calculation:
The variance of a random variable
By constructing a table we can do the calculations clearly using the mean of
The sum of right-most column gives the variation of
The standard deviation
Conclusion:
The standard deviation is found to be
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Connect Hosted by ALEKS Access Card or Elementary Statistics
- Negate the following compound statement using De Morgans's laws.arrow_forwardQuestion 6: Negate the following compound statements, using De Morgan's laws. A) If Alberta was under water entirely then there should be no fossil of mammals.arrow_forwardNegate the following compound statement using De Morgans's laws.arrow_forward
- Characterize (with proof) all connected graphs that contain no even cycles in terms oftheir blocks.arrow_forwardLet G be a connected graph that does not have P4 or C3 as an induced subgraph (i.e.,G is P4, C3 free). Prove that G is a complete bipartite grapharrow_forwardProve sufficiency of the condition for a graph to be bipartite that is, prove that if G hasno odd cycles then G is bipartite as follows:Assume that the statement is false and that G is an edge minimal counterexample. That is, Gsatisfies the conditions and is not bipartite but G − e is bipartite for any edge e. (Note thatthis is essentially induction, just using different terminology.) What does minimality say aboutconnectivity of G? Can G − e be disconnected? Explain why if there is an edge between twovertices in the same part of a bipartition of G − e then there is an odd cyclearrow_forward
- Let G be a connected graph that does not have P4 or C4 as an induced subgraph (i.e.,G is P4, C4 free). Prove that G has a vertex adjacent to all othersarrow_forwardWe consider a one-period market with the following properties: the current stock priceis S0 = 4. At time T = 1 year, the stock has either moved up to S1 = 8 (with probability0.7) or down towards S1 = 2 (with probability 0.3). We consider a call option on thisstock with maturity T = 1 and strike price K = 5. The interest rate on the money marketis 25% yearly.(a) Find the replicating portfolio (φ, ψ) corresponding to this call option.(b) Find the risk-neutral (no-arbitrage) price of this call option.(c) We now consider a put option with maturity T = 1 and strike price K = 3 onthe same market. Find the risk-neutral price of this put option. Reminder: A putoption gives you the right to sell the stock for the strike price K.1(d) An investor with initial capital X0 = 0 wants to invest on this market. He buysα shares of the stock (or sells them if α is negative) and buys β call options (orsells them is β is negative). He invests the cash balance on the money market (orborrows if the amount is…arrow_forwardDetermine if the two statements are equivalent using a truth tablearrow_forward
- Question 4: Determine if pair of statements A and B are equivalent or not, using truth table. A. (~qp)^~q в. р л~9arrow_forwardDetermine if the two statements are equalivalent using a truth tablearrow_forwardQuestion 3: p and q represent the following simple statements. p: Calgary is the capital of Alberta. A) Determine the value of each simple statement p and q. B) Then, without truth table, determine the va q: Alberta is a province of Canada. for each following compound statement below. pvq р^~q ~рл~q ~q→ p ~P~q Pq b~ (d~ ← b~) d~ (b~ v d) 0 4arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
