
Concept explainers
6-111 As noted in Section 6-8C, the amount of external pressure that must be applied to a more concentrated solution to stop the passage of solvent molecules across a semipermeable membrane is known as the osmotic pressure 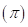 The osmotic pressure obeys a law similar in form to the
The osmotic pressure obeys a law similar in form to the 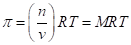 Substituting for pressure and solving for osmotic pressures gives the following equation: RT MRT, where M is the concentration or molarity of the solution.
Substituting for pressure and solving for osmotic pressures gives the following equation: RT MRT, where M is the concentration or molarity of the solution.
(a) Determine the osmotic pressure at 25°C of a 0.0020 M sucrose (C12H22O11) solution.
(b) Seawater contains 3.4 g of salts for every liter of solution. Assuming the solute consists entirely of NaCl (and complete dissociation of the NaCI salt), calculate the osmotic pressure of seawater at 25°C.
(c) The average osmotic pressure of blood is 7.7 atm at 25°C. What concentration of glucose (C6H12O6) will be isotonic with blood?
(d) Lysozyme is an enzyme that breaks bacterial cell walls. A solution containing 0.150 g of this enzyme in 210. mL of solution has an osmotic pressure of 0.953 torr at 25°C. What is the molar mass of lysozyme?
(e) The osmotic pressure of an aqueous solution of a certain protein was measured in order to determine the protein's molar mass. The solution contained 3.50 mg of protein dissolved in sufficient water to form 5.00 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of the solution at 25°C was found to be 1.54 torr. Calculate the molar mass of the protein.
(a)
Interpretation:
The osmotic pressure of given sucrose solution should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Isotonic solutions are solutions in which both the solutions contain same osmolarity. Osmolarity is a term used for multiplication of molarity of the solution with numbers of each particles of the solute. It depends on one gram of solute present in 1000 grams of solution. Osmotic pressure is the pressure which is applied externally on more concentrated solution that stops the movement of solute form semipermeable membrane. Osmotic pressure follows the ideal gas law and following is the equation for it:
Where,
- Π= osmotic pressure
- M= molarity of compound
- R= the gas constant
- T= temperature in Kelvin
Answer to Problem 99P
The sucrose solution contains 0.049atm at
Explanation of Solution
The data given is as follow.
Temperature =
Molarity =0.0020M.
From above mentioned equation for osmotic pressure,
The osmotic pressure is 0.049atm for given sucrose solution.
(b)
Interpretation:
The osmotic pressure of seawater at
Concept Introduction:
Isotonic solutions are solutionsin which both the solutions contain same osmolarity. Osmolarity is a term used for multiplication of molarity of the solution with numbers of each particles of the solute. It depends on one gram of solute present in 1000 grams of solution. Osmotic pressure is the pressure which is applied externally on more concentrated solution that stops the movement of solute form semipermeable membrane. Osmotic pressure follows the ideal gas law and following is the equation for it:
Where,
- Π= osmotic pressure
- M= molarity of compound
- R= the gas constant
- T= temperature in Kelvin
Answer to Problem 99P
The osmotic pressure of given NaCl containing seawater solution is 2.845atm.
Explanation of Solution
The data given is follow,
Temperature =
NaCl=3.4g per liter.
First calculating molarity of NaCl.
For each formula, NaCl dissociate into two ions;
Molarity of NaCl solution=
For osmotic pressure of NaCl solution,
The osmotic pressure of given NaCl containing seawater solution is 2.845atm.
(c)
Interpretation:
The concentration of glucose should be calculated to make it isotonic with blood.
Concept Introduction:
Isotonic solutions are solutionsin which both the solutions contain same osmolarity. Osmolarity is a term used for multiplication of molarity of the solution with numbers of each particles of the solute. It depends on one gram of solute present in 1000 grams of solution. Osmotic pressure is the pressure which is applied externally on more concentrated solution that stops the movement of solute form semipermeable membrane. Osmotic pressure follows the ideal gas law and following is the equation for it:
Where,
- Π= osmotic pressure
- M= molarity of compound
- R= the gas constant
- T= temperature in Kelvin
Answer to Problem 99P
The solution should contain 0.314M of glucose to become isotonic with blood.
Explanation of Solution
The osmotic pressure of blood is 7.7atm at 298K temperature.
To find out the concentration of glucose that should be isotonic with blood,
The solution should contain 0.314M of glucose to become isotonic with blood.
(d)
Interpretation:
The molar mass of lysozymes in solution should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Isotonic solutions are solutionsin which both the solutions contain same osmolarity. Osmolarity is a term used for multiplication of molarity of the solution with numbers of each particles of the solute. It depends on one gram of solute present in 1000 grams of solution. Osmotic pressure is the pressure which is applied externally on more concentrated solution that stops the movement of solute form semipermeable membrane. Osmotic pressure follows the ideal gas law and following is the equation for it:
Where,
- Π= osmotic pressure
- M= molarity of compound
- R= the gas constant
- T= temperature in kelvin
Answer to Problem 99P
The molar mass of lysozymes is
Explanation of Solution
Osmotic pressure =0.953torr= 0.00125atm (1 torr =0.001315atm).
Temperature=298K.
Calculating the moles of lysozyme in solution,
Now calculating molar mass for lysozyme,
(e)
Interpretation:
The molar mass of protein in solution should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Isotonic solutions are solutionsin which both the solutions contain same osmolarity. Osmolarity is a term used for multiplication of molarity of the solution with numbers of each particles of the solute. It depends on one gram of solute present in 1000 grams of solution. Osmotic pressure is the pressure which is applied externally on more concentrated solution that stops the movement of solute form semipermeable membrane. Osmotic pressure follows the ideal gas law and following is the equation for it:
Where,
- Π= osmotic pressure
- M= molarity of compound
- R= the gas constant
- T= temperature in Kelvin
Answer to Problem 99P
The molar mass of protein is
Explanation of Solution
Osmotic pressure =1.54torr=0.002026atm (1 torr =0.001315atm).
Temperature=298K.
Calculating the moles of protein in solution,
Now calculating molar mass for lysozyme,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
INTRO.TO GENERAL,ORGAN...-OWLV2 ACCESS
- Draw the stepwise mechanism for the reactionsarrow_forwardPart I. a) Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone b) Pinacol (2,3-dimethyl, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture of pina colone (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) and 2, 3-dimethyl - 1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable mechanism the formation of the products Forarrow_forward3. The explosive decomposition of 2 mole of TNT (2,4,6-trinitrotoluene) is shown below: Assume the C(s) is soot-basically atomic carbon (although it isn't actually atomic carbon in real life). 2 CH3 H NO2 NO2 3N2 (g)+7CO (g) + 5H₂O (g) + 7C (s) H a. Use bond dissociation energies to calculate how much AU is for this reaction in kJ/mol.arrow_forward
- Part I. Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone and answer the ff: Pinacol (2,3-dimethyl, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture of pina colone and (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) 2,3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable mechanism the formation of the products Forarrow_forwardShow the mechanism for these reactionsarrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanismarrow_forward
- Draw a structural formula of the principal product formed when benzonitrile is treated with each reagent. (a) H₂O (one equivalent), H₂SO₄, heat (b) H₂O (excess), H₂SO₄, heat (c) NaOH, H₂O, heat (d) LiAlH4, then H₂Oarrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanism for the reactionsarrow_forwardDraw stepwise mechanismarrow_forward
- Part I. Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone and answer the ff: a) Give the major reason for the exposure of benzophenone al isopropyl alcohol (w/acid) to direct sunlight of pina colone Mechanism For b) Pinacol (2,3-dimethy 1, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) and 2, 3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable the formation of the productsarrow_forwardwhat are the Iupac names for each structurearrow_forwardWhat are the IUPAC Names of all the compounds in the picture?arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





