
Concept explainers
FILE The Downtown Parking Authority of Tampa, Florida, reported the following information for a sample of 250 customers on the number of hours cars are parked and the amount they are charged.
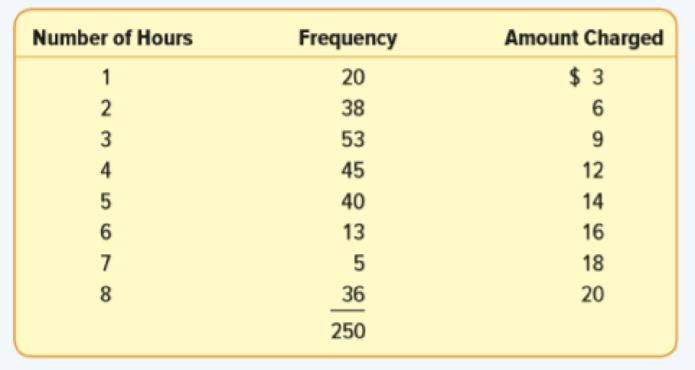
- a. Convert the information on the number of hours parked to a
probability distribution. Is this a discrete or a continuous probability distribution? - b. Find the
mean and the standard deviation of the number of hours parked. How would you answer the question: How long is a typical customer parked? - c. Find the mean and the standard deviation of the amount charged.
a.
Convert the number of hours parked to a probability distribution.
Identify whether this is a discrete or continuous probability distribution.
Answer to Problem 8E
The probability distribution of number of hours parked is as follows:
| Number of hours | Probability |
| 1 | 0.08 |
| 2 | 0.152 |
| 3 | 0.212 |
| 4 | 0.18 |
| 5 | 0.16 |
| 6 | 0.052 |
| 7 | 0.02 |
| 8 | 0.144 |
This is a discrete random variable.
Explanation of Solution
Probability distribution:
The possible outcomes of an experiment and the probability associated with each of its outcome is called probability distribution.
The probability distribution of the number of hours parked is calculated as follows.
| Number of hours | Frequency | Amount charged | Probability |
| 1 | 20 | 3 | |
| 2 | 38 | 6 | |
| 3 | 53 | 9 | |
| 4 | 45 | 12 | |
| 5 | 40 | 14 | |
| 6 | 13 | 16 | |
| 7 | 5 | 18 | |
| 8 | 36 | 20 | |
| Total | 250 | 1 |
Here, the random variable is the number of hours parked, which takes only a certain number of separated values. Hence, it is a discrete random variable.
b.
Find the mean and standard deviation of the number of hours parked.
Explain the duration of a typical customer parked.
Answer to Problem 8E
The mean of the number of hours parked is 4.144.
The standard deviation of the number of hours parked is 2.0908.
A typical customer parked for 4.144 hours.
Explanation of Solution
The mean number of hours parked is calculated as follows:
Therefore, the mean number of hours parked is 4.144.
The standard deviation of the number of hours parked is calculated as follows:
Therefore, the standard deviation of the number of hours parked is 2.0908.
The typical value that is used to represent the central location of probability distribution is the mean. Therefore, the typical customer parked is 4.144 hours.
c.
Calculate the mean and the standard deviation of the amount charged.
Answer to Problem 8E
The mean of the amount charged is 11.532.
The standard deviation of the amount charged is 5.0049.
Explanation of Solution
Mean:
The central location of probability distribution is called mean. It is also called as expected value. The mean of a discrete probability distribution is a weighted average in which the possible random variables are weighted by its corresponding probability values. It is denoted as
Variance:
The variance describes the amount of spread in a probability distribution. It is denoted as
The mean of the amount charged is calculated as follows:
Therefore, the mean of the amount charged is 11.532.
The standard deviation of the amount charged is calculated as follows:
Therefore, the standard deviation of the amount charged is 5.0049.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Statistical Techniques in Business and Economics
- A company found that the daily sales revenue of its flagship product follows a normal distribution with a mean of $4500 and a standard deviation of $450. The company defines a "high-sales day" that is, any day with sales exceeding $4800. please provide a step by step on how to get the answers in excel Q: What percentage of days can the company expect to have "high-sales days" or sales greater than $4800? Q: What is the sales revenue threshold for the bottom 10% of days? (please note that 10% refers to the probability/area under bell curve towards the lower tail of bell curve) Provide answers in the yellow cellsarrow_forwardFind the critical value for a left-tailed test using the F distribution with a 0.025, degrees of freedom in the numerator=12, and degrees of freedom in the denominator = 50. A portion of the table of critical values of the F-distribution is provided. Click the icon to view the partial table of critical values of the F-distribution. What is the critical value? (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardA retail store manager claims that the average daily sales of the store are $1,500. You aim to test whether the actual average daily sales differ significantly from this claimed value. You can provide your answer by inserting a text box and the answer must include: Null hypothesis, Alternative hypothesis, Show answer (output table/summary table), and Conclusion based on the P value. Showing the calculation is a must. If calculation is missing,so please provide a step by step on the answers Numerical answers in the yellow cellsarrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL



