
EBK ENGINEERING MECHANICS
15th Edition
ISBN: 9780137569830
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: VST
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 7RP
Determine the horizontal and vertical components of force at pins A and C of the two-member frame.
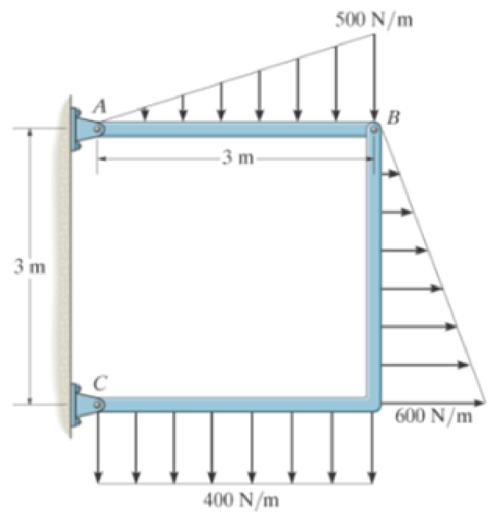
Prob. R6-7
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
SCFM Calculation: (Q1)
A pneumatic system running a manufacturing cell works on 80 psi and requires a flow rate of 10 CFM to operate.
A compressor must be selected to run the cell. Calculate the amount of air going into the compressor to run this cell. (Hint: This will be in SCFM)
Accurate to two decimals. Do not write the unit.
: +00
العنوان
>scóny
: +
개
العنوان
I need a actanicu urawing wit
д
い
Ants
nation
Taxi pu +9635.
The guide vane angle of a reaction turbine (Francis type
make 20° with the tangent. The moving blade angle at entry is
120°. The external diameter of runner is 450 mm and the internal
diameter is 300 mm. Runner width at entry is 62.5mm and at exit
100mm. Calculate the blade angle t exit for radial discharge.
۲/۱
=
44
985
:+B
العنوان
I need a actanicu urawing with Car nation
The guide vane angle of a reaction turbine (Francis type
make 20° with the tangent. The moving blade angle at entry is
120° The external diameter of runner is 450 mm and the internal
diameter is 300 mm. Runner width at entry is 62.5mm and at exit
100mm. Calculate the blade angle at exit for radial discharge.
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK ENGINEERING MECHANICS
Ch. 6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss....Ch. 6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss....Ch. 6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss....Ch. 6 - Determine the greatest load P that can be applied...Ch. 6 - Identify the zero-force members in the truss....Ch. 6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss....Ch. 6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss in...
Ch. 6 - Members AB and BC can each support a maximum...Ch. 6 - Members AB and BC can each support a maximum...Ch. 6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss....Ch. 6 - If the maximum force that any member can support...Ch. 6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6 - Prob. 22PCh. 6 - Determine the force in members BC, CF, and FE....Ch. 6 - Determine the force in members LK, KC, and CD of...Ch. 6 - Determine the force in members KJ, KD, and CD of...Ch. 6 - Determine the force in members EF, CF, and BC of...Ch. 6 - Determine the force in members DC, HC, and HI of...Ch. 6 - Determine the force in members ED, EH, and GH of...Ch. 6 - Determine the force in members HG, HE and DE of...Ch. 6 - Determine the force in members CD, HI, and CH of...Ch. 6 - Prob. 39PCh. 6 - Determine the force in members CD, CF, and CG and...Ch. 6 - Determine the force developed in members FE, EB,...Ch. 6 - Determine the force in members CD, CJ, GJ, and CG...Ch. 6 - Prob. 48PCh. 6 - Determine the force in members HI, FI, and EF of...Ch. 6 - Determine the force P needed to hold the 60-lb...Ch. 6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6 - If a 100-N force is applied to the handles of the...Ch. 6 - Determine the normal force that the 100-lb plate A...Ch. 6 - Determine the force P needed to lift the load....Ch. 6 - Prob. 19FPCh. 6 - Prob. 20FPCh. 6 - Determine the components of reaction at A and C....Ch. 6 - Determine the components of reaction at C. Prob....Ch. 6 - Determine the components of reaction at E. Prob....Ch. 6 - Determine the components of reaction at D and the...Ch. 6 - Determine the force P required to hold the 100-lb...Ch. 6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6 - The bridge frame consists of three segments which...Ch. 6 - Determine the reactions at supports A and B. Prob....Ch. 6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6 - The compound beam is pin supported at B and...Ch. 6 - When a force of 2 lb is applied to the handles of...Ch. 6 - The hoist supports the 125-kg engine. Determine...Ch. 6 - Prob. 88PCh. 6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6 - The pipe cutter is clamped around the pipe P. If...Ch. 6 - Five coins are stacked in the smooth plastic...Ch. 6 - The nail cutter consists of the handle and the two...Ch. 6 - A man having a weight of 175 lb attempts to hold...Ch. 6 - Prob. 97PCh. 6 - If a force of F = 350 N is applied to the handle...Ch. 6 - Prob. 106PCh. 6 - If a force of F = 50 lb is applied to the pads at...Ch. 6 - The spring has an unstretched length of 0.3 m....Ch. 6 - The spring has an unstretched length of 0.3 m....Ch. 6 - The piston C moves vertically between the two...Ch. 6 - Prob. 113PCh. 6 - The platform scale consists of a combination of...Ch. 6 - The three pin-connected members shown in the top...Ch. 6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6 - Determine the force in member GJ and GC of the...Ch. 6 - Determine the force in members GF, FB, and BC of...Ch. 6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6 - Determine the resultant forces at pins B and C on...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Gay-Lussac's Law: (Q2) A gas in a pressure vessel has a temperature of 40 °C and a pressure of 20 psi. Heat is added and its pressure rises to 80 psi. What is the new temperature in °C? Use Two decimal places. Do not write the unit.arrow_forward:+B العنوان I need a actanicu urawing with Car nation The guide vane angle of a reaction turbine (Francis type make 20° with the tangent. The moving blade angle at entry is 120° The external diameter of runner is 450 mm and the internal diameter is 300 mm. Runner width at entry is 62.5mm and at exit 100mm. Calculate the blade angle at exit for radial discharge.arrow_forwardThe volume of a gas is increased, and the temperature is maintained consent. The original volume was 1200 mm3 and its pressure was 100 psi. What is the new pressure in psi, if the volume is increased to 2250 mm3? Use Two decimal places. Do not write the unit.arrow_forward
- :+B العنوان I need a actanicu urawing with Car nation The guide vane angle of a reaction turbine (Francis type make 20° with the tangent. The moving blade angle at entry is 120° The external diameter of runner is 450 mm and the internal diameter is 300 mm. Runner width at entry is 62.5mm and at exit 100mm. Calculate the blade angle at exit for radial discharge.arrow_forwardThe guide vane angle of a reaction turbine (Francis type make 20° with the tangent. The moving blade angle at entry is 120°. The external diameter of runner is 450 mm and the internal diameter is 300 mm. Runner width at entry is 62.5mm and at exit 100mm. Calculate the blade angle at exit for radial discharge.arrow_forwardanswer this as soon as possible, please.arrow_forward
- A piston–cylinder device contains 50 kg of water at 250 kPa and 25°C. The cross-sectional area of the piston is 0.1 m2. Heat is now transferred to the water, causing part of it to evaporate and expand. When the volume reaches 0.26 m3, the piston reaches a linear spring whose spring constant is 100 kN/m. More heat is transferred to the water until the piston rises 20 cm more. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Determine the work done during this process. The work done during this process is kJ.arrow_forwardA 4-m × 5-m × 7-m room is heated by the radiator of a steam-heating system. The steam radiator transfers heat at a rate of 10,000 kJ/h, and a 100-W fan is used to distribute the warm air in the room. The rate of heat loss from the room is estimated to be about 5000 kJ/h. If the initial temperature of the room air is 10°C, determine how long it will take for the air temperature to rise to 25°C. Assume constant specific heats at room temperature. The gas constant of air is R = 0.287 kPa·m3/kg·K (Table A-1). Also, cv = 0.718 kJ/kg·K for air at room temperature (Table A-2). Steam enters the radiator system through an inlet outside the room and leaves the system through an outlet on the same side of the room. The fan is labeled as W sub p w. The heat is given off by the whole system consisting of room, radiator and fan at the rate of 5000 kilojoules per hour. It will take 831 Numeric ResponseEdit Unavailable. 831 incorrect.s for the air temperature to rise to 25°C.arrow_forwardA piston–cylinder device contains 50 kg of water at 250 kPa and 25°C. The cross-sectional area of the piston is 0.1 m2. Heat is now transferred to the water, causing part of it to evaporate and expand. When the volume reaches 0.26 m3, the piston reaches a linear spring whose spring constant is 100 kN/m. More heat is transferred to the water until the piston rises 20 cm more. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Determine the final pressure and temperature. The final pressure is kPa. The final temperature is ºC. Find the work done during the processarrow_forward
- A garden hose attached with a nozzle is used to fill a 20-gal bucket. The inner diameter of the hose is 1 in and it reduces to 0.53 in at the nozzle exit. The average velocity in the hose is 8 ft/s and the density of water is 62.4 lbm/ft3. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Determine the volume and mass flow rates of water through the hose. The volume flow rate of water through the hose is ft3/s. The mass flow rate of water through the hose is lbm/s. The change in time? What is the exit velocity?arrow_forwardA 23-ft3 rigid tank initially contains saturated refrigerant-134a vapor at 160 psia. As a result of heat transfer from the refrigerant, the pressure drops to 50 psia. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Determine the final temperature. Use data from refrigerant tables. The final temperature is ºF.arrow_forwardA 23-ft3 rigid tank initially contains saturated refrigerant-134a vapor at 160 psia. As a result of heat transfer from the refrigerant, the pressure drops to 50 psia. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Determine the heat transfer. The heat transfer is Btu.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Physics 33 - Fluid Statics (1 of 10) Pressure in a Fluid; Author: Michel van Biezen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mzjlAla3H1Q;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY