
Principles of Managerial Finance (14th Edition) (Pearson Series in Finance)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133507690
Author: Lawrence J. Gitman, Chad J. Zutter
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 6.7P
Term structure of interest rates The following yield data for a number of highest-quality corporate bonds existed at each of the three points in time noted.
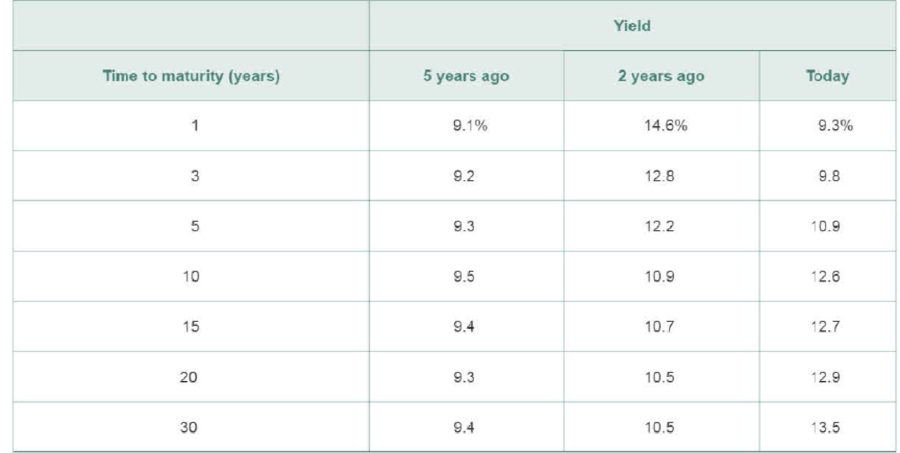
a. On the same set of axes, draw the y1eld curve at each of the three given times.
b. Label each curve in part a with its general shape (downward sloping, upward sloping, flat).
c. Describe the general interest rate expectation existing at each of the three times, assuming the expectations theory holds.
d. Examine the data from 5 years ago. According to the expectations theory, what approximate return did investors expect a 5-year bond to pay as of today?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Answer it
QUESTION #1:
A) What is the Net Operating Profit After Tax (NOPAT) for 2024?B) What is the Operating Cash Flow for 2024?
C) What is the Free Cash Flow for 2024?
Note: Marketable securities are non-operating current assets, and short-term debt (bank loan) is a non-operating current liability. Both of these items are excluded from the calculation of net operating working capital.
D) If the stock trades for $85 per share at the end of 2024, and there are 315,000 shares outstanding, what is the MVA in 2024?
E) Given that the firm’s WACC is 14%, what is the EVA during 2024?
F) Create common size income statement and balance sheet for 2024, 2023 and 2022.
G) Using 2022 as the base year, create income statement and balance sheet percentage change analysis for 2024 and 2023.
QUESTION #2:
In addition to the AAA Ltd. financial statements in Problem One, you are given more information as follows.
Sales are forecast to increase by 80% in 2025.
Short-term Debt, Long-term Debt, and Common…
Brightwoodę Furniture provides the following financial data for a
given enod:
Sales
Less Variable E
Contribwaon Margin
Less Fixed Expenses
et Income
-
Aount ($) Per Unit ($)
150,000
3
L96,000
13
10
35,000
25,000
a. What is the company's CM ratio?
b. If quarterly sales increase by $5,200 and there is no change in fixed
expenses, by how much would you expect quarterly net operating
income to increase?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Principles of Managerial Finance (14th Edition) (Pearson Series in Finance)
Ch. 6.1 - Prob. 1FOPCh. 6.1 - Prob. 6.1RQCh. 6.1 - What is the term structure of interest rates, and...Ch. 6.1 - For a given class of similar-risk securities, what...Ch. 6.1 - Prob. 6.4RQCh. 6.1 - List and briefly describe the potential issuer-...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 1FOECh. 6.2 - What are typical maturities, denominations, and...Ch. 6.2 - Differentiate between standard debt provisions and...Ch. 6.2 - How is the cost of bond financing typically...
Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 6.9RQCh. 6.2 - Prob. 6.10RQCh. 6.2 - Compare the basic characteristics of Eurobonds and...Ch. 6.3 - Why is it important for financial managers to...Ch. 6.3 - Prob. 6.13RQCh. 6.3 - Prob. 6.14RQCh. 6.3 - Prob. 6.15RQCh. 6.4 - Prob. 6.16RQCh. 6.4 - What relationship between the required return and...Ch. 6.4 - If the required return on a bond differs from its...Ch. 6.4 - As a risk-averse investor, would you prefer bonds...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 6.20RQCh. 6 - Prob. 1ORCh. 6 - Learning Goals 5, 6 ST6- 1 Bond valuation Lahey...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.2STPCh. 6 - Prob. 6.1WUECh. 6 - The yields for Treasuries with differing...Ch. 6 - The YTMs for Treasuries with differing maturities...Ch. 6 - Assume that the rate of inflation expected over...Ch. 6 - Calculate the risk premium for each of the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.6WUECh. 6 - Prob. 6.7WUECh. 6 - Assume a 5-year Treasury bond has a coupon rate of...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.1PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.2PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.3PCh. 6 - Yield curve A firm wishing to evaluate interest...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.5PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.6PCh. 6 - Term structure of interest rates The following...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.8PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.9PCh. 6 - Bond interest payments before and after taxes...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.11PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.12PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.13PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.14PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.16PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.20PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.21PCh. 6 - Prob. 6.23PCh. 6 - Bond valuation: Semiannual interest Find the value...Ch. 6 - Prob. 1SE
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- If image is blurr then comment i will write values in comment . dont amswer with unclear data i will give unhelarrow_forwardQUESTION #1: ABC Inc. is debating the purchase of a new digital printer that will replace an older printer. The printer they acquired 2 years ago for $500,000 is worth $220,000 today and will have a salvage value of $80,000 after 5 more years. The printer generates revenues of $750,000 per year. The costs of operating the printer are $480,000 per year. The company currently has $110,000 invested in net operating working capital. The investment in net operating working capital will remain at this level for the remaining 5 years of the project. The new printer will cost $830,000. It will cost $60,000 to install the new printer. The new printer will generate revenues of $1,120,000 per year. In addition, the costs of operating the new printer will be $550,000 per year. The company will have to increase its investment in net operating working capital to $175,000 at time zero. The investment in operating new working capital will remain at this level for the remaining 5 years of the…arrow_forwardQUESTION #1: ABC Inc. is debating the purchase of a new digital printer that will replace an older printer. The printer they acquired 2 years ago for $500,000 is worth $220,000 today and will have a salvage value of $80,000 after 5 more years. The printer generates revenues of $750,000 per year. The costs of operating the printer are $480,000 per year. The company currently has $110,000 invested in net operating working capital. The investment in net operating working capital will remain at this level for the remaining 5 years of the project. The new printer will cost $830,000. It will cost $60,000 to install the new printer. The new printer will generate revenues of $1,120,000 per year. In addition, the costs of operating the new printer will be $550,000 per year. The company will have to increase its investment in net operating working capital to $175,000 at time zero. The investment in operating new working capital will remain at this level for the remaining 5 years of the…arrow_forward
- QUESTION #1: A) What is the Net Operating Profit After Tax (NOPAT) for 2024?B) What is the Operating Cash Flow for 2024? C) What is the Free Cash Flow for 2024? Note: Marketable securities are non-operating current assets, and short-term debt (bank loan) is a non-operating current liability. Both of these items are excluded from the calculation of net operating working capital. D) If the stock trades for $85 per share at the end of 2024, and there are 315,000 shares outstanding, what is the MVA in 2024? E) Given that the firm’s WACC is 14%, what is the EVA during 2024? F) Create common size income statement and balance sheet for 2024, 2023 and 2022. G) Using 2022 as the base year, create income statement and balance sheet percentage change analysis for 2024 and 2023. QUESTION #2: In addition to the AAA Ltd. financial statements in Problem One, you are given more information as follows. Sales are forecast to increase by 80% in 2025. Short-term Debt, Long-term Debt, and Common…arrow_forwardQUESTION #1: ABC Inc. is debating the purchase of a new digital printer that will replace an older printer. The printer they acquired 2 years ago for $500,000 is worth $220,000 today and will have a salvage value of $80,000 after 5 more years. The printer generates revenues of $750,000 per year. The costs of operating the printer are $480,000 per year. The company currently has $110,000 invested in net operating working capital. The investment in net operating working capital will remain at this level for the remaining 5 years of the project. The new printer will cost $830,000. It will cost $60,000 to install the new printer. The new printer will generate revenues of $1,120,000 per year. In addition, the costs of operating the new printer will be $550,000 per year. The company will have to increase its investment in net operating working capital to $175,000 at time zero. The investment in operating new working capital will remain at this level for the remaining 5 years of the…arrow_forwardSolve!arrow_forward
- QUESTION #1: A) What is the Net Operating Profit After Tax (NOPAT) for 2024?B) What is the Operating Cash Flow for 2024? C) What is the Free Cash Flow for 2024? Note: Marketable securities are non-operating current assets, and short-term debt (bank loan) is a non-operating current liability. Both of these items are excluded from the calculation of net operating working capital. D) If the stock trades for $85 per share at the end of 2024, and there are 315,000 shares outstanding, what is the MVA in 2024? E) Given that the firm’s WACC is 14%, what is the EVA during 2024? F) Create common size income statement and balance sheet for 2024, 2023 and 2022. G) Using 2022 as the base year, create income statement and balance sheet percentage change analysis for 2024 and 2023. QUESTION #2: In addition to the AAA Ltd. financial statements in Problem One, you are given more information as follows. Sales are forecast to increase by 80% in 2025. Short-term Debt, Long-term Debt, and Common…arrow_forwardEthical dilemma: Staci Sutter worsk for IIBS as an analyst and is responsible for assigning a value to the stock of ProTech Incorporated that will soon be sold as an IPO. The financial information that Staci has been given suggests that the company is financially strong. Although she has not been able to validate information a friend provided to her via e-mail, Staci is concerned that the financial information she has been provided by ProTech might paint a better financial picture than actually exists. Staci’s concern has been inflated as the result of pressure from her boss to set a good price for the IPO. In addition, it has been reported (rumored) that Staci’s boss is a friend (perhaps close) with the CEO of ProTech. Staci has completed her analysis based on the information she was provided by ProTech, and she is ready to assign a price to the company’s stock. But, if the additional, unconfirmed information she has is correct, the price she sets might differ from what her analysis…arrow_forwardAfter checking her inventory, Yao-lin discovered she had excess supplies in her warehouse. How does she account for this?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning

Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...
Finance
ISBN:9781285190907
Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark Bradshaw
Publisher:Cengage Learning
What are Money Markets?; Author: The CISI;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ipOYM0sfW7M;License: Standard Youtube License