
Concept explainers
Benson Pharmaceuticals uses a process-costing system to compute the unit costs of the over-the-counter cold remedies that it produces. It has three departments: mixing, encapsulating, and bottling. In mixing, the ingredients for the cold capsules are measured, sifted, and blended (with materials assumed to be uniformly added throughout the process). The mix is transferred out in gallon containers. The encapsulating department takes the powdered mix and places it in capsules (which are necessarily added at the beginning of the process). One gallon of powdered mix converts into 1,500 capsules. After the capsules are filled and polished, they are transferred to bottling, where they are placed in bottles that are then affixed with a safety seal, lid, and label. Each bottle receives 50 capsules.
During March, the following results are available for the first two departments:
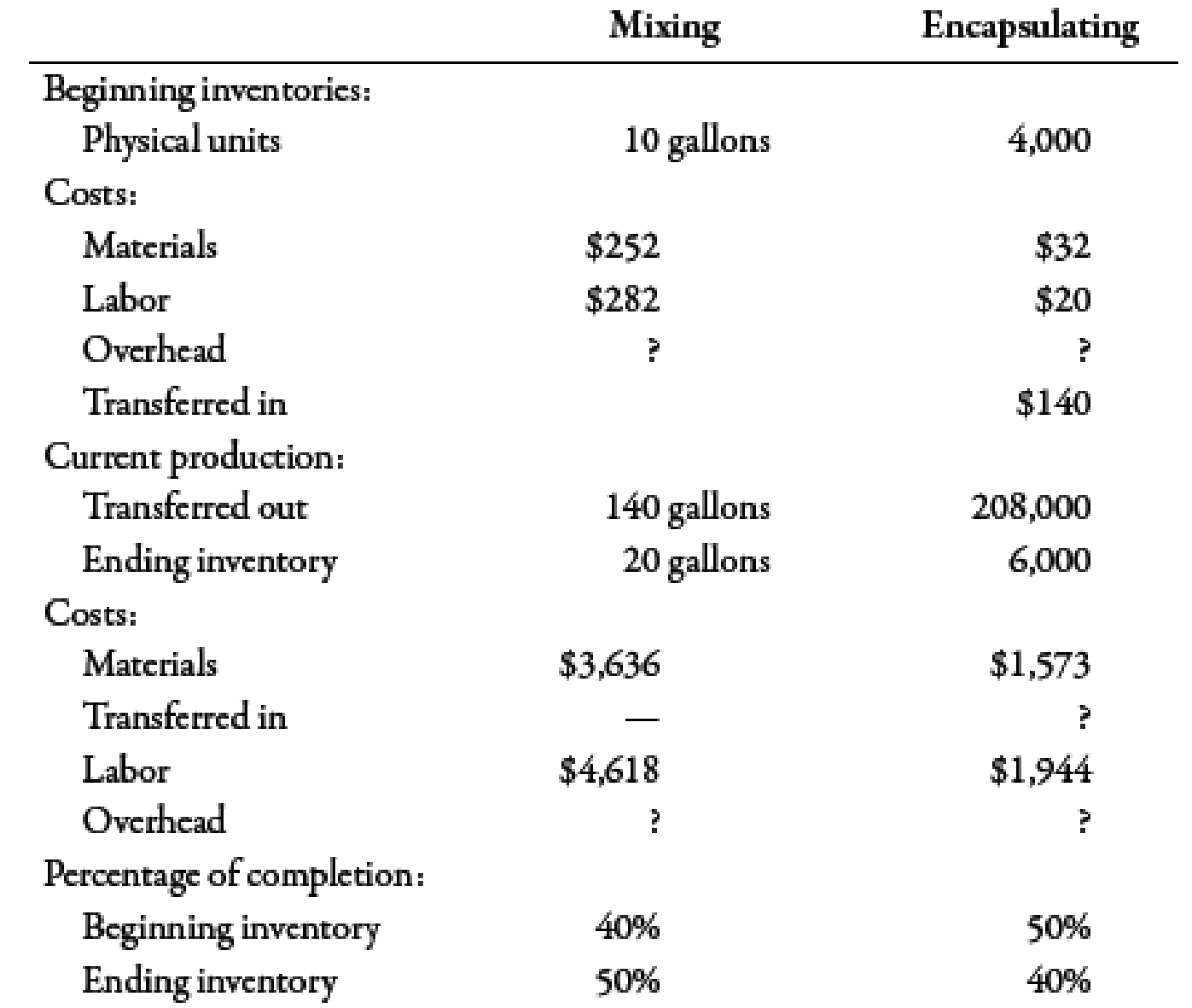
Required:
- 1. Prepare a production report for the mixing department using the weighted average method. Follow the five steps outlined in the chapter. (Note: Round to two decimal places for the unit cost.)
- 2. Prepare a production report for the encapsulating department using the weighted average method. Follow the five steps outlined in the chapter. (Note: Round to four decimal places for the unit cost.)
- 3. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Explain why the weighted average method is easier to use than FIFO. Explain when weighted average will give about the same results as FIFO.
1.
Present a production report for the mixing department using weighted average method.
Explanation of Solution
Weighted Average Method:
Weighted average method is an inventory valuation method. In this method, cost is divided by equivalent units to obtain unit cost. This unit cost is used to value the inventory units.
Step 1: Physical flow analysis:
| Particulars | Units |
| Units to account for: | |
| Units in beginning WIP | 10 |
| Add: Units started during the period1 | 150 |
| Units to account for | 160 |
| Units accounted for: | |
| Units completed and transferred | 140 |
| Add: Units in ending WIP | 20 |
| Units accounted for | 160 |
Table (1)
Step 2: Computation of equivalent units:
| Particulars | Units |
| Units completed and transferred | 140 |
| Equivalent units from ending inventory | 10 |
| Equivalent units | 150 |
Table (2)
Step 3: Computation of unit cost:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Cost of beginning inventory: | |
| Material | 252 |
| Labor | 282 |
| Overhead | 564 |
| Total cost of beginning inventory (A) | 1,098 |
| Cost incurred: | |
| Material | 3,636 |
| Labor | 4,618 |
| Overhead | 9,236 |
| Total cost incurred (B) | 17,490 |
| Total manufacturing cost | 18,588 |
| Unit cost |
123.92 |
Table (3)
Step 4: Valuation of inventories:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Cost of goods transferred | 17,348.8 |
| Cost of ending WIP | 1239.2 |
| Total value | 18,588 |
Table (4)
Step 5: Cost reconciliation:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Cost of goods transferred | 17,348.8 |
| Cost of ending WIP | 1239.2 |
| Total value | 18,588 |
| Total cost of beginning inventory | 1,098 |
| Total cost incurred | 17,490 |
| Total manufacturing cost | 18,588 |
Table (5)
Working Notes:
1. Computation of units started during the period:
2.
Present a production report for the encapsulating department using weighted average method.
Explanation of Solution
Step 1: Physical flow analysis:
| Particulars | Units |
| Units to account for: | |
| Units in beginning WIP | 4,000 |
| Add: Units started during the period1 | 210,000 |
| Units to account for | 214,000 |
| Units accounted for: | |
| Units completed and transferred | 208,000 |
| Add: Units in ending WIP | 6,000 |
| Units accounted for | 214,000 |
Table (6)
Step 2: Computation of equivalent units:
| Particulars | Units |
| Units completed and transferred | 208,000 |
| Equivalent units from ending inventory | 2,400 |
| Equivalent units | 210,400 |
Table (7)
Step 3: Computation of unit cost:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Cost of beginning inventory: | |
| Material | 32 |
| Labor | 20 |
| Overhead | 30 |
| Transferred in | 140 |
| Total cost of beginning inventory (A) | 222 |
| Cost incurred: | |
| Material | 1,573 |
| Transferred in | 17,348.8 |
| Labor | 1,944 |
| Overhead | 2,916 |
| Total cost incurred (B) | 23,781.8 |
| Total manufacturing cost | 24,003.8 |
| Unit cost |
0.1141 |
Table (8)
Step 4: Valuation of inventories:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Cost of goods transferred | 23,732.8 |
| Cost of ending WIP | 273.84 |
| Total value | 24,006.64 |
Table (9)
Step 5: Cost reconciliation:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Cost of goods transferred | 23,732.8 |
| Cost of ending WIP | 273.84 |
| Total value | 24,006.64 |
| Total cost of beginning inventory | 222 |
| Total cost incurred | 23,781.8 |
| Total manufacturing cost | 24,003.8 |
Table (10)
Working Notes:
1.
Computation of units started during the period:
3.
Discuss whether or not weighted average method is easier than FIFO. Also, discuss the situation in which weighted average will give about the same results as FIFO.
Explanation of Solution
It is easier to compute unit cost in case of weighted average method, because all equivalent units are categorized in one class.
Weighted average would provide similar result from FIFO, in case, costs are not much fluctuating and are similar from previous periods.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Managerial Accounting
- Provide correct answer please general accountingarrow_forwardWhat is the value of ending long term debt? Accounting questionarrow_forwardCompany B had an estimated 230,000 direct labor hours, $486,000 manufacturing overhead, and 27,000 machine hours. The actual were 220,700 direct labor hours, 38,600 machine hours, and $505,000 manufacturing overhead. They determine overhead based upon machine hours. Calculate the predetermined overhead rate.arrow_forward
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning

