
Concept explainers
Calculate inventory amounts when costs are declining (LO6–3)
During the year, Trombley Incorporated has the following Inventory transactions.
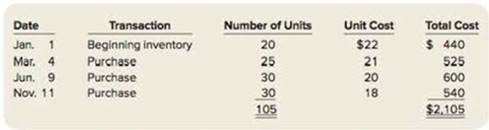
For the entire year, the company sells 81 units of inventory for $30 each.
Required:
1. Using FIFO, calculate (a) ending inventory, (b) cost of goods sold, (c) sales revenue, and (d) gross profit.
2. Using LIFO, calculate (a) ending inventory, (b) cost of goods sold, (c) sales revenue, and (d) gross profit.
3. Using weighted-average cost, calculate (a) ending inventory, (b) cost of goods sold, (c) sales revenue, and (d) gross profit.
4. Determine which method will result in higher profitability when inventory costs are declining.
1. (a)
To calculate: The cost of ending inventory.
Explanation of Solution
Perpetual Inventory System:
Perpetual Inventory System refers to the inventory system that maintains the detailed records of every inventory transactions related to purchases, and sales on a continuous basis. It shows the exact on-hand-inventory at any point of time.
First-in-First-Out:
In First-in-First-Out method, the costs of the initially purchased items are considered as cost of goods sold, for the items which are sold first. The value of the ending inventory consists of the recent purchased items.
Ending Inventory: It represents the quantity and price of the goods unsold and laying at the store at the end of a particular period.
- Calculate the cost of ending inventory:
| Calculation of Cost of Ending Inventory | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| November, 11 | 24 | 18 | 432 |
| Ending Inventory | 24 | 432 | |
Table 1
Note:
- The ending inventory is 24 units.
- In FIFO method the ending inventory comprises of the inventory purchased last, because the inventory purchased first were sold first.
- Therefore, the ending inventory of 24 units from November 11th purchases.
Working notes:
- Calculate the total Cost and units of Goods Available for Sales:
| Particulars | Number of units | Rate per unit ($) | Total cost ($) |
| Beginning inventory | 20 | 22 | 440 |
| Purchases on May, 4 | 25 | 21 | 525 |
| Purchases on June, 9 | 30 | 20 | 600 |
| Purchases on November, 11 | 30 | 18 | 540 |
| Total goods available for sales | 105 | 2,105 |
Table 2
- Calculate the units of ending inventory:
Therefore, the cost of Ending Inventory in the FIFO is $432.
1. (b)
To calculate: The cost of goods sold.
Explanation of Solution
Cost of goods sold:
Cost of goods sold is the accumulate total of all direct cost incurred in manufacturing the goods or the products which has been sold during a period. Cost of goods sold involves direct material, direct labor, and manufacturing overheads.
Determine the cost of goods sold:
| Particulars | Number of units | Rate per unit ($) | Total cost ($) |
| Beginning inventory | 20 | 22 | 440 |
| Purchases on May, 4 | 25 | 21 | 525 |
| Purchases on June, 9 | 30 | 20 | 600 |
| Purchases on November, 11 | 6 | 18 | 108 |
| Cost of goods sold | 81 | 1,673 |
Table 3
Note:
- units are sold.
- As it is FIFO method the earlier purchased items will sell first.
- Hence, the cost of goods sold will be the earlier purchased items.
Therefore, the cost of goods sold in the FIFO Method is $1,673.
1. (c)
To calculate: the Sales Revenue.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the amount of sales revenue:
Therefore, the sales revenue in FIFO method is $2.430.
1. (d)
To calculate: The gross profit.
Explanation of Solution
Gross profit is the difference between the sales and the cost of goods sold.
Calculate the gross profit:
| Calculation of Gross Margin | |
| Details | Amount ($) |
| Sales | 2,430 (1) |
| Less: Cost of Goods Sold (Refer to table 4) | ($1,673) |
| Gross Margin | 757 |
Table 4
Therefore, the amount of Gross margin in FIFO method is $757.
2. (a)
To calculate: The cost of ending inventory.
Explanation of Solution
Perpetual Inventory System:
Perpetual Inventory System refers to the inventory system that maintains the detailed records of every inventory transactions related to purchases, and sales on a continuous basis. It shows the exact on-hand-inventory at any point of time.
Last-in-Last-Out:
In Last-in-First-Out method, the costs of last purchased items are considered as the cost of goods sold, for the items which are sold first. The value of the closing stock consists of the initial purchased items.
- Calculate the cost of ending inventory.
| Calculation of Cost of Ending Inventory | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Beginning Inventory | 20 | 22 | 440 |
| Purchase on March, 4 | 4 | 21 | 84 |
| Ending Inventory | 24 | 22 | 524 |
Table 5
Note:
- The ending inventory is 24 units (Refer to Table 2).
- In LIFO method the ending inventory comprises of the inventory purchased first, because the inventory purchased last were sold first.
- Therefore, the ending inventory of 24 units is from the beginning inventory.
Therefore, the cost of Ending Inventory in the LIFO method is $524.
2. (b)
To calculate: The cost of goods sold.
Explanation of Solution
Cost of goods sold:
Cost of goods sold is the accumulate total of all direct cost incurred in manufacturing the goods or the products which has been sold during a period. Cost of goods sold involves direct material, direct labor, and manufacturing overheads.
Determine the cost of goods sold:
| Particulars | Number of units | Rate per unit ($) | Total cost ($) |
| Purchases on November, 11 | 30 | 18 | 540 |
| Purchases on June, 9 | 30 | 20 | 600 |
| Purchases on May, 4 | 21 | 21 | 441 |
| Cost of goods sold | 81 | 1,581 |
Table 6
Note:
- units are sold.
- As it is LIFO method the recent purchased items will sell first.
- Hence, the cost of goods sold will be the recent purchased items.
Therefore, the Cost of Goods Sold in the LIFO Method is $1,581.
2. (c)
To calculate: the Sales Revenue.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the amount of sales revenue:
Therefore, the sales revenue in LIFO method is $2,430.
2. (d)
To calculate: The gross profit.
Explanation of Solution
Gross profit is the difference between the sales and the cost of goods sold.
Calculate the gross profit:
| Calculation of Gross Margin | |
| Details | Amount ($) |
| Sales | 2,430 (2) |
| Less: Cost of Goods Sold (Refer to table 8) | ($1,581) |
| Gross Margin | 849 |
Table 7
Therefore, the amount of Gross margin in LIFO method is $849.
3. (a)
To calculate: The cost of ending inventory.
Explanation of Solution
Perpetual Inventory System:
Perpetual Inventory System refers to the inventory system that maintains the detailed records of every inventory transactions related to purchases, and sales on a continuous basis. It shows the exact on-hand-inventory at any point of time.
Weighted-average cost method:
Under Weighted average cost method, the company calculates a new average cost after every purchase is made. It is determined by dividing the cost of goods available for sale by the units on hand.
- Calculate the cost of ending inventory:
Working note:
- Calculate the Weighted-average cost:
Therefore, the cost of Ending Inventory in the Weighted-average-cost Method is $481,142.
3. (b)
To calculate: The cost of goods sold.
Explanation of Solution
Cost of goods sold:
Cost of goods sold is the accumulate total of all direct cost incurred in manufacturing the goods or the products which has been sold during a period. Cost of goods sold involves direct material, direct labor, and manufacturing overheads.
Calculate the Cost of Goods Sold.
Therefore, the Cost of goods sold in the Weighted-average-cost Method is $1,623.86.
3. (c)
To calculate: the Sales Revenue.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the amount of sales revenue:
Therefore, the sales revenue in Weighted-average-cost Method is $2,430.
3. (d)
To calculate: The gross profit.
Explanation of Solution
Gross profit is the difference between the sales and the cost of goods sold.
Calculate the gross profit:
| Calculation of Gross Margin | |
| Details | Amount ($) |
| Sales | 2,430 (7) |
| Less: Cost of Goods Sold | (1,623.86) (5) |
| Gross Margin | 806.14 |
Table 8
Therefore, the amount of Gross margin in Weighted-average-cost Method is $806.14.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Compare the profitability in the three methods:
| Methods | FIFO | LIFO | WA |
| Gross Margin | $757 | $849 | 806.14 |
Table 9
The gross margin computed by using the LIFO method results higher profitability when inventory costs are declining in comparison to the other two methods.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Financial accounting
- Assume your company uses the periodic inventory costing method, and the inventory count left out an entire warehouse of goods that were in stock at the end of the year, with a cost value of $222,000. How will this affect your net income in the current year? How will it affect next years net income?arrow_forwardReid Company uses the periodic inventory system. On January 1, it had an inventory balance of 250,000. During the year, it made 613,000 of net purchases. At the end of the year, a physical inventory showed it had ending inventory of 140,000. Calculate Reid Companys cost of goods sold for the year.arrow_forwardLast year, Nikkola Company had net sales of 2,299,500,000 and cost of goods sold of 1,755,000,000. Nikkola had the following balances: Refer to the information for Nikkola Company above. Required: Note: Round answers to one decimal place. 1. Calculate the average inventory. 2. Calculate the inventory turnover ratio. 3. Calculate the inventory turnover in days. 4. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Based on these ratios, does Nikkola appear to be performing well or poorly?arrow_forward
- Kulsrud Company would like to estimate the current inventory level. Using the gross profit method and the following information, estimate the current inventory level for Kulsrud Company. Goods available for sale 100,000 Net sales 150,000 Normal gross profit as a percent of sales 40%arrow_forwardAnalyzing Inventory The recent financial statements of McLelland Clothing Inc. include the following data: Required: 1. Calculate McLellands gross profit ratio (rounded to two decimal places), inventory turnover ratio (rounded to three decimal places), and the average days to sell inventory (assume a 365-day year and round to two decimal places) using the FIFO inventory costing method. Be sure to explain what each ratio means. 2. Calculate McLellands gross profit ratio (rounded to two decimal places), inventory turnover ratio (rounded to three decimal places), and the average days to sell inventory (assume a 365-day year and round to two decimal places) using the LIFO inventory costing method. Be sure to explain what each ratio means. 3. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Which ratios-the ones computed using FIFO or LIFO inventory values-provide the better indicator of how successful McLelland was at managing and controlling its inventory?arrow_forwardCalculate the cost of goods sold dollar value for A67 Company for the month, considering the following transactions under three different cost allocation methods and using perpetual inventory updating. Provide calculations for weighted average (AVG).arrow_forward
- Hurst Companys beginning inventory and purchases during the fiscal year ended December 31, 20-2, were as follows: There are 1,200 units of inventory on hand on December 31, 20-2. REQUIRED 1. Calculate the total amount to be assigned to the cost of goods sold for 20-2 and ending inventory on December 31 under each of the following periodic inventory methods: (a) FIFO (b) LIFO (c) Weighted-average (round calculations to two decimal places) 2. Assume that the market price per unit (cost to replace) of Hursts inventory on December 31 was 18. Calculate the total amount to be assigned to the ending inventory on December 31 under each of the following methods: (a) FIFO lower-of-cost-or-market (b) Weighted-average lower-of-cost-or-market 3. In addition to taking a physical inventory on December 31, Hurst decides to estimate the ending inventory and cost of goods sold. During the fiscal year ended December 31, 20-2, net sales of 100,000 were made at a normal gross profit rate of 35%. Use the gross profit method to estimate the cost of goods sold for the fiscal year ended December 31 and the inventory on December 31.arrow_forwardThe moving average inventory cost flow assumption is applicable to which of the following inventory systems? Questions M7-6 and M7-7 are based on the following data: City Stationers Inc. had 200 calculators on hand on January 1, 2019, costing 18 each. Purchases and sales of calculators during the month of January were as follows: City uses a periodic inventory system. According to a physical count, 150 calculators were on hand at January 31, 2019.arrow_forwardRefer to the information for Morgan Inc. above. If Morgan uses a perpetual inventory system, what is the cost of ending inventory under FIFO at April 30? a. $32,500 b. $38,400 c. $63,600 d. $69,500arrow_forward
- Lower of Cost or Market Garcia Company uses FIFO, and its inventory at the end of the year was recorded in the accounting records at $17,800. Due to technological changes in the market, Garcia would be able to replace its inventory for $16,500. Required: 1. Using the lower of cost or market method, what amount should Garcia report for inventory on its balance sheet at the end of the year? 2. Prepare the journal entry required to value the inventory at the lower of cost or market.arrow_forwardJessie Stores uses the periodic system of calculating inventory. The following information is available for December of the current year when Jessie sold 500 units of inventory. Using the FIFO method, calculate Jessies inventory on December 31 and its cost of goods sold for December. RE7-11 Using the information from RE7-10, calculate Jessie Storess inventory on December 31 and its cost of goods sold for December using the LIFO method.arrow_forwardBeginning inventory, purchases, and sales for WCS12 are as follows: Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the weighted average method, determine (a) the weighted average unit cost after the October 22 purchase, (b) the cost of goods sold on October 29, and (c) the inventory on October 31.arrow_forward
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





