
Costing inventory
Golden Eagle Company begun operations in 2016 by selling a single product. Data on purchases and sales for the year were as follows:
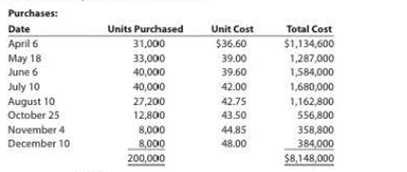
| Sales: | |
| April | 16,000 units |
| May | 16,000 |
| June | 20,000 |
| July | 24,000 |
| August | 28,000 |
| September | 28.000 |
| October | 18,000 |
| November | 10,000 |
| December | 8,000 |
| Total units | 168,000 |
| Total sales | $10,000,000 |
On January 4, 2017, the president of the company, Connie Kilmer, asked for your advice on costing the 32,000-unit physical inventory that was taken on December 51, 2016. Moreover, since the firm plans to expand its product line, she asked for your advice on the use of a perpetual inventory system in the future.
- 1. Determine the cost of the December 31. 2016, inventory under the periodic system, using the (a) first-m, first-out method, (b) last-in, first-out method, and (c) weighted average cost method.
- 2. Determine the gross profit for the year under each of the three methods in (1).
- 3. a. Explain varying viewpoints why each of the three inventory costing methods may best reflect the results of operations for 2016.
- b. Which of the three inventory costing methods may best reflect the replacement cost of the inventory on the
balance sheet as of December 31, 2016:' - c. Which inventory costing method would you choose to use for income tax purposes? Why?
- d. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using a perpetual inventory system. From the data presented in this case, is there any indication of the adequacy of inventory' levels during the year?
1. (a)
Periodic Inventory System:
Periodic inventory system is a system, in which the inventory is updated in the accounting records on a periodic basis such as at the end of each month, quarter or year. In other words, it is an accounting method which is used to determine the amount of inventory at the end of each accounting period.
First-in-First-Out:
In First-in-First-Out method, the costs of the initially purchased items are considered as cost of goods sold, for the items which are sold first. The value of the ending inventory consists of the recent purchased items.
Last-in-Last-Out:
In Last-in-First-Out method, the costs of last purchased items are considered as the cost of goods sold, for the items which are sold first. The value of the closing stock consists of the initial purchased items.
Weighted-average cost method:
Under Weighted average cost method, the company calculates a new average cost after every purchase is made. It is determined by dividing the cost of goods available for sale by the units on hand.
To determine: The cost of inventory on December 31, 2016 using first in first out method under periodic inventory system.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the cost of ending inventory as follows:
| Details | Units | Unit Price | Total |
| (A) | (B) | (A) × (B) | |
| December 10 | 8,000 | 48 | 384,000 |
| November 4 | 8,000 | 44.85 | 358,800 |
| October 25 | 12,800 | 43.50 | 556,800 |
| August 10 | 3,200 | 42.75 | 136,800 |
| Total | 32,000 | 1,436,400 |
Table (1)
Hence, the ending inventory on December 31, 2016 under First in First out Method is $1,436,400.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the cost of ending inventory as follows:
| Details | Units | Unit Price | Total |
| (A) | (B) | (A) × (B) | |
| April 6 | 31,000 | 36.60 | 1,134,600 |
| May 18 | 1,000 | 39.00 | 39,000 |
| Total | 32,000 | 1,173,600 |
Table (2)
Hence, the ending inventory on December 31, 2016 under Last in First out Method is $1,173,600.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the cost of ending inventory as follows:
The value of ending inventory is calculated by multiplying ending inventory with weighted average cost per unit.
Working note:
The weighted average unit cost is calculated as follows:
Hence, the ending inventory on December 31, 2016 under weighted average method is $1,303,680.
2.
Explanation of Solution
The table showing all the three methods of inventory is as follows:
| Details | FIFO ($) |
LIFO ($) |
Weighted Average ($) |
| Sales | 10,000,000 | 10,000,000 | 10,000,000 |
Less: Cost of merchandise sold (Refer Table 4) |
6,711,600 | 6,974,400 | 6,844,320 |
| Gross Profit | 3,288,400 | 3,025,600 | 3,155,680 |
Table (3)
Working Note:
Calculate the cost of merchandise sold under the three methods.
| Details | FIFO ($) |
LIFO ($) |
Weighted Average ($) |
| Cost of Merchandise Available For Sale | 8,148,000 | 8,148,000 | 8,148,000 |
| Less: Ending Inventory | 1,436,400 (a) | 1,173,600 (b) | 1,303,680 (c) |
| Cost of Merchandise Sold | 6,711,600 | 6,974,400 | 6,844,320 |
Table (4)
3. (a)
To Explain: The reason for each of the three inventory costing methods might best reflect the results of operations for 2016.
Explanation of Solution
- Most often the LIFO method is considered as the best method for reflecting the results of operations as it matches the recent merchandise purchase cost against the current year sales. As a result, the gross profit determined is best reflects the result of current year operations.
- In the present case, the gross profit of $3,025,600 best reflects the matching of the most current merchandise cost of $6,974,400 against the current sales of $10,000,000. As a result, the effects of price fluctuations on the income of operations are minimum, incase, the current sales of merchandise exceeds the current year’s merchandise. LIFO could not best match the current merchandise cost with the current sales. This is because the cost of goods sold includes the cost of some beginning inventory purchased in the prior years. Thus, in such case, LIFO could not be able to satisfy the current matching concept. This kind of situation is generally experienced by the companies whose ending inventory consistently increases in each year. Hence, LIFO method is considered to be the best method for matching the expenses against the expenses.
- However, FIFO is considered as best method when the physical flow of the merchandise is consistent. It is mostly adopted by the companies who intend to sell the merchandise in order of their purchases made. In such a case, it approximates the results of operations based on specific identification of costs.
- While, the weighted average cost method lies somewhere in between LIFO and FIFO. The effects of the price fluctuations are averaged for calculating the merchandise cost and income from operations.
Hence, to decide which inventory costing method best reflects the income from operations depends upon the Company G’s emphasis on which of the aforesaid parameters:
- Whether it emphasizes on matching the current year merchandise cost against the current year sales (LIFO method).
- Whether it emphasizes on the physical flow of merchandise (FIFO method).
- Whether it equally emphasizes on both matching concept and physical flow of goods.
(b)
To Find: The three inventory costing methods that may best reflect the replacement cost of the inventory on the balance sheet as of December 31, 2016.
Explanation of Solution
Among the three inventories costing methods that reflects the replacement cost of the inventory on the balance sheet as of December 31, 2016 is FIFO method. This is because it includes the most recently purchased merchandise in its ending inventory. The Company G’s ending inventory of $1,436,000 as on December 31, 2016 represents the recent purchases during the period August to December. Thus, FIFO method most appropriately approximates the replacement cost of the ending inventory than the other two inventory methods.
(c)
To Explain: The inventory costing that would be used for income tax purposes.
Explanation of Solution
- During inflation on rising price trend LIFO method would be helpful for income tax purposes. This is because it results in lesser income from operations which fetch less income tax.
- In the present case, the Company G should use LIFO method for lowering its income tax. LIFO method includes the most recent purchases that increases the cost of goods sold thereby decreasing the net income.
- However, for decreasing price trend, FIFO method would be useful for income tax purposes. This is because, it would include the prior period purchases carrying higher prices in its cost of goods sold. As a result, it would decrease the net income and thus, the income tax.
(d)
To Discuss: The advantages and disadvantages of using a perpetual inventory system.
Explanation of Solution
The advantages of using a perpetual inventory system are stated below:
- It is an effective method of controlling inventory. Any sort of inventory shortages can be determined by comparing the ending inventory with the subsidiary account balance.
- It determines the accurate value of inventories to be used for preparing interim statements.
- It helps in maintaining the adequate level of inventories. The regular track records of the perpetual inventory help the company for timely recorder of the merchandise to avoid loss of sales and prevent excess accumulated inventory on hand.
- It is analyzed that from the period April through July, the company has ordered more inventory irrespective to the accumulated excess inventory. In such a case, the perpetual inventory system if adopted would have helped to avoid the occurrence of an excessive accumulated inventory.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
FINANCIAL AND MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING
- ayco Inc. started its operations in 2022. Its sales during 2022, all on account, totalled $700,000. The company collected $500,000 in cash from customers during the year and wrote off $8,000 in uncollectible accounts. The company set up an allowance for doubtful accounts at December 31, 2022, its fiscal year-end, and determined the account balance to be $14,000. The unadjusted balances of selected accounts at December 31, 2023 are as follows: Accounts receivable $ 300,000 Allowance for doubtful accounts (debit) 10,000 Sales revenue (including 80 percent in sales on account) 800,000 Aging of the accounts receivable on December 31, 2023, resulted in an estimate of $11,000 in potentially uncollectible accounts. Required: 1. Prepare the journal entries to record all the transactions during 2022 and post them to appropriate T-accounts. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.)…arrow_forwardCalculate the sample size based on the specifications in Buhi's contract. Make sure it is within budget, reasonable to obtain, and that you use appropriate inputs relative to market research best practices. Use the calculator to adjust the sample size statement. Use the agreed-upon sample size in Buhi's contract: 996. In your secondary research, find the target population size (an estimate of those in the United States looking to purchase luggage in the category in the next two years). You will use this target population size for each sample size estimate. Adjust the provided sample size calculator inputs to find the rest of the figures that get you to the agreed-upon sample size. The caveats from Buhi are that you must: Use the market research standard for your confidence level. Use a confidence interval that is better than the market research standard for your confidence interval.arrow_forwardThe partnership of Keenan and Kludlow paid the following wages during this year: Line Item Description Amount M. Keenan (partner) $108,000 S. Kludlow (partner) 96,000 N. Perry (supervisor) 54,700 T. Lee (factory worker) 35,100 R. Rolf (factory worker) 27,200 D. Broch (factory worker) 6,300 S. Ruiz (bookkeeper) 26,000 C. Rudolph (maintenance) 5,200 In addition, the partnership owed $250 to Rudolph for work he performed during December. However, payment for this work will not be made until January of the following year. The state unemployment tax rate for the company is 2.95% on the first $9,000 of each employee's earnings. Compute the following: ound your answers to the nearest cent. a. Net FUTA tax for the partnership for this year b. SUTA tax for this yeararrow_forward
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning




