
Critical Thinking:
Designing aircraft seats
When designing seats for aircraft, we want to have sufficient room so that passengers are comfortable and safe, but we don’t want too much room, because fewer seats could be installed and profits would drop. It has been estimated that removing one row of seats would cost around $8 million over the life of an aircraft.
Figure 6-22(a) shows an important human consideration: The buttock-to-knee length. The accompanying table includes relevant buttock- to-knee length parameters obtained from studies of large numbers of people. Figure 6-22(b) shows a traditional aircraft seat, and Figure 6-22(c) shows the new SkyRider seat design by the Italian company Aviointeriors. The SkyRider seat is dramatically different from traditional aircraft seats. The seats are like saddles, and they are higher so that passenger legs slant downward with weight on the legs. The most dramatic difference is that SkyRider seats have much less legroom. The distance of 23 in. shown in Figure 6-22(c) is a distance of 30 in. to 32 in. for most current economy seats. As of this writing, the SkyRider seats have not yet been approved by the Federal Aviation Administration, but approval would allow a new class of seating with very low fares.
When designing aircraft seats, we must make some hard choices. If we are to accommodate everyone in the population, we will have a sitting distance that is so costly in terms of reduced seating that it might not be economically feasible. Some questions we must address are: (1) What percentage of the population are we willing to exclude? (2) How much extra room do we want to provide for passenger comfort and safety?
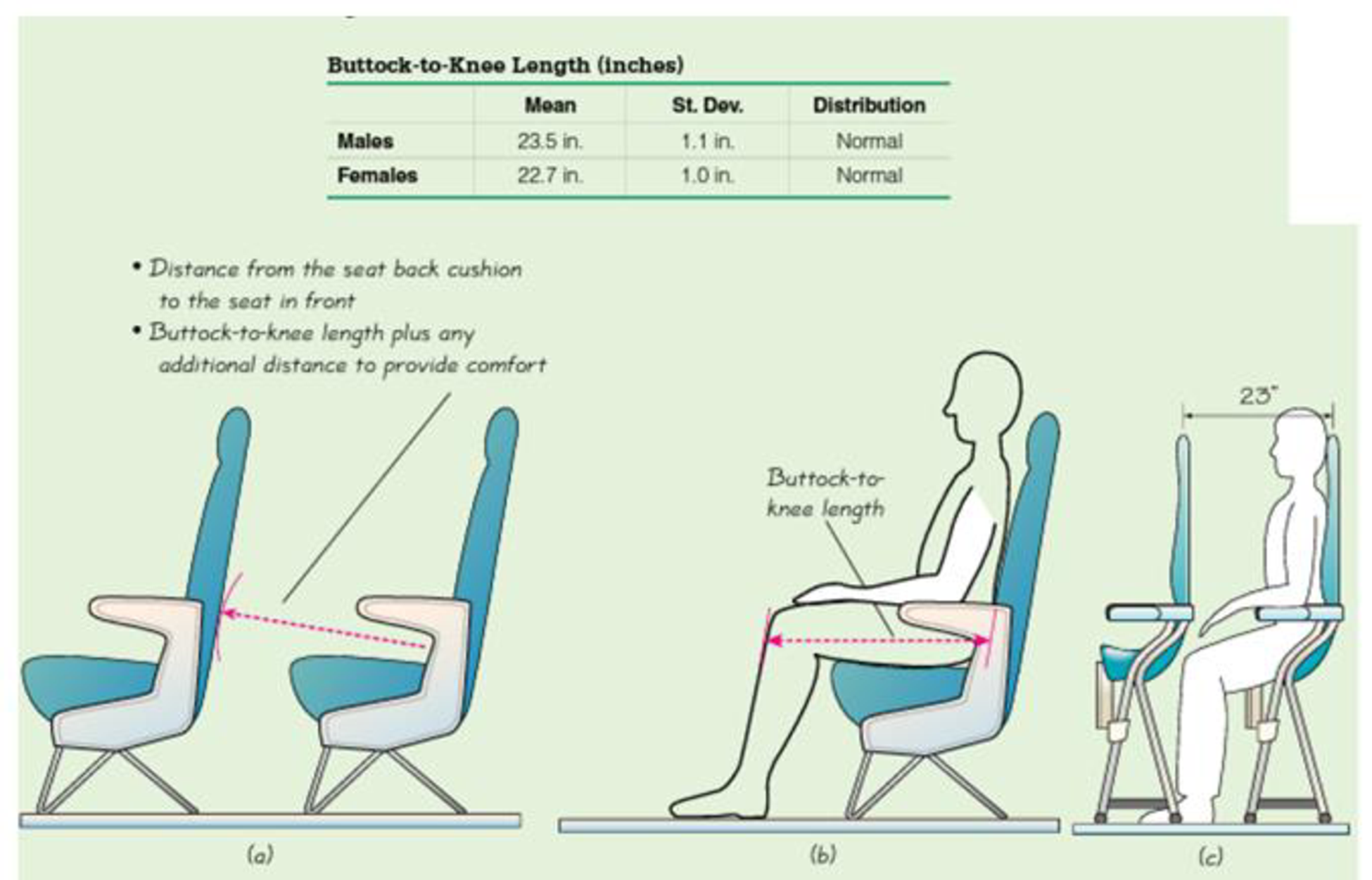
Figure 6-22 Distances Used In the Design of Aircraft Seats
5. Seat pitch is defined to be the distance between the same point on two successive seats. In addition to buttock-to-knee length, what other important factor affects the choice of seat pitch?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Essentials of Statistics Books a la carte Plus NEW MyLab Statistics with Pearson eText - Access Card Package (5th Edition)
- 2. Which of the following statements are (not) true? lim sup{An U Bn} 818 lim sup{A, B} 818 lim inf{An U Bn} 818 818 lim inf{A, B} An An A, Bn- A, BnB →B = = = lim sup A, U lim sup Bn; 818 818 lim sup A, lim sup Bn; 818 81U lim inf A, U lim inf Bn; 818 818 lim inf A, lim inf Bn; n→X 818 An U BRAUB as no; An OBRANB as n→∞.arrow_forwardThroughout, A, B, (An, n≥ 1), and (Bn, n≥ 1) are subsets of 2. 1. Show that AAB (ANB) U (BA) = (AUB) (AB), Α' Δ Β = Α Δ Β, {A₁ U A2} A {B₁ U B2) C (A1 A B₁}U{A2 A B2).arrow_forward16. Show that, if X and Y are independent random variables, such that E|X|< ∞, and B is an arbitrary Borel set, then EXI{Y B} = EX P(YE B).arrow_forward
- Proposition 1.1 Suppose that X1, X2,... are random variables. The following quantities are random variables: (a) max{X1, X2) and min(X1, X2); (b) sup, Xn and inf, Xn; (c) lim sup∞ X and lim inf∞ Xn- (d) If Xn(w) converges for (almost) every w as n→ ∞, then lim- random variable. → Xn is aarrow_forwardExercise 4.2 Prove that, if A and B are independent, then so are A and B, Ac and B, and A and B.arrow_forward8. Show that, if {Xn, n ≥ 1) are independent random variables, then sup X A) < ∞ for some A.arrow_forward
- 8- 6. Show that, for any random variable, X, and a > 0, 8 心 P(xarrow_forward15. This problem extends Problem 20.6. Let X, Y be random variables with finite mean. Show that 00 (P(X ≤ x ≤ Y) - P(X ≤ x ≤ X))dx = E Y — E X.arrow_forward(b) Define a simple random variable. Provide an example.arrow_forward17. (a) Define the distribution of a random variable X. (b) Define the distribution function of a random variable X. (c) State the properties of a distribution function. (d) Explain the difference between the distribution and the distribution function of X.arrow_forward16. (a) Show that IA(w) is a random variable if and only if A E Farrow_forward15. Let 2 {1, 2,..., 6} and Fo({1, 2, 3, 4), (3, 4, 5, 6}). (a) Is the function X (w) = 21(3, 4) (w)+711.2,5,6) (w) a random variable? Explain. (b) Provide a function from 2 to R that is not a random variable with respect to (N, F). (c) Write the distribution of X. (d) Write and plot the distribution function of X.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





