
To calculate: The monthly savings of Person BB.
Introduction:
The series of payments that are made at equal intervals is an
Answer to Problem 57QP
The monthly savings of Person BB is $3,362.78.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Person BB wishes to save money to fulfill his three objectives. They are as follows:
- The first objective of Person BB is to retire at thirty years from now with a retirement amount of $20,000 for a month for every 25 years, the first payment will be expected at thirty years and a month from present
- The second objective of Person BB is to buy a cabin in the Place R within ten years at an projected cost of $375,000
- The third objective of Person B is to leave an inheritance of $2,000,000 to Person F after he passes on and at the last of the 25 years of withdrawal
Person BB can afford to save $25,000 for a month for the next ten years if he can earn the effective annual cost of 7% after his retirement and 10% before his retirement.
Time line of the cash flow:
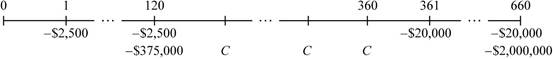
Note: The cash flows from the given information takes place monthly basis, the given interest rate is an effective annual rate. As the cash flows take place on a monthly basis, it is essential to compute the effective monthly rate by finding the annual percentage rate through monthly compounding, and then dividing it by 12. The preretirement annual percentage rate is calculated as follows:
Formula to calculate the effective annual rate:
Compute the effective annual rate:
Compute the annual percentage rate with the effective annual rate:
Hence, the annual percentage rate is 0.0957 or 9.57%.
The annual percentage rate for the post-retirement is calculated as follows:
Formula to calculate the effective annual rate:
Compute the effective annual rate:
Compute the annual percentage rate with the effective annual rate:
Hence, the annual percentage rate is 0.067 or 6.78%.
First, it is essential to compute the retirement needs of Person BB. The amount that is essential for the retirement is the
Formula to calculate the present value
Note: C denotes the payments, r denotes the rate of exchange, and t denotes the period.
Compute the present value annuity for without fee:
Formula to calculate the present value:
Compute the present value:
Hence, the present value is $368,498.36.
Person BB will be saving $2,500 per month for the upcoming ten years until he buys the cabin. The value of his savings after ten years is calculated as follows:
Formula to calculate the
Note: C denotes the annual cash flow or the annuity payment, r denotes the rate of interest, and t denotes the number of payments.
Compute the future value annuity of Person BB:
Hence, the future value of the annuity is $499,659.64.
The amount that remains in the hands of Person BB after the purchase of the cabin is as follows:
Note: The amount that remains in the hands of Person BB is calculated by subtracting the cost of the cabin from the calculated future value of the annuity.
Hence, the amount that Person BB has in his hands is $124,659.64.
Person BB still has twenty years until the retirement and at the time when he is ready to retire, the amount he would receive is as follows:
Formula to compute the future value:
Note: C denotes the annual cash flow or the annuity payment, r denotes the rate of interest, and t denotes the number of payments.
Compute the future value:
Hence, the future value is $838,647.73.
Thus, when Person BB is ready for the retirement based on his present savings, he will be short of the below amount:
Thus, the above calculated amount is the future value of the monthly savings that Person BB has to make between ten to thirty years.
Hence, the future value of an annuity of Person BB is $2,415,347.07.
Compute the monthly savings of Person BB using the Formula of the future value of an annuity:
Hence, the monthly savings of Person BB is $3,362.78.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Fundamentals of Corporate Finance (Special Edition for Rutgers Business School)
- Ends Mar 30 Discuss in detail what is Free Cash Flows and how is it calculated. Also define what is a Sunk Cost as well as an Opportunity Cost. 0arrow_forwardSubscribe Explain in detail what is a firm's Capital Structure? What is and how does a firm's Financial Policy impact its Capital Structure? Finally, what is opportunity costs and how does it affect a firm's Capital Structure?arrow_forwardWhat is the answer of this finance wuarrow_forward
- Do you think market efficiency varies significantly between developed and emerging markets, and if so, how should companies or investors adjust their strategies in each environment?arrow_forwardDescribe the key stages of the audit progress and indicate how each stage contribute to a comprehensive auditarrow_forwardregulations 28 of the company act no 71 of 2008 regulates on the category of companies which are required to be audited, list three types of companies that are required to be audited regulations 43 speak of the social and ethics committee. it is a must that certain companies appoint such a committee. list these three types of companies in terms of regulation 43. more so what is the function of the social and ethics committee.arrow_forward
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT PFIN (with PFIN Online, 1 term (6 months) Printed...FinanceISBN:9781337117005Author:Randall Billingsley, Lawrence J. Gitman, Michael D. JoehnkPublisher:Cengage Learning
PFIN (with PFIN Online, 1 term (6 months) Printed...FinanceISBN:9781337117005Author:Randall Billingsley, Lawrence J. Gitman, Michael D. JoehnkPublisher:Cengage Learning Pfin (with Mindtap, 1 Term Printed Access Card) (...FinanceISBN:9780357033609Author:Randall Billingsley, Lawrence J. Gitman, Michael D. JoehnkPublisher:Cengage Learning
Pfin (with Mindtap, 1 Term Printed Access Card) (...FinanceISBN:9780357033609Author:Randall Billingsley, Lawrence J. Gitman, Michael D. JoehnkPublisher:Cengage Learning


