
(a)
Interpretation: The two characteristic arrow pushing patterns for the given mechanism is to be interpreted.
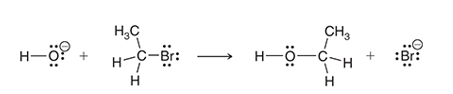
Concept introduction:
A
(b)
Interpretation: The process is the be interpreted as exothermic and endothermic for the given reaction with the help of the energy profile diagram.
Concept introduction:
The energy profile diagram shows the progress of the chemical reaction. It is the curve between the energy and reaction coordinate of the reaction. It can be used to predict the formation of transition state and product from the given reactant.
(c)
Interpretation: The
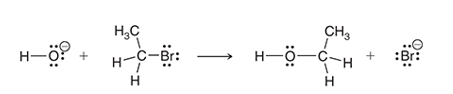
Concept introduction:
Entropy is the measurement of the randomness of a chemical system. As the randomness increases, the entropy of the system also increases. Entropy gets affected by the number of molecules in a system, physical state, and presence of ions.
(d)
Interpretation: The
Concept introduction:
A chemical reaction involves the conversion of one or more reactant molecules to product molecules. The Gibb’s equation provides the relation between
(e)
Interpretation: The transition state and its location on the energy diagram for the given reaction is to be interpreted.
Concept introduction:
A chemical reaction involves the conversion of one or more reactant molecules to product molecules. The reactant molecules come close to each other and collide effectively to form the transition state that further changes to the product.
(f)
Interpretation: The closeness of transition state to reactant or product is to be interpreted for the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
A chemical reaction involves the conversion of one or more reactant molecules to product molecules. The reactant molecules come close to each other and collide effectively to form the transition state that further changes to the product.
(g)
Interpretation: The order of reaction is to be interpreted for the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
The rate of a chemical reaction can be defined as the change in the concentration of the reactant within the given time. The rate law states that the rate of the chemical reaction is directly proportional to the active concentration of the reactant molecules. The proportionality constant is called the rate constant.
(h)
Interpretation: The effect of the doubled concentration of the hydroxide ion is to be interpreted for the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
The rate of a chemical reaction can be defined as the change in the concentration of the reactant within the given time. The rate law states that the rate of the chemical reaction is directly proportional to the active concentration of the reactant molecules. The proportionality constant is called the rate constant.
(i)
Interpretation: The effect of increasing the temperature is to be interpreted for the given reaction.
Concept introduction:
The energy profile diagram shows the progress of the chemical reaction. It is the curve between the energy and reaction coordinate of the reaction. It can be used to predict the formation of transition state and product from the given reactant.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- 2. Predict the product(s) that forms and explain why it forms. Assume that any necessary catalytic acid is present. .OH HO H₂N OHarrow_forwardconsider the rate of the reaction below to be r. Whats the rate after each reaction? Br + NaCN CN + NaBr a. Double the concentration of alkyl bromide b. Halve the concentration of the electrophile & triple concentration of cyanide c. Halve the concentration of alkyl chloridearrow_forwardPredict the organic reactant that is involved in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactant. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forward
- What are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forwardWhat is the organic molecule X of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardWhat are is the organic molecule X and product Y of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forward
- At 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Without using graphs, calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/(mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forwardPredict the organic products that form in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forward
- What are the products of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardWhat would happen if you added the HCI to the Grignard reagent before adding benzophenone? Draw a reaction mechanism to support your answer.arrow_forwardAt 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/ (mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





