
Corporate Finance Plus MyLab Finance with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (4th Edition) (Berk, DeMarzo & Harford, The Corporate Finance Series)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780134408897
Author: Jonathan Berk, Peter DeMarzo
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 4P
Suppose the current zero-coupon yield curve for risk-free bonds is as follows:
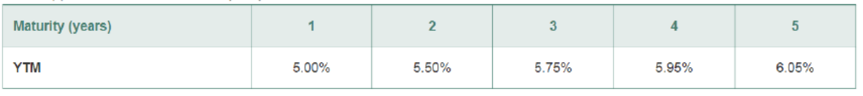
- a. What is the price per $100 face value of a two-year, zero-coupon, risk-free bond?
- b. What is the price per $100 face value of a four-year, zero-coupon, risk-free bond?
- c. What is the risk-free interest rate for a five-year maturity?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
How much do investor psychology and market sentiment play into stock price movements? Do these emotional reactions having a bigger impact on short-term swings, or do they also shape long-term trends in a meaningful way?
Explain The business of predatory tax return preparation, including: How they deceive the working poor,The marketing tactics the preparers use, and Other than paying high fees, what negative impact can the use of these unqualified and unregulated preparers have on the taxpayer?
Explain the changes in tax return preparation you would like to see in Alabama, based on what has been successful in other states.
Chapter 6 Solutions
Corporate Finance Plus MyLab Finance with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (4th Edition) (Berk, DeMarzo & Harford, The Corporate Finance Series)
Ch. 6.1 - What is the relationship between a bonds price and...Ch. 6.1 - The risk-free interest rate for a maturity of...Ch. 6.2 - If a bonds yield to maturity does not change, how...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 2CCCh. 6.2 - How does a bonds coupon rate affect its...Ch. 6.3 - How do you calculate the price of a coupon bond...Ch. 6.3 - How do you calculate the price of a coupon bond...Ch. 6.3 - Explain why two coupon bonds with the same...Ch. 6.4 - There are two reasons the yield of a defaultable...Ch. 6.4 - What is a bond rating?
Ch. 6.5 - Why do sovereign debt yields differ across...Ch. 6.5 - What options does a country have if it decides it...Ch. 6 - A 30-year bond with a face value of 1000 has a...Ch. 6 - Assume that a bond will make payments every six...Ch. 6 - The following table summarizes prices of various...Ch. 6 - Suppose the current zero-coupon yield curve for...Ch. 6 - Prob. 5PCh. 6 - Prob. 6PCh. 6 - Suppose a five-year, 1000 bond with annual coupons...Ch. 6 - Prob. 8PCh. 6 - Explain why the yield of a bond that trades at a...Ch. 6 - Prob. 10PCh. 6 - Prob. 11PCh. 6 - Consider the following bonds: Bond Coupon Rate...Ch. 6 - Prob. 14PCh. 6 - Prob. 17PCh. 6 - Prob. 18PCh. 6 - Prob. 19PCh. 6 - Prob. 20PCh. 6 - Prob. 22PCh. 6 - Prob. 23PCh. 6 - Suppose you are given the following information...Ch. 6 - Prob. 26PCh. 6 - Grumman Corporation has issued zero-coupon...Ch. 6 - The following table summarizes the yields to...Ch. 6 - Prob. 30PCh. 6 - Prob. 31PCh. 6 - A BBB-rated corporate bond has a yield to maturity...Ch. 6 - Prob. 33PCh. 6 - Prob. 34PCh. 6 - Prob. 35P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Explain the understanding (or misunderstanding) of the working poor with tax return preparation within one page report.arrow_forwardExplain the regulations or requirements for tax return preparers in Alabama.arrow_forwardquestion 1. Toodles Inc. had sales of $1,840,000. Cost of goods sold, administrative and selling expenses, and depreciation expenses were $1,180,000, $185,000 and $365,000 respectively. In addition, the company had an interest expense of $280,000 and a tax rate of 35 percent. (Ignore any tax loss carry-back or carry-forward provisions.)Arrange the financial information for Toodles Inc. in an income statement and compute its OCF?Question 2 Anti-Pandemic Pharma Co. Ltd. reports the following information in its income statement: Sales = $5,250,000;Costs = $2, 173,000;Other expenses = $187,400; Depreciation expense = $79,000; Interest expense= $53,555; Taxes = $76,000; Dividends = $69,000. $136,700 worth of new shares were also issued during the year and long-term debt worth $65,300 was redeemed.a) Compute the cash flow from assetsb) Compute the net change in working capitalQuestion 3Footfall Manufacturing Ltd. reports the following financial information at the end of the current year:…arrow_forward
- Accrued Interest PayableCompute the interest for December accrued on each of the following notes payable owed by Riff-Raff'n Yell Inc., on December 31: Day of Calendar: 1 Lender: New Age Principal: $10,000 Interest Rate: 5% Term (Days) 120 Day of Calendar: 8 Lender: Wyvern Tavern Principal: $8,000 Interest Rate: 6% Term (Days) 90 Day of Calendar: 17 Lender: Cedar Tree Principal: $15,000 Interest Rate: 4% Term (Days) 90 Note: Use 360 days for calculations and round to the nearest dollar. Riff-Raff'n Yell, Inc. Lender (in alphabetical order) Accrued Interest Cedar Tree Answer 1 New Age Answer 2 Wyvern Tavern Answer 3arrow_forwardQuestion Footfall afacturing pers The following fancial information at the end of the current years Inventory turnover ratio Fixed accetturnover ratio bot to assets ratia set profit ang ross profit margin the given information to fill at the templates for income statement and balance sheet geb In Statement of Footfall Manufacturing Ltd. for the year ending RELEASED BY THE CL MOME2003, FEBRUARY 9, 3005 Sales December 31, 20 Cast of other expec Earnings befo Camings afterarrow_forwardTreasury securities are issued and backed by the U.S. government and, therefore, are considered to be the lowest-risk securities on the market. As an investor looking for protection against inflation, you are considering the purchase of inflation-adjusted bonds known as U.S. Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS). With these securities, the face value (which is paid at maturity) and the bond interest rate (which is paid semiannually) is regularly adjusted to account for inflation. However, for this problem only, assume the semi-annual interest payment (called the bond dividend) remains the same. You purchased a 10-year $10,000 TIPS bond with dividend of 4% per year payable semiannually (i.e., $200 every 6 months). Assume there is no inflation adjustment for the first 5 years, but in years 6 through 10, the bond face value increases by $850 each year. You use an expected investment return of 11% per year compounded semiannually. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an…arrow_forward
- Nataro, Incorporated, has sales of $698,000, costs of $344,000, depreciation expense of $89,000, interest expense of $54,000, and a tax rate of 21 percent. What is the net income for this firm? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to the nearest whole number, e.g., 32. Net incomearrow_forwardGreenland is a small country with only listed stocks on its stock exchange. Using the following data create a market capitalisation index. Stock Price on Index Creation Number of Shares issued Day $45 300 B $70 500 C $18 600 D $11 900 If the value of the stock index is set at 100 on the index creation date, what will be the value of the index when stock prices are the following: Stock A Stock Price $35 B $78 C $15 D $9arrow_forwardLight Sweet Petroleum, Inc., is trying to evaluate a generation project with the following cash flows. If the company requires a return of 12 percent on its investments, what is the project's NPV? What are the IRRS for the project? Year 0 $ (45,000,000) Year 1 $ 71,000,000 Year 2 $ (15,000,000) Required return 12% Complete the following analysis. Do not hard code values in your calculations. Use a "Guess" of .99 to calculate the higher IRR and -.99 to calculate the lower IRR. You must use the built-in Excel functions to answer this question. NPV Higher IRR Lower IRRarrow_forward
- Bethesda Mining Company reports the following balance sheet information for 2021 and 2022: Assets Current assets 2021 BETHESDA MINING COMPANY Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2021 and 2022 Liabilities and Owners' Equity Current liabilities Accounts payable Notes payable 2021 $ 190,422 85,520 2022 Cash Accounts receivable Inventory $ 47,858 61,781 124,912 $ 60,783 82,139 190,747 Total $ 275,942 Total $ 234,551 $ 333,669 Long-term debt $ 238,000 Owners' equity Fixed assets Common stock and paid-in surplus Accumulated retained earnings $ 217,000 161,656 Net plant and equipment Total assets $ 658,047 $ 589,628 $ 378,656 $ 892,598 $ 923,297 Total liabilities and owners' equity $ 892,598 Total 2022 $ 198,111 137,088 $ 335,199 $ 174,750 $ 217,000 196,348 $ 413,348 $ 923,297 Based on the balance sheets given, calculate the following financial ratios for each year: Calculate the following financial ratios for each year: a. Current ratio. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round…arrow_forwardMary decides to buy a Treasury note futures contract for delivery of $100,000 face amount in September, at a price of 120′24.0. At the same time, Eric decides to sell a Treasury note futures contract if he can get a price of 120′24.0 or higher. The exchange, in turn, agrees to sell one Treasury note contract to Mary at 120′24.0 and to buy one contract from Eric at 120′24.0. The price of the Treasury note decreases to 120′10.5. Calculate Eric's balance on margin account. Assume that initial margin is $1,890. Please note that loss should be entered with minus sign. Round the answer to two decimal places.arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College

Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395083
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:Cengage Learning


EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:9781337514835
Author:MOYER
Publisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:9781947172685
Author:OpenStax
Publisher:OpenStax College
The U.S. Treasury Markets Explained | Office Hours with Gary Gensler; Author: U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uKXZSzY2ZbA;License: Standard Youtube License